Acute partition syndrome requires emergency surgery. Non-surgical treatment is not successful in this case. The surgery performed is called fasciotomy where the doctor will make an incision and cut the fascia covering the infected region.
Full Answer
What happens if there is no treatment for acute compartment syndrome?
Jan 20, 2022 · Acute compartment syndrome is considered a surgical emergency since, without proper treatment, it can lead to ischemia and eventually necrosis. Generally, acute compartment syndrome is considered a clinical diagnosis. However, intracompartmental pressure (ICP) > 30 mmHg can be used as a threshold to aid in diagnosis.
How can compartment syndrome be prevented?
Oct 19, 2020 · Acute compartment syndrome is the most common type of compartment syndrome. About three-quarters of the time, acute compartment syndrome is caused by a broken leg or arm. Acute compartment ...
What are the diagnostic criteria for acute compartment syndrome?
Mar 27, 2015 · Compartment syndrome is a painful condition caused by the increased intracompartmental pressure (ICP) within a closed osteofascial compartment. It is both acute and chronic. Acute compartment syndrome (ACS) is a surgical emergency, and unless the pressure is relieved quickly, necrosis of the soft tissues and permanent disability may occur.
What are the two types of compartment syndrome?
Nonsurgical Treatment for Chronic Compartment Syndrome. If chronic compartment syndrome is causing pain, weakness, numbness, or tightness in your muscles during or after exercise, your NYU Langone doctor may recommend avoiding high-impact exercise and using custom orthotic shoe inserts to relieve stress during physical activity.

What is the treatment for acute compartment syndrome?
What are 3 ways to treat compartment syndrome?
Physical therapy, orthotics (inserts for shoes), and anti-inflammatory medicines are sometimes suggested. They have had questionable results for relieving symptoms. Your symptoms may subside if you avoid the activity that caused the condition.
What can you not do with anterior compartment syndrome?
How is compartment syndrome diagnosed and treated?
How is chronic compartment syndrome treated?
What causes chronic compartment syndrome?
What is chronic exertional compartment syndrome?
What are the 5 P's of compartment syndrome?
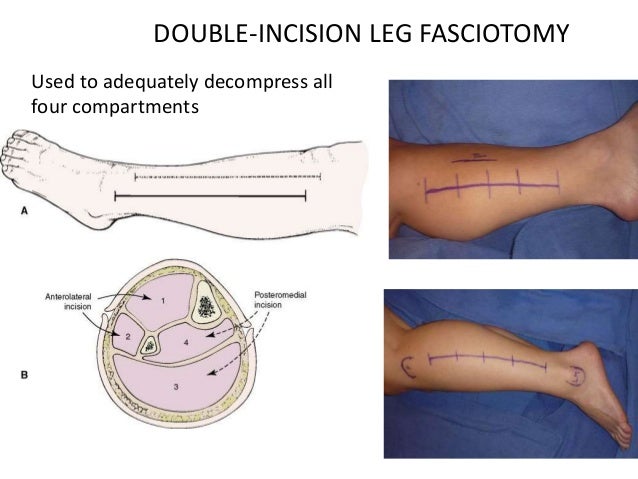
What is a fasciotomy procedure?
How is compartment syndrome of the leg treated?
What are the 6 cardinal signs of compartment syndrome?
How is acute compartment syndrome diagnosed?
What is the best treatment for chronic exertional compartment syndrome?
A surgical procedure called fasciotomy is the most effective treatment of chronic exertional compartment syndrome. It involves cutting open the inflexible tissue encasing each of the affected muscle compartments. This relieves the pressure.
What is compartment pressure?
This test, often called compartment pressure measurement, is the gold standard for diagnosing chronic exertional compartment syndrome. The test involves the insertion of a needle or catheter into your muscle before and after exercise to make the measurements. Because it's invasive and mildly painful, compartment pressure measurement usually isn't ...
How to stop leg pain from running?
Use orthotics or wear better athletic shoes. Limit your physical activities to those that don't cause pain, especially focusing on low-impact activities such as cycling or an elliptical trainer. For example, if running bothers your legs, try swimming. Or try running on softer surfaces.
What is a NIRS test?
NIRS is a newer technique that measures the amount of oxygen in your blood in the affected tissue. The test is done at rest and after physical activity. This helps determine if your muscle compartment has decreased blood flow.
What is the most common type of compartment syndrome?
Acute compartment syndrome is the most common type of compartment syndrome. About three-quarters of the time, acute compartment syndrome is caused by a broken leg or arm. Acute compartment syndrome develops rapidly over hours or days.
What is compartment syndrome?
Compartment syndrome occurs when excessive pressure builds up inside an enclosed muscle space in the body. Compartment syndrome usually results from bleeding or swelling after an injury. The dangerously high pressure in compartment syndrome impedes the flow of blood to and from the affected tissues. It can be an emergency, requiring surgery ...
Can steroids cause compartment syndrome?
Taking anabolic steroids can also contribute to developing compartment syndrome. Another form of compartment syndrome, called chronic compartment syndrome, develops over days or weeks. Also called exertional compartment syndrome, it may be caused by regular, vigorous exercise.
How long does it take for compartment syndrome to develop?
Compartment Syndrome Symptoms. Acute compartment syndrome usually develops over a few hours after a serious injury to an arm or leg. Some symptoms of acute compartment syndrome include: A new and persistent deep ache in an arm or leg. Pain that seems greater than expected for the severity of the injury.
What happens to the fascia after injury?
After an injury, blood or edema (fluid resulting from inflammation or injury) may accumulate in the compartment. The tough walls of fascia cannot easily expand, and compartment pressure rises, preventing adequate blood flow to tissues inside the compartment.
How long does it take for cramps to go away after exercise?
Symptoms of chronic compartment syndrome (exertional compartment syndrome) include worsening aching or cramping in the affected muscle (buttock, thigh, or lower leg) within a half-hour of starting exercise. Symptoms usually go away with rest, and muscle function remains normal.
What to do if you have compartment syndrome?
If chronic compartment syndrome is causing pain, weakness, numbness, or tightness in your muscles during or after exercise, your NYU Langone doctor may recommend avoiding high-impact exercise and using custom orthotic shoe inserts to relieve stress during physical activity. If symptoms persist or worsen, your doctor may recommend surgery.
How long does it take for compartment syndrome to go away?
It may take weeks or months for symptoms of compartment syndrome to completely disappear, and recovery time varies depending on the severity of the condition. After you’ve healed, you may gradually incorporate exercise into your routine, as long as the pain does not return.
What is the best medicine for muscle pain?
Doctors may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen to reduce inflammation and swelling in the affected muscle compartments and alleviate pain. These medications are available without a prescription and are taken by mouth.
How to treat chronic compartment syndrome?
Chronic compartment syndrome usually responds well to rest from activities that cause pain. Ice and elevation along with anti-inflammatory medications will help to control the swelling that causes the pressure. Sports massage may help to stretch the fascia to accommodate any swelling or growth of the muscle.
Is compartment syndrome a medical emergency?
Pain, numbness, a feeling of pressure, and some swelling usually accompany this condition. Acute compartment syndrome is a medical emergency whereas the chronic syndrome, although still painful and a danger to the blood vessels and nerves, can be treated more conservatively. Both conditions must be treated, however, ...
What is compartment syndrome?
Compartment syndrome is a condition that develops when the pressure inside the fascia surrounding the muscles and bone increases without relief and can cause destruction of the capillaries and nerve cells inside.
Is compartment syndrome common in the lower leg?
The quadriceps muscle is another likely candidate for this condition but due to its size and the lesser incidence of injury it is still far less common than lower leg compartment syndrome.
What is the lateral compartment?
The lateral compartment is the fourth compartment in the lower leg. The anterior compartment is the most commonly injured of the four compartments. Acute compartment syndrome results from trauma to the muscle or bone in the compartment. This trauma leads to bleeding inside the compartment.
What is the anterior compartment of the tibia?
The anterior compartment houses the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallicus longus, and the peroneus tertius muscles and is bordered by the tibia and fibula. The superficial posterior compartment covers the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles and is behind the tibia and fibula. The deep posterior compartment is tucked in between the tibia and fibula and contains the flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallicus longus, popliteus and the tibialis posterior. Also running through this compartment are the posterior tibial artery and vein along with the tibial nerve.
What is the superficial posterior compartment?
The superficial posterior compartment covers the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles and is behind the tibia and fibula. The deep posterior compartment is tucked in between the tibia and fibula and contains the flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallicus longus, popliteus and the tibialis posterior.
Is compartment syndrome acute or chronic?
Compartment syndrome may be acute or chronic. Acute compartment syndrome (ACS) is usually caused by trauma, i.e., closed leg fracture or contusion, although the trauma may be relatively minor. Intense exercise can also caused an ACS as well but this would be uncommon. ACS is a medical emergency requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment.
What is compartment syndrome?
Definition: Compartment syndrome is a clinical condition in which increased pressure within a closed anatomical space compromises the circulation and function of the tissues within that space. This compromise in circulation may result in temporary or permanent damage to muscles and nerves. Compartment syndrome may be acute or chronic.
What is ACS in medical terms?
Intense exercise can also caused an ACS as well but this would be uncommon. ACS is a medical emergency requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment.
What is CCS in running?
Chronic compartment syndrome (CCS) is an exercise-induced condition characterized by recurrent pain and disability. Symptoms subside when the offending activity (usually running) is stopped but return when the activity is resumed. CCS may be considered an uncommon though important cause of exercise-induced leg and/or foot pain.
What is CCS in sports?
Chronic compartment syndrome (CCS) is an exercise-induced condition characterized by recurrent pain and disability. Symptoms subside when the offending activity (usually running) is stopped but return when the activity is resumed.
What causes CCS?
All theories concerning the cause of CCS propose that an increase in tissue pressure to a critical level results in a compromise in tissue perfusion. Increased tissue pressure may result from limited or decreased compartment volume (tight thickened fascia), increased compartment content (muscle swelling and hypertrophy) or externally applied pressure (taping or casts).
Can exercise cause leg pain?
CCS is an uncommon though important cause of exercise-induced leg pain. It must be differentiated from the many other common and uncommon causes of leg pain associated with exercise. If CCS is suspected, intracompartment pressure testing should be considered. Once the diagnosis is established treatment options can be considered though surgical fasciotomy is definitive and curative for those individuals who wish to continue with vigorous exercise.

Diagnosis
- Other exercise-related problems are more common than chronic exertional compartment syndrome, so your doctor may first try to rule out other causes — such as shin splints or stress fractures — before moving on to more specialized testing. Results of physical exams for chronic exertional compartment syndrome are often normal. Your doctor might prefer to examine you af…
Treatment
- Options to treat chronic exertional compartment syndrome include both nonsurgical and surgical methods. However, nonsurgical measures are typically successful only if you stop or greatly reduce the activity that caused the condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- To help relieve the pain of chronic exertional compartment syndrome, try the following: 1. Use orthoticsor wear better athletic shoes. 2. Limit your physical activities to those that don't cause pain,especially focusing on low-impact activities such as cycling or an elliptical trainer. For example, if running bothers your legs, try swimming. Or try...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. He or she may refer you to a doctor who specializes in sports medicine or orthopedic surgery. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment.