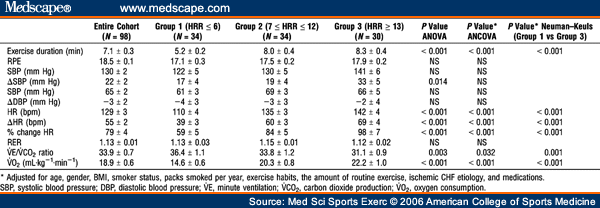
Medications for bradycardia
Bradycardia
Heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute.
Why is peak heart rate important in cardiovascular training?
Working in your peak heart rate zone in cardiovascular training helps increase your anaerobic threshold , the point at which your energy sources move from utilizing a higher percentage of fat to utilizing a higher percentage of carbohydrates. It also increases the caloric burn during and after exercise.
What is a good target heart rate for exercise?
Target Heart Rate and Estimated Maximum Heart Rate. For moderate-intensity physical activity, a person's target heart rate should be 50 to 70% of his or her maximum heart rate. This maximum rate is based on the person's age. An estimate of a person's maximum age-related heart rate can be obtained by subtracting the person's age from 220.
What can I do to slow down my heartbeat?
However, you may need medication or other medical treatment to slow down your heartbeat. During cardioversion, shocks are delivered to your chest by the cardioversion machine while your heart rhythm is monitored. Vagal maneuvers. Your doctor may ask you to perform an action, called a vagal maneuver, during an episode of a fast heartbeat.
What is your heart rate recovery?
Your heart rate recovery is the difference between your heart rate at the end of your workout and one minute after. So, if you end your workout with a heart rate of 130 beats per minute and after one minute of rest your heart rate is at 110 beats per minute, your recovering heart rate is 20 beats per minute.
How do I lower my peak heart rate?
How to lower your resting heart rateGet moving. The most common cause of a high resting heart rate is a sedentary lifestyle, where you spend a lot of time not moving. ... Manage stress. ... Avoid caffeine and nicotine. ... Maintain a healthy weight. ... Stay hydrated. ... Sleep well. ... How long does it take to lower your heart rate?
Is it good to train in peak heart rate?
The American Heart Association recommends exercising with a target heart rate of 50 to 75 percent of your maximum heart rate for beginners, and for moderately intense exercise. You can work at 70 to 85 percent of your maximum heart rate during vigorous activity.
How long should I be in my peak heart rate?
“For daily exercise, aim to be at your THR for 30 minutes for most days of the week,” she says “The ACSM and CDC recommend that healthy adults strive for 150 minutes per week in their THR zone.” During interval training you should attempt to tease the 80 to 90 percent of your maximum heart rate zone during your harder ...
What happens when you reach peak heart rate?
It is possible to exceed the upper limit of your zone without any ill effects, as long as you do not have coronary artery disease or are at risk for a heart attack. What it may do, though, is leave you with a musculoskeletal injury. Exercising above 85% of your target heart rate could bring you sore joints and muscles.
Does peak heart rate burn fat?
In general, the higher the heart rate, the more fat the body burns compared with other calorie sources, such as carbohydrates. This has led many to believe that hitting and staying in the fat burning heart rate zone is the best way to burn fat and lose weight.
Is peak heart rate better than cardio?
Generally, you will burn more calories in the peak zone as opposed to doing Cardio. But doing or exercising in the cardio means that you can exercise longer in that zone, and burn just as much calories there than in the peak.
Is it good to be in peak heart rate zone Fitbit?
So as you age, the peak heart rate becomes lower and lower, which isn't the best measurement especially for those that are fairly active. I'd say as not as you're not feeling any chest discomforts during and after your runs, not much to worry about.
Will my heart rate decrease as I get fitter?
The more fit you are, the lower your resting heart rate; for very fit people, it's in the range of 40 to 50 beats per minute.
How long can you stay at max heart rate?
How long can you stay at your maximum heart rate? Since your max heart rate is attained by the most strenuous level of physical exertion your body is capable of, it is only sustainable for very short periods of time. For the average person, this likely falls somewhere between 10 seconds and 1 minute.
Is it OK to workout at 180 heart rate?
For example, a 40-year-old woman has a max heart rate of 180 beats per minute (bpm). To exercise in the lower-intensity zone, multiply 180 times 50% or 60%. The target heart rate would range from 90 to 108 for a low-intensity workout.
What is the target heart rate for moderate intensity exercise?
For moderate-intensity physical activity, your target heart rate should be between 64% and 76% 1, 2 of your maximum heart rate. You can estimate your maximum heart rate based on your age. To estimate your maximum age-related heart rate, subtract your age from 220.
What is the best heart rate for a 35 year old?
For vigorous-intensity physical activity, your target heart rate should be between 77% and 93% 1, 2 of your maximum heart rate. To figure out this range, follow the same formula used above, except change “64 and 76%” to “77 and 93%”. For example, for a 35-year-old person, the estimated maximum age-related heart rate would be calculated as 220 – 35 years = 185 beats per minute (bpm). The 77% and 93% levels would be: 1 77% level: 185 x 0.77 = 142 bpm, and 2 93% level: 185 x 0.93 = 172 bpm
How to feel radial pulse?
You can feel the radial pulse on the artery of the wrist in line with the thumb. Place the tips of the index and middle fingers over the artery and press lightly. Do not use the thumb. Take a full 60-second count of the heartbeats, or take for 30 seconds and multiply by 2.
What is the target heart rate for moderate intensity?
In the age category closest to yours, read across to find your target heart rates. Target heart rate during moderate intensity activities is about 50-70% of maximum heart rate, while during vigorous physical activity it’s about 70-85% of maximum.
How to check your heart rate?
Now that you have a target, you can monitor your heart rate to make sure you’re in the zone. As you exercise, periodically check your heart rate. A wearable activity tracker makes it super easy, but if you don’t use one you can also find it manually: 1 Take your pulse on the inside of your wrist, on the thumb side. 2 Use the tips of your first two fingers (not your thumb) and press lightly over the artery. 3 Count your pulse for 30 seconds and multiply by 2 to find your beats per minute.
What is the normal heart rate for adults?
For most of us (adults), between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm) is normal.1 The rate can be affected by factors like stress, anxiety, hormones, medication, and how physically active you are. An athlete or more active person may have a resting heart rate as low as 40 beats per minute. Now that’s chill!
Do medications affect heart rate?
Important Note: Some drugs and medications affect heart rate, meaning you may have a lower maximum heart rate and target zone. If you have a heart condition or take medication, ask your healthcare provider what your heart rate should be.
How to keep your heart rate steady?
Heart Rate Tips to Keep in Mind 1 Start at your beginning. Before getting overly concerned about your heart rate, Martin says, it’s best to simply get moving. If you haven’t exercised much before, start where you’re comfortable (around 50 percent of maximum heart rate) and gradually exert yourself more over time. 2 Listen to your body. Your body provides other indicators of how hard it’s working that you need to consider along with heart rate. Pay attention to how hard you’re breathing or sweating, and stop if you feel very uncomfortable, Martin says. Devices recording your heart rate have been known to malfunction, for example—another reason listening to your body is important. 3 Remember that target heart rate is just a guide. “Don’t get overly fixated on numbers,” Martin says. Ideally, they just push you to work a little harder.
What is the target heart rate for a 50 year old?
Therefore, the target heart rate that a 50-year-old would want to aim for during exercise is 85 to 145 beats per minute.
How to check your resting heart rate?
First, it helps to know your resting heart rate, Martin says. Find your pulse (inside your wrist, on the thumb side, is a good place). Then count the number of beats in a minute—that’s your resting heart rate. (Alternately, you can take your pulse for 30 seconds and double it.)
What is the average heart rate?
The average resting heart rate is between 60 and 100, he says. The more fit you are, the lower your resting heart rate; for very fit people, it’s in the range of 40 to 50 beats per minute. Target heart rate is generally expressed as a percentage (usually between 50 percent and 85 percent) of your maximum safe heart rate.
What is the procedure to treat tachycardia?
Open-heart surgery may be needed in some cases to destroy an extra electrical pathway causing tachycardia. Tachycardia may also be treated with a maze procedure. During this procedure, a surgeon makes small incisions in heart tissue to create a pattern or maze of scar tissue.
How to diagnose tachycardia?
A thorough physical exam, medical history and testing is required to diagnose tachycardia. To diagnose your condition and determine the specific type of tachycardia, your doctor will evaluate your symptoms, perform a physical examination, and ask you about your health habits and medical history. Several heart tests also may be necessary ...
What is an EKG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical signal from your heart to check for different heart conditions. Electrodes are placed on your chest to record your heart's electrical signals, which cause your heart to beat. The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printer. An electrocardiogram, also called an ECG ...
How does ablation work?
Cardiac ablation is a procedure to scar or destroy tissue in your heart that's allowing incorrect electrical signals to cause an abnormal heart rhythm. Diagnostic catheters are threaded through blood vessels to your heart where they are used to map your heart's electrical signals. Ablation catheters transmit heat or cold to scar or destroy tissue. This illustration shows ablation catheters being applied near the pulmonary veins in a type of cardiac ablation called pulmonary vein isolation, which is often used to treat atrial fibrillation.
Why is scar tissue used for tachycardia?
Because scar tissue doesn't conduct electricity, it interferes with stray electrical impulses that cause some types of tachycardia. Surgery is usually used only when other treatment options don't work or when surgery is needed to treat another heart disorder. Tachycardia consultation at Mayo Clinic.
What is the most common test for tachycardia?
An electrocardiogram, also called an ECG or EKG, is the most common tool used to diagnose tachycardia. It's a painless test that detects and records your heart's electrical activity using small sensors (electrodes) attached to your chest and arms. An ECG records the timing and strength of electrical signals as they travel through your heart.
How does cardioversion work?
Cardioversion. In this procedure, a shock is delivered to your heart through paddles, an automated external defibrillator (AED) or patches on your chest. The current affects the electrical impulses in your heart and restores a normal heartbeat.
What is the name of the fast heart rate?
Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a fast heart rate that starts in the upper chambers of the heart. Some forms of this particular tachycardia are paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) or paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT).
What is the name of the condition where the heart beats faster than normal?
Sinus tachycardia is a normal increase in the heart rate. In this condition, the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node, sends out electrical signals faster than usual. The heart rate is faster than normal, but the heart beats properly.
What is ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is most often associated with disorders that interfere with the heart’s electrical conduction system. These disorders can include: Lack of coronary artery blood flow, depriving oxygen to heart tissue. Cardiomyopathy distorting the heart’s structure. Medication side effects.
Which profile is most likely to have atrial or supraventricular tachycardia?
A profile for atrial or SVT. In general, those most likely to have atrial or supraventricular tachycardia are: Children (SVT is the most common type of arrhythmia in kids) Women, to a greater degree than men. Anxious young people. People who are physically fatigued.
What happens when the heart is tachycardic?
In cases of ventricular tachycardia, electrical signals in the heart’s lower chambers fire abnormally. This interferes with electrical impulses coming from the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s natural pacemaker. The disruption results in a faster than normal heart rate.
What does it mean when your heart beats too fast?
Tachycardia refers to a heart rate that’s too fast. How that’s defined may depend on your age and physical condition. Generally speaking, for adults, a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute (BPM) is considered too fast. View an animation of tachycardia.
Can slowing heart rate cause sinus tachycardia?
Simply slowing the heart rate could cause more harm if your rapid heartbeat is a symptom of a more serious or long-term problem.
What Is Heart Rate Recovery?
If you’ve taken a fitness class or personal training session, you may have heard people mention your heart rate recovery. Heart rate recovery is different from your target heart rate (a heart rate you aim to raise yours to during exercise) or normal resting heart rate (your heart rate when you have not been doing any activity).
Why Heart Rate Recovery Matters
Heart rate recovery is important because it can be used to understand how the heart recovers after stress. Exercise intentionally and safely adds stress to the body. The stress from exercise helps you maintain healthy muscles and lungs, as well as cardiovascular (the heart and blood vessels) health.
How to Test Your Recovery Heart Rate
Your heart rate recovery is simply a measure of how your heart rate changes after exercise. You can manually check your heart rate by feeling for your pulse on your wrist, counting for 15 seconds, and multiplying the number by 4. Then after one minute, repeat the test.
Factors That Affect Your Recovery Heart Rate
More than just your overall fitness level impacts your heart rate recovery. So, to track change in your heart rate recovery, it’s important to understand how these factors affect it.
How to Improve Your Heart Rate Recovery
Now that you understand heart rate recovery, you may be wondering how to improve it. First, make sure you consider the other factors that may impact your heart rate recovery, like not getting enough sleep, caffeine intake, and dehydration.
Summary
Heart rate recovery measures how quickly your heart rate returns to a resting rate. You can use your recovery heart rate to assess your fitness level and overall cardiovascular health.
A Word From Verywell
Maintaining a healthy heart is important for preventing disease and maintaining your well-being as you age. Staying active and increasing how often you move throughout the day helps improve your recovery after workouts. If you have any questions or concerns about your heart rate recovery, talk with your healthcare professional.
What to do if you have palpitations?
If your palpitations are brief and there are no other worrisome signs or symptoms, make an appointment to see your doctor. Your doctor can help you find out if your palpitations are harmless or a symptom of a more serious heart condition. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment:
What is the best test for palpitations?
If your doctor suspects that your palpitations are caused by an arrhythmia or other heart condition, tests might include: Electrocardiogram (ECG). In this noninvasive test, a technician places leads on your chest that record the electrical signals that make your heart beat. An ECG can help your doctor detect problems in your heartbeat ...
How often should you record your heartbeat on a Holter monitor?
This portable ECG device is intended to monitor your heart activity over a week to a few months.
Do you have to have heart palpitations to get treatment?
Unless your doctor finds that you have a heart condition, heart palpitations seldom require treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend ways for you to avoid the triggers that cause your palpitations. If your palpitations are caused by a condition, such as an arrhythmia, treatment will focus on correcting the condition.