What do you use to treat hyperkalemia?
What medications are used to treat hyperkalemia?
- A diet low in potassium (for mild cases).
- Discontinue medications that increase blood potassium levels.
- Intravenous administration of glucose and insulin, which promotes movement of potassium from the extracellular space back into the cells.
When to correct hyperkalemia?
lab diagnosis
- Hyperkalemia is variably defined as potassium >5.5 mM or >5.0 mM, depending on the source.
- Pseudohyperkalemia refers to artificially elevated potassium due to: (a) Hemolysis. ...
- Point-of-care testing is generally accurate, but it cannot detect hemolysis. ...
What is the emergency treatment of hypokalemia?
- Intravenous KCl should be given at a rate that does not exceed 10 mEq/h. ...
- Administration of IV KCl should be done through a central venous catheter if available. ...
- Potassium chloride salt substitutes are a good source of oral K +. ...
When to treat hyperkalemia?
“Many patients are managed in primary care, with secondary care giving advice and, in some cases, not seeing them for long periods of time. This change will allow people who are living with heart failure and chronic kidney disease, to more readily access treatments that can help manage persistent hyperkalemia.”

What Is Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium levels)?
Hyperkalemia happens when potassium levels in a person’s blood are higher than normal.Normal levels of potassium in the blood are generally between...
Who Can Get Hyperkalemia?
Anyone can get hyperkalemia, but there are some groups who are more at risk. People who have kidney disorders, infants, elderly patients in hospita...
What Are The Symptoms of Hyperkalemia (High Blood Potassium levels)?
A person with high levels of blood potassium may not have any symptoms. However, if symptoms do exist, they may include: 1. Muscle weakness 2. Irre...
What Causes High Blood Potassium Levels?
Hyperkalemia can have a variety of causes: 1. Increased total body potassium 2. Cells releasing extra potassium into the bloodstream 3. Lack of ald...
What Are The Problems Related to Having High Blood Potassium?
The possible problems that have been found in people with hyperkalemia are: 1. Irregular heartbeat 2. Cardiac arrest (heart attack) 3. Changes in n...
How long does it take for hyperkalemia to come on?
Symptoms often come and go and may come on gradually over weeks or months. Dangerously high potassium levels affect the heart and cause a sudden onset of life-threatening problems. Hyperkalemia symptoms include: Abdominal (belly) pain and diarrhea. Chest pain.
How to get rid of high potassium in urine?
Options include: Diuretics: Also called water pills, these drugs make you pee more often. Your body gets rid of potassium mainly in urine. Intravenous (IV) therapy: Extremely high potassium levels need immediate treatment. You’ll receive an IV infusion of calcium to protect your heart.
What is potassium binder?
Potassium binders: A daily medication binds to excess potassium in the intestines. You pass the potassium when you poop. Your provider may recommend binders if other treatments don’t lower potassium levels. Potassium binders come in oral and enema form.
What does high potassium mean?
Hyperkalemia (High Potassium) People with hyperkalemia have high potassium levels in their blood. Signs like fatigue and muscle weakness are easy to dismiss. A low-potassium diet and medication changes often bring potassium numbers to a safe level. An extremely high potassium level can cause a heart attack and requires immediate medical care.
What happens if you have too much potassium in your blood?
Potassium is an essential nutrient found in foods. This nutrient helps your nerves and muscles function. But too much potassium in your blood can damage your heart and cause a heart attack. You can’t always tell when your potassium levels are high.
Can hyperkalemia be a long term problem?
Changes to your diet and medication often resolve mild cases of hyperkalemia. With the right care, most people don’t have long-term complications from hyperkalemia. Your healthcare provider may order more frequent blood tests to ensure your potassium levels stay within a healthy range.
Does potassium build up in blood?
As a result, potassium builds up in your blood. In addition to conditions like kidney disease, these factors also contribute to hyperkalemia: A high-potassium diet, which can result from potassium supplements and salt substitutes. Medications that contain potassium, such as certain high blood pressure medicines.
What causes hyperkalemia in kidneys?
Advanced kidney disease is a common cause of hyperkalemia. A diet high in potassium. Eating too much food that is high in potassium can also cause hyperkalemia, especially in people with advanced kidney disease. Foods such as cantaloupe, honeydew melon, orange juice, and bananas are high in potassium. Drugs that prevent the kidneys ...
How to get potassium out of your body?
Some people may also need special medicine to help remove extra potassium from the body and keep it from coming back. This may include: Water pills (diuretics) help rid your body of extra potassium. They work by making your kidney create more urine. Potassium is normally removed through urine.
Why does potassium increase with diabetes?
This occurs because your body, in response to severe burns or injuries releases extra potassium in your blood. Poorly controlled diabetes. When diabetes is not controlled, it has a direct effect on your kidneys which are responsible for balancing potassium in your body.
Why does potassium rise?
This can cause your potassium levels to rise. Other (less common) causes include: Taking extra potassium , such as salt substitutes or supplements. A disorder called “Addisons disease”, which can occur if your body does not make enough of certain hormones.
How to check potassium level?
A blood test can find the level of potassium in your blood. High potassium is usually found by chance during a routine blood test. Your healthcare provider will also give you a complete physical checkup. You will be asked about your medical history, your diet, and the medicines you take.
What foods have potassium?
High protein foods such as meat, fish, and chicken also have potassium, but you need a balance of high protein foods to stay healthy. Portion size is very important. A dietitian can help you create a meal plan that gives you the right amount of potassium and protein to meet your needs.
What happens if you have high potassium levels?
If hyperkalemia comes on suddenly and you have very high levels of potassium, you may feel heart palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, or vomiting. Sudden or severe hyperkalemia is a life-threatening condition. It requires immediate medical care.
What causes hyperkalemia?
Chronic kidney disease is the most common cause of hyperkalemia. Next, if your potassium level is high, you’ll probably get an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to check your heart’s electrical activity. To do an ECG, a doctor or other health care professional will attach electrodes to your legs and chest using stickers, ...
What is the best way to lower potassium levels?
You’ll need urgent treatments to quickly lower your potassium level. These may include intravenous (IV) calcium, insulin and glucose, and albuterol. These shift potassium out of your blood and into your body's cells.
What to do if your kidneys aren't removing enough acid from your body?
After that, another option is to take a potassium-binding agent, either patiromer (Veltassa), sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate), or sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma).
What to do if you have too much potassium in your body?
You will also need to remove the extra potassium from your body -- these treatments include diuretics (water pills) and dialysis. If it’s not a crisis, you may still need medicines to help flush out the excess potassium, just not quite as urgently.
Can you get dialysis for hyperkalemia?
Severe hyperkalemia is a medical emergency. You might need dialysis. But if it’s a mild case, you and your doctor may be able to manage it without you staying in a hospital. The first thing your doctor will likely do is retest your potassium level to see if the first test was accurate.
Do kidneys flush out potassium?
Normally, healthy kidneys flush out any extra potassium. But if you have kidney problems or some other conditions (such as type 1 diabetes, heart failure, or liver disease) or take certain medications, your body might not be able to do that as well as it should. Decide on Next Steps.
Can hyperkalemia be managed as an outpatient?
Think Long-Term. If your doctor finds that your hyperkalemia is mild, your condition may be something you can manage as an outpatient, meaning that you don’t have to stay in a hospital. You’ll know you’re on the mend when your potassium levels return to normal and stay that way.
What is the difference between hyperkalemia and potassium?
Hyperkalemia results either from the shift of potassium out of cells or from abnormal renal potassium excretion. Cell shift leads to transient increases in the plasma potassium concentration, whereas decreased renal excretion of potassium leads to sustained hyperkalemia. Impairments in renal potassium excretion can be the result ...
What foods cause hyperkalemia?
Foods naturally rich in potassium include bananas (a medium-sized banana contains 451 mg or 12 mmol of potassium) and potatoes (844 mg or 22 mmol in a large baked potato with skin).
What is the effect of mineralocorticoid levels on potassium?
Decreased mineralocorticoid levels or activity due to disturbances in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system will impair renal potassium secretion. Such disturbances can be the result of diseases or drugs ( Figure 1 ). 13, 16, 17
What happens to potassium after a meal?
After a meal, release of insulin not only regulates the plasma glucose concentration, it also causes potassium to move into cells until the kidneys have had sufficient time to excrete the dietary potassium load and reestablish total-body potassium content. Exercise, beta-blockers.
What causes a spurious increase in potassium concentration?
A spurious increase in plasma potassium concentration along with a low plasma calcium concentration raises the possibility of calcium chelation and release of potassium in a sample tube contaminated with the anticoagulant ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid.
How does insulin affect potassium?
Insulin lowers the plasma potassium concentration by promoting its entry into cells. To avoid hypoglycemia, 10 units of short-acting insulin should be accompanied by a 50-g infusion of glucose, increased to 60 g if 20 units of insulin are given. 24. Beta-2 receptor agonists produce a similar effect.
Where does potassium reabsorbed in the proximal tubule?
Decreased distal delivery of sodium. Under normal circumstances, potassium is freely filtered across the glomerulus and then mostly reabsorbed in the proximal tubule and thick ascending limb. Potassium secretion begins in the distal convoluted tubule and increases in magnitude into the collecting duct.
What is the best treatment for hyperkalemia?
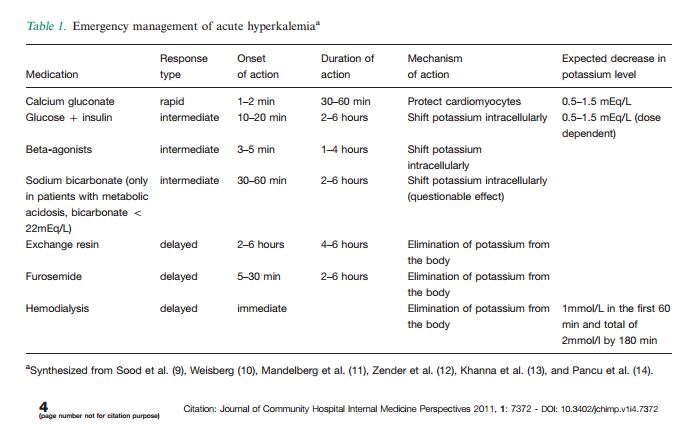
Calcium gluconate should be used as a first-line agent in patients with EKG changes or severe hyperkalemia to protect cardiomyocytes. Insulin and glucose combination is the fastest acting drug that shifts potassium into the cells. B-agonists can be used in addition to insulin to decrease plasma potassium levels.
What is the mechanism of hyperkalemia?
The change in resting membrane potential caused by hyperkalemia is the principle pathophysiologic mechanism behind most of its symptoms. The decrease in the resting membrane potential decreases the number of sodium channels activated that in turn decrease the magnitude of inward sodium current.
What is the most reliable method to remove potassium from the body?
Hemodialysis remains the most reliable method to remove potassium from the body and should be used in cases refractory to medical treatment. Prompt detection and proper treatment are crucial in preventing lethal outcomes. Keywords: hyperkalemia, review, treatment, potassium, hyperkalemic.
What is pseudohyperkalemia?
Pseudohyperkalemia (fictitious hyperkalemia) Pseudohyperkalemia commonly arises from shifts of potassium from blood cells to blood plasma by mechanical trauma during venipuncture or during the clotting process in vitro. These effects are further enhanced when there is marked leukocytosis or thrombocytosis.
What are the distribution abnormalities of potassium?
Distribution abnormalities of potassium are seen during metabolic acidosis, insulin deficiency, aldosterone deficiency, adrenergic antagonists, and tissue damage. During metabolic acidosis, there is a significant extracellular shift of intracellular potassium in exchange for protons leading to hyperkalemia.
How long does potassium stay in the blood?
Serum potassium level starts trending down within 10–20 min of insulin and glucose administration with maximal action in 60 min: The effect lasts for 2–6 hours.
Is sodium bicarbonate effective for hyperkalemia?
Exchange resin has very slow action and is therefore indicated for treatment of chronic hyperkalemia. Hemodialysis is the most effective and reliable method to remove potassium from the body.
How to diagnose hyperkalemia?
How it’s diagnosed. A blood test or urine test can help your doctor diagnose hyperkalemia. Your doctor will routinely do blood tests during your annual checkup or if you’ve recently started a new medication. Any problems with your potassium levels will show up on these tests.
What is the best treatment for high potassium?
If you have high potassium due to kidney failure, hemodialysis is your best treatment option. Hemodialysis uses a machine to remove waste from your blood, including excess potassium, when your kidneys cannot filter your blood effectively.
What to do if your potassium is too high?
If your levels are dangerously high, your doctor may prescribe hospitalization or dialysis. But if your potassium levels are slightly elevated and you don’t have any other symptoms of hyperkalemia, your doctor may choose to monitor your condition and order a follow-up test.
Why is it important to have regular checkups for potassium?
This is because you may not be aware you have high potassium levels until you start developing symptoms.
What causes potassium to rise?
In these cases, extra potassium leaks from your body cells into your bloodstream. Burns or crush injuries where a large number of muscle cells are injured can cause these effects.
Can high potassium cause heart failure?
You may not have any symptoms at all. But if your potassium levels are high enough to cause symptoms, you may have: In extreme cases, high potassium can cause paralysis or heart failure. If left untreated, high potassium levels can cause your heart to stop.
Is potassium level 5.5 mmol/L dangerous?
A potassium level higher than 5.5 mmol/L is critically high, and a potassium level over 6 mmol/L can be life-threatening. Small variations in ranges may be possible depending on the laboratory. Whether you have mild or severe hyperkalemia, you should get prompt medical attention to prevent possible complications.
What is the FDA approved treatment for hyperkalemia?
Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma) was approved by the FDA in May 2018 to treat hyperkalemia in adults. It preferentially captures potassium in exchange for hydrogen and sodium, which reduces the free potassium concentration in the lumen of the GI tract, and thereby lowers the serum potassium level.
How long after hyperkalemia can you measure potassium?
Measurement of potassium levels at least 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 hours after identification and treatment of hyperkalemia is recommended. [ 64] Discontinue any potassium-sparing drugs or dietary potassium. If the patient is taking digoxin, look for evidence of digitalis toxicity.
How much potassium does SPS lower?
SPS can decrease serum potassium by 2 mEq/L. Oral SPS is useful in patients with advanced renal failure who are not yet on dialysis or transplant candidates. One or more daily doses of 15 g can control mild to moderate hyperkalemia effectively, with little inconvenience to patients.
How to treat cardiac toxicity?
Step 1. Administer intravenous (IV) calcium to ameliorate cardiac toxicity, if present. Infuse calcium chloride or calcium gluconate (10 mL of a 10% solution over 2-3 minutes). Onset of action occurs within minutes ; duration of action is 30 minutes to an hour . [ 65] Step 2.
Can sodium zirconium be used for hyperkalemia?
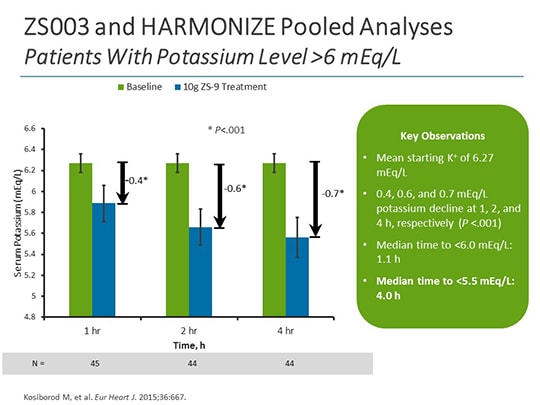
Like patiromer, sodium zirconium cyclosilicate should not be used as an emergency treatment for life-threatening hyperkalemia because of its delayed onset of action. Approval was based on the HARMONIZE clinical trial in patients with serum potassium levels of 5.1 mEq/L or higher.
Is a surgical intervention needed for hyperkalemia?
Surgical Therapy. Surgical intervention generally is not needed for the care of a patient with hyperkalemia. Patients with metabolic acidosis and consequent hyperkalemia due to ischemic gut obviously require exploration.
Can potassium be increased with cation exchange resin?
If the patient has only a moderate elevation in potassium level and no electrocardiographic (ECG) abnormalities, excretion can be increased by using a cation exchange resin or diuretics, and the source of excess potassium (eg, increased intake or inhibited excretion) can be corrected. [ 63]
What foods are high in potassium?
Limit the amount of potassium you eat. Foods that are high in potassium include bananas, tomatoes, oranges, turkey, and milk. Orange juice, citrus juices, and tomato juice are also high in potassium. Do not use salt substitutes. You may need to meet with a dietitian to help plan the best meals for you.
Can you refuse treatment?
You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.