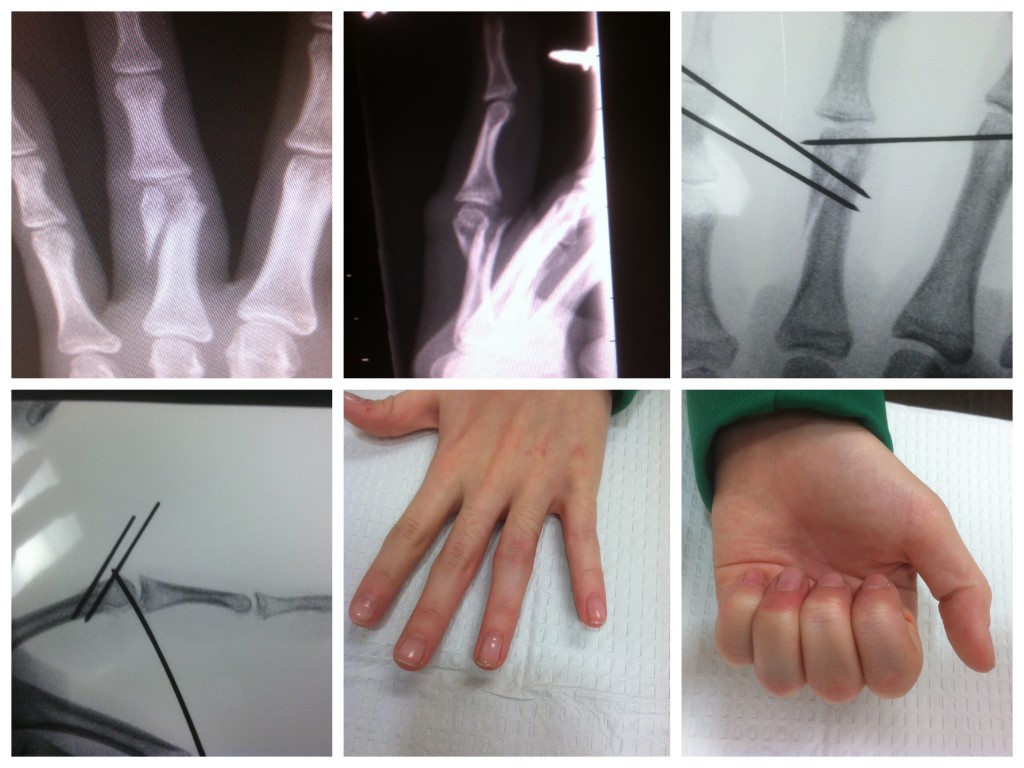
What is Percutaneous Fixation for broken bones?
Percutaneous fixation means the provider inserts stabilizing devices, such as pins or wires, through the skin from one bone fragment to the other, usually using imaging guidance. These stabilizers are usually left in position for four to six weeks and then removed when the fracture is healed.
What is the percutaneous technique for the treatment of pelvic fractures?
The percutaneous technique is recommended for non-displaced or slightly displaced fractures, and in obese, osteoporotic and elderly patients who cannot receive total joint arthroplasty. We recommend the use of intramedullary cannulated screws. Fracture reductions are achieved by manual traction of the affected bones.
What are the different types of fracture treatments?
Fracture treatments include: Closed manipulation means the provider does not surgically open the fracture site. Instead, the provider manipulates the fractured bone non-surgically to restore correct alignment. ORIF means the provider repairs the fracture through a surgical incision, often with the use of plates, screws, or rods.
What is the treatment for a closed reduction fracture?
Generally, bones heal best when immobilized, so treatment often involves casting the broken bone (or fracture), and may require surgery to set the bone in place. Prior to casting or fixation, the broken bone(s) must be returned to its proper position. “Closed” reduction is manipulation of a fracture without an incision.
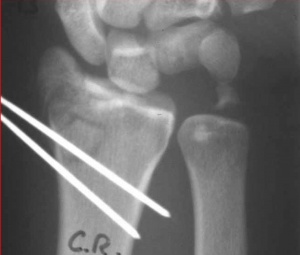
What is percutaneous skeletal fixation of fracture?
Percutaneous skeletal fixation is the surgical procedure of treating fractures by inserting surgical implants through the skin. It is applicable in the treatment of fractures in the pelvis and other bones in the body, including the spine.
What are the three types of treatment for fractures?
Treatment includes immobilising the bone with a plaster cast, or surgically inserting metal rods or plates to hold the bone pieces together. Some complicated fractures may need surgery and surgical traction.
Do percutaneous pins go through bone?
Percutaneous Pinning is a way of fixing fractures in bones and joints in which small thin wires are drilled through the bone. These wires are often left sticking out of the skin, so that they can be removed in clinic without going back to the operating room.
What are the methods of fracture treatment?
The three main treatment options for bone fractures are:Casting.Open reduction, and internal fixation- this involves a surgery to repair the fracture-frequently, metal rods, screws or plates are used to repair the bone, and remain in place, under the skin, after the surgery.More items...•
What types of fractures are most difficult to repair?
Example: A comminuted fracture is the most difficult to repair due to the bone having fractured into numerous pieces. Multiple bone pieces require more effort to hold them together in the ideal position for healing.
Which type of fracture usually requires surgery?
The more severe the fracture is, the more likely it is that surgery will be recommended. For example, an open or comminuted fracture will require surgery to ensure that the bone fully grows back together and safely supports your weight.
How are percutaneous pins inserted?
Percutaneous pinning is a technique used by orthopedic and podiatric surgeons for the stabilization of unstable fractures. Percutaneous pinning involves inserting wires through a person's skin for stabilizing the fractured bone.
When are percutaneous pins removed?
The percutaneous pins are usually removed three to four weeks post fixation, once the fracture has united 2. In many centers around the world, this procedure is performed in the clinic setting without the use of analgesia 3.
How do you remove percutaneous pins?
0:001:40MoraMD: Pin Removal Following Wrist Surgery- Dr Steve Mora - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe area with some with some alcohol these pins are bent like this just to allow me to grab them andMoreThe area with some with some alcohol these pins are bent like this just to allow me to grab them and pull them out. See. They come right out.
What are the 4 types of fractures?
Although there are many types of bone fractures, there are four main categories a fracture usually falls under: displaced, non-displaced, open and closed.
What is worse a fracture or a break?
Some people assume that fractured bones are more serious than broken bones, while others assume it's the other way around. But the truth is that these terms are used interchangeably, and they have the same meaning to medical professionals.
What are the 5 stages of bone healing?
However, these stages have considerable overlap.Hematoma Formation (Days 1 to 5) This stage begins immediately following the fracture. ... Fibrocartilaginous Callus Formation (Days 5 to 11) ... Bony Callus Formation (Days 11 to 28) ... Bone Remodelling (Day 18 onwards, lasting months to years)
VERTEBROPLASTY
Vertebroplasty is performed to stabilize a fractured vertebra and prevent further collapse, which is accomplished by cement injection only into the vertebra through percutaneously placed transpedicular needles. No attempt to restore vertebral height or create a cavity for the cement is made with vertebroplasty.
VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION
A vertebral augmentation procedure attempts to restore height to a fractured vertebral body in addition to stabilizing the fracture. This is done by mechanical creation of a cavity within the vertebral body (for example, using a balloon, peek implant, or curette), followed by injection of cement into the cavity.
CODING CASE EXAMPLES
A vertebroplasty is performed at T7 using bilateral transpedicular needle placement and injection of cement. Biplane fluoroscopic guidance.
What is a vertebroplasty?
Vertebroplasty is an image-guided therapy in which a cement, a fast-setting polymer, is injected into a pathologic vertebral body. The purpose of this procedure is to relieve pain and disability. It can be used in the setting of painful osteoporotic compression fractures, pathologic fractures from underlying neoplasms, or structurally compromised vertebrae. It has been used for osteoporotic or malignant fractures. The procedure was first described by Galibert et al [ 1] who found that the “internal casting” provided by polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) injected into a symptomatic vertebral hemangioma provided substantial pain relief.
What is kyphoplasty in vertebroplasty?
Kyphoplasty differs from vertebroplasty by adding an important additional step: insertion and inflation of a balloon before cement delivery, which also serves to restore vertebral body height and spine alignment. [ 2] .
Abstract
Closed manipulative reduction and percutaneous fixation of a displaced sacral fracture is a treatment alternative that offers several advantages. The fracture is reduced and stabilized without an extensile surgical exposure. The risks of surgical wound problems, especially infection, are lessened.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The authors reviewed 75 consecutive patients treated operatively for unstable sacral fractures. Instability was identified based on radiographic disruptions and displacements as well as pelvic motion to clinical examination under fluoroscopy.
RESULTS
Fifty-seven patients were available for postoperative evaluations. One elderly male patient was crushed by a tractor and died from multiple system organ failure 2 weeks after injury. Two other patients did not return to the clinic for followup. Return examinations ranged from 4 to 48 months, with a mean of 15.5 months.
How long does a percutaneous fixation last?
These stabilizers are usually left in position for four to six weeks and then removed when the fracture is healed.
What is the application of the cast in a fracture?
The application of the cast is inherent to the fracture treatment procedure code. If, however, the provider subsequently applies or replaces the cast during a follow-up encounter, report the procedure code for casting.
What is the CPT code for a fracture of the tibial shaft?
In this case, the correct CPT® code for the initial treatment is 27750 Closed treatment of tibial shaft fracture (with or without fibular fracture); without manipulation.#N#If you were to use the diagnosis presentation term “open tibial shaft fracture” for CPT® code selection, however, you would inappropriately select 27758 Open treatment of tibial shaft fracture (with or without fibular fracture), with plate/screws, with or without cerclage.
What does it mean when a fracture is open?
An open fracture means that a fracture fragment has pierced the skin, exposing the fractured bone to air. Providers might use phrases like “puncture site” or “open wound down to the fracture site” to reference an open fracture. Conversely, a closed fracture does not produce an open wound at the fracture site, and the fractured bone is not exposed ...
What is closed treatment without manipulation?
Closed treatment without manipulation involves the use of medical supplies to stabilize the fracture site while it heals or to support weight-bearing during the healing period. Supplies used in closed treatment without manipulation include casts, splints, slings, walking boots, braces, and crutches.
Is it easy to code a fracture?
Fractures are common but coding them isn’t always easy. Correct coding relies on you knowing how to identify both the presentation and treatment of the fracture.#N#To differentiate between the type of fracture and the type of treatment provided:
What is the difference between Colles' and Pott's fracture?
Colles’ fracture: A fracture of the lower end of the radius, with the lower fragment displaced backward.
What is a fracture of the atlas?
Fissure fracture: A crack extending from a surface into, but not through, a long bone. Jefferson’s fracture: Fracture of the atlas (first cervical vertebra). Lead pipe fracture: The bone cortex is slightly compressed and bulged on one side, with a slight crack on the other side of the bone.
What is a ping pong fracture?
Ping-pong fracture: A type of depressed skull fracture usually seen in young children, resembling the indentation that can be produced with the finger into a ping-pong ball; when elevated it resumes and retains its normal position.
What percentage of a surgeon should be paid for a preoperative procedure in Utah?
Ideally, the surgeon in Utah should get 17 percent for the preoperative portion and 63 percent for the operative or surgical portion. If the surgeon knows that the patient is not staying for postop care, he should apply modifier 54 Surgical care only to the billed fracture care code.
Is a fracture the same as a broken bone?
To set the record straight, here’s everything you wanted to know about fractures, but were afraid to ask. What Is a Fracture? Many people believe a fracture is a “hairline break,” or a certain type of broken bone. That is not true: A fracture and a broken bone are the same thing.
Overview
In 1984, vertebroplasty was first successfully performed in France for the treatment of a cervical vertebral hemangioma (see image below). [ 1]
Fractures and osteoporosis
The fractures may be as a result of bone weakened by osteoporosis, trauma, or tumors such as metastases, multiple myeloma, and hemangioma. Osteoporosis, however, accounts for most fractures. The disease accounts for an estimated annual incidence of 700,000 fractures per year; of these, approximately 260,000 are vertebral compression fractures.