
Medication
· Behavioral elements of narcolepsy treatment involve lifestyle strategies that are meant to combat excessive daytime sleepiness, prevent accidental injuries, and fortify physical, mental, and emotional health. People with narcolepsy can adapt these non-medical treatment methods to fit their individual situation. Planned Naps
Nutrition
Sodium oxybate (Xyrem®) is the only FDA-approved medication used to treat daytime sleepiness and cataplexy in patients with narcolepsy. It is taken in liquid form before bedtime and 2.5 to 4 hours later and not during the daytime. Due to its high sodium content, patients using sodium oxybate are advised to limit salt in the diet. Stimulants
How to cure narcolepsy naturally?
· Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to control sleep-wake cycles. People with narcolepsy may feel rested after waking, but then feel very sleepy throughout much of the day. Many individuals with narcolepsy also experience uneven and interrupted sleep that can involve waking up frequently during the night.
Can you cure narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy can be described as a neurological condition involving a person’s reduced ability to manage the sleep-wake cycle. Although people suffering from narcolepsy can’t be cured, they can be helped. Treatment for this disorder is tailored to each individual and is based on the person’s symptoms and therapeutic response.
Is there a cure for narcolepsy?
· Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by overwhelming daytime drowsiness and sudden attacks of sleep. People with narcolepsy often find it difficult to stay awake for long periods of time, regardless of the circumstances. Narcolepsy can cause serious disruptions in your daily routine.
What are the five signs of narcolepsy?
It acts on the histamine receptors and mimics histamine. Pitolisant uses the histamine receptors to prompt your brain to stay awake. Solriamfetol ( Sunosi ): This dual-acting dopamine and...
What is the best treatment for narcolepsy?
Stimulants. Drugs that stimulate the central nervous system are the primary treatment to help people with narcolepsy stay awake during the day. Doctors often try modafinil (Provigil) or armodafinil (Nuvigil) first for narcolepsy.
What is the main cause of narcolepsy?
What causes narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is often caused by a lack of the brain chemical hypocretin (also known as orexin), which regulates wakefulness. The lack of hypocretin is thought to be caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking the cells that produce it or the receptors that allow it to work.
What are the 5 signs of narcolepsy?
There are 5 main symptoms of narcolepsy, referred to by the acronym CHESS (Cataplexy, Hallucinations, Excessive daytime sleepiness, Sleep paralysis, Sleep disruption). While all patients with narcolepsy experience excessive daytime sleepiness, they may not experience all 5 symptoms.
Can narcolepsy be treated?
There's no specific cure for narcolepsy, but you can manage the symptoms and minimise their impact on your daily life. Making some simple changes to your sleeping habits can sometimes help. If your symptoms are more severe, you'll usually need to take medicine.
How can you tell if someone has narcolepsy?
SymptomsExcessive daytime sleepiness. People with narcolepsy fall asleep without warning, anywhere, anytime. ... Sudden loss of muscle tone. ... Sleep paralysis. ... Changes in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. ... Hallucinations.
Is narcolepsy a mental illness?
However, narcolepsy is frequently misdiagnosed initially as a psychiatric condition, contributing to the protracted time to accurate diagnosis and treatment. Narcolepsy is a disabling neurodegenerative condition that carries a high risk for development of social and occupational dysfunction.
How do you get tested for narcolepsy?
The diagnosis of narcolepsy is usually supported by test results from a polysomnogram and the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT). A polysomnogram helps your physician assess brain activity during sleep, in particular, how frequently and when REM activity is occurring.
How can I stop feeling sleepy?
Get Up and Move Around to Feel Awake. ... Take a Nap to Take the Edge Off Sleepiness. ... Give Your Eyes a Break to Avoid Fatigue. ... Eat a Healthy Snack to Boost Energy. ... Start a Conversation to Wake Up Your Mind. ... Turn Up the Lights to Ease Fatigue. ... Take a Breather to Feel Alert. ... If You're Driving, Pull Over When Sleepy.More items...•
Can people with narcolepsy drive?
Is It Legal to Drive With Narcolepsy? Yes, but it may not be safe. You need to be medically able to drive, which includes being able to stay awake.
What foods help narcolepsy?
Research is limited, but some people with narcolepsy say their symptoms improve when they follow a ketogenic (or keto) diet, which is a restrictive, low-carbohydrate, high-fat, moderate-protein diet. “There's some clinical data from small studies of low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet in people with narcolepsy,” Li says.
What drugs cause narcolepsy?
Drug Abuse as a Cause of NarcolepsySteroids, including prednisone.Diet pills.Drugs that treat high blood pressure, like beta blockers.Hormones, such as oral contraceptives.Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder stimulant medications.Some antidepressants.
Does narcolepsy affect memory?
Narcolepsy can present challenges to daily living: in addition to sleepiness, people with narcolepsy may experience mental fogginess, poor memory, and hallucinations.
Can you prevent narcolepsy?
You can't prevent narcolepsy. Treatment may reduce the number of attacks. Avoid situations that trigger the condition if you are prone to attacks of narcolepsy.
Can you just develop narcolepsy?
About 1 in 2,000 people develop narcolepsy. It can develop as early as 10 years old through 25 years old. If there's a presence of narcolepsy in your family medical history, you are 20 – 40 % more likely to develop this sleep disorder.
Can emotional trauma cause narcolepsy?
Central nervous system disorders such as tumors and vascular legions involving the hypothalamus can cause secondary narcolepsy. In addition, brain trauma can contribute to post-traumatic narcolepsy despite lack of any definite brain lesion.
What part of the brain is affected by narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy develops as a result of changes in the hypothalamus region of your brain. This small gland is located above your brain stem. The hypothalamus helps regulate the release of hormones that affect numerous parts of your body. For example, it's responsible for releasing hypocretins, which help regulate sleep.
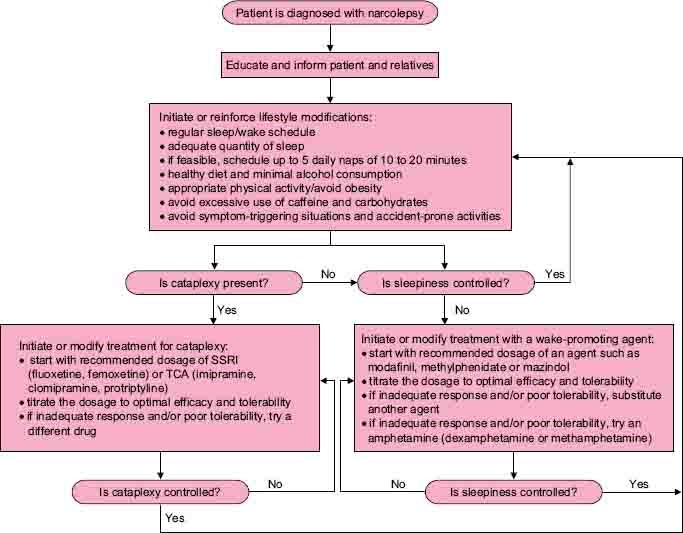
How to treat narcolepsy?
Treatment for narcolepsy can be broken down into two categories: 1 Behavioral approaches employ changes in lifestyle and daily habits to manage symptoms and reduce the likelihood of other physical and emotional challenges that often affect people with narcolepsy. 2 Medications can be prescribed to address symptoms. The use of medications is known as pharmacotherapy.
Is narcolepsy curable?
Narcolepsy is not curable. It is considered to be a lifelong condition. For the majority of patients, symptoms stay relatively stable over time. A significant number see symptom improvement 4 or, in some rare cases, remission 5 as they age.
What are the risks of narcolepsy?
Its central symptom is excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), which may involve falling asleep involuntarily, even while eating or driving. People with narcolepsy face safety risks including a three- to four-fold increase 2 in their chances of being in an automobile accident. Narcolepsy symptoms can also cause significant impairment in school, work, ...
What are the behavioral elements of narcolepsy?
Behavioral elements of narcolepsy treatment involve lifestyle strategies that are meant to combat excessive daytime sleepiness, prevent accidental injuries, and fortify physical, mental, and emotional health. People with narcolepsy can adapt these non-medical treatment methods to fit their individual situation.
Is narcolepsy a life threatening condition?
People with narcolepsy are at a higher risk of accidents while driving, operating heavy machinery, or engaging in other safety-critical activities. Accidents can be life-threatening, making the prevention of involuntary sleep an important element of narcolepsy care.
Can narcolepsy cause accidents?
Well-timed naps may enable safer driving for short distances. The risk of accidents can depend on the severity t of excessive daytime sleepiness as well as the presence of other symptoms, like cataplexy.
Can narcolepsy cause fragmented sleep?
Treating fragmented sleep in people with narcolepsy can be challenging. Typical prescription sleep medications, such as benzodiazepines or “Z drugs,” have a strong sedative effect that can persist into the morning, worsening daytime EDS.
What is narcolepsy in medical terms?
Eric Suni. Medically Reviewed by. Dr. John DeBanto. Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder that is often misunderstood. It is characterized by severe and persistent daytime sleepiness that can cause impairments in school, work, and social settings as well as heighten the risk of serious accidents and injuries.
What is the best medication for narcolepsy?
Some of the most commonly prescribed medications for narcolepsy include: 1 Modafinil and armodafinil: These two wakefulness-promoting drugs are chemically similar and are typically the first therapy for EDS. 2 Methylphenidate: This is a type of amphetamine that can reduce EDS. 3 Solriamfetol: This drug was approved by the FDA in 2019 and has shown comparable effects on EDS as modafinil 21. 4 Sodium oxybate: This medication can reduce cataplexy, EDS, and nighttime sleep disturbances, but it may take weeks to affect EDS 22. 5 Pitolisant: Approved by the FDA in 2019, pitolisant is a wakefulness-promoting medication that has also shown a positive effect on cataplexy.
How rare is narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is relatively rare. NT1 affects between 20 and 67 people per 100,000 in the United States. According to a population based study in Olmstead county Minnesota, NT1 is two to three times more common 4 than NT2, which is estimated to affect between 20 to 67 people per 100,000.
What are the symptoms of narcolepsy?
The symptoms of narcolepsy can have notable effects during both daytime and night time. The most common symptoms include: Excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS): EDS is the cardinal symptom of narcolepsy, affecting all people with the disorder. EDS involves an urge to sleep that can feel irresistible, and it arises most frequently in monotonous ...
Can you stop narcolepsy while pregnant?
A survey found that the majority of experts recommend stopping narcolepsy medications 24 when trying to conceive as well as when pregnant and breastfeeding. Discontinuing medication may require changes to behavioral approaches and other accommodations to safely cope with symptoms without medication.
What is NT1 in a patient?
NT1 was formerly known as “narcolepsy with cataplexy.”. Not all patients who are diagnosed with NT1 experience episodes of cataplexy. NT1 can also be diagnosed when a person has low levels of hypocretin-1, a chemical in the body that helps control wakefulness.
Is NT2 a cataplexy?
NT2 was formerly known as “narcolepsy without cataplexy.” People with NT2 have many similar symptoms as people with NT1, but they do not have cataplexy or low levels of hypocretin-1.
What is narcolepsy disorder?
What is narcolepsy? Narcolepsy is a neurological (nervous system) disorder that affects the brain’s ability to control sleep and wakefulness. If you have narcolepsy, you experience excessive daytime sleepiness and may have uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep during the daytime.
What is narcolepsy symptom?
Symptoms include excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy and sleep paralysis. Many medications are available to treat narcolepsy. Making certain lifestyle changes and joining support groups can help you better manage living with narcolepsy.
Can narcolepsy cause sleepiness?
If you have narcolepsy, you experience excessive daytime sleepiness and may have uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep during the daytime. These sudden sleep “attacks” may occur during any type of activity and at any time of the day. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How many people have narcolepsy?
Approximately one in 2,000 Americans has narcolepsy. The disorder affects males and females equally. Up to 10% of people who have narcolepsy have a relative who also has the disorder. Narcolepsy occurs in people of all ages, but the first sign of daytime sleepiness usually appears in the teenage years or twenties.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 narcolepsy?
Persons with type 1 narcolepsy have excessive daytime sleepiness plus cataplexy and/or low levels of a chemical in the brain called hypocretin. Type 2 narcolepsy (previously called narcolepsy without cataplexy). Persons with type 2 narcolepsy have excessive daytime sleepiness but do not have cataplexy and have normal levels of hypocretin.
What causes REM sleep?
Brain injury or tumor. In a small number of patients, the area of brain that controls REM sleep and wakefulness can be injured by trauma, tumor or disease. Infections. Environmental toxins, such as pesticides, heavy metals and secondhand smoke.
How long does cataplexy last?
Cataplexy usually lasts a few seconds to several minutes. You remain fully conscious during these attacks. The rate of attacks ranges from a few in a lifetime to several per day.
What is the best treatment for narcolepsy?
Central nervous system stimulants are the main treatments used for excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy, and these stimulants include Amphetamine, Methylphenidate, Modafinil, Dextroamphetamine and Armodafinil.
Can narcolepsy be cured?
Although people suffering from narcolepsy can’t be cured, they can be helped. Treatment for this disorder is tailored to each individual and is based on the person’s symptoms and therapeutic response. It could well take months, or even longer, to achieve effective control of symptoms.
Is narcolepsy a neurological disorder?
Narcolepsy can be described as a neurological condition involving a person’s reduced ability to manage the sleep-wake cycle. Although people suffering from narcolepsy can’t be ...
Can narcolepsy run in families?
The symptoms of narcolepsy are generally first noticed in young adults or teenagers, but narcolepsy can occur in both women and men at any age. In fact, there’s strong evidence that narcolepsy could run in families, because approximately 10% of people diagnosed with narcolepsy with cataplexy already have a close family member with this neurological disorder. As mentioned previously, narcolepsy can be confused with depression, and it’s true that there is a link between these two disorders. The co-occurrence of depression in narcolepsy patients has produced mixed results, though, with different studies producing numbers anywhere between 6% and 50%.
Is there a cure for narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is a chronic condition for which there's no cure. However, medications and lifestyle changes can help you manage the symptoms. Support from others — family, friends, employers, teachers — can help you cope with narcolepsy.
What is narcolepsy characterized by?
Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by overwhelming daytime drowsiness and sudden attacks of sleep. People with narcolepsy often find it difficult to stay awake for long periods of time, regardless of the circumstances. Narcolepsy can cause serious disruptions in your daily routine. Sometimes, narcolepsy can be accompanied by ...
What are the risk factors for narcolepsy?
There are only a few known risk factors for narcolepsy, including: 1 Age. Narcolepsy typically begins in people between 10 and 30 years old. 2 Family history. Your risk of narcolepsy is 20 to 40 times higher if you have a family member who has narcolepsy.
What is narcolepsy sleep disorder?
Overview. Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by overwhelming daytime drowsiness and sudden attacks of sleep. People with narcolepsy often find it difficult to stay awake for long periods of time, regardless of the circumstances. Narcolepsy can cause serious disruptions in your daily routine.
What is the difference between narcolepsy and cataplexy?
Sometimes, narcolepsy can be accompanied by a sudden loss of muscle tone (cataplexy), which can be triggered by strong emotion. Narcolepsy that occurs with cataplexy is called type 1 narcolepsy. Narcolepsy that occurs without cataplexy is known as type 2 narcolepsy.
What is narcolepsy without cataplexy?
Narcolepsy that occurs without cataplexy is known as type 2 narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is a chronic condition for which there's no cure. However, medications and lifestyle changes can help you manage the symptoms. Support from others — family, friends, employers, ...
Is narcolepsy a chronic condition?
Narcolepsy that occurs without cataplexy is known as type 2 narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is a chronic condition for which there's no cure. However, medications and lifestyle changes can help you manage the symptoms. Support from others — family, friends, employers, teachers — can help you cope with narcolepsy.
How to help narcolepsy?
There are several things you can do at home to help improve the symptoms of narcolepsy and include the following: Maintain a regular sleep schedule. Many people have an improvement in their symptoms if they maintain a regular sleep schedule, usually seven to eight hours of sleep per night. Schedule naps during the day.
What are the best medications for narcolepsy?
Drugs that act as stimulants and/or reduce the other symptoms of narcolepsy are standard treatments for the condition. They include: Armodafinil ( Nuvigil ): This drug is similar to Provigil. It is also used to reduce excessive daytime sleepiness. Headache and nausea are the most common side effects. Methylphenidate Hcl ( Daytrana, Ritalin ...
What is Xywav used for?
Sodium oxybate ( Xyrem, Xywav): This drug is used to treat a small subset of people with narcolepsy who have excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy that does not respond to the other medications. It is the only drug approved by the FDA for cataplexy.
Is Wakix a controlled substance?
It has a history of abuse as a recreational drug; therefore, the FDA has classified it as a controlled substance. Pitolisant ( Wakix ): This new drug is also used to treat those who experience excessive daytime sleep.
Does Pitolisant work on histamine receptors?
It acts on the histamine receptors and mimics histamine. Pitolisant uses the histamine receptors to prompt your brain to stay awake. Solriamfetol ( Sunosi ): This dual-acting dopamine and norepinephrinere uptake inhibitor is also used to treat narcolepsy.
What are the side effects of Prozac?
Side effects of Prozac and the other SSRIs also include stomach upset and sexual dysfunction.
Medications to Treat Narcolepsy
There are several medications that can combat and help reduce the effects of narcolepsy. Typically, these medications fall into two categories: stimulants that promote alertness and wakefulness; and anti-depressants and sedatives that help ensure a more regulated sleep, treat cataplexy, and can decrease overall anxiety.
Lifestyle changes
Because narcolepsy is a chronic lifelong condition with a wide range of different symptoms and causes, it is important to seek medical help to determine the right combination of medication and lifestyle adjustments. Besides medications, there are several ways people can adapt their lifestyle to reduce the effects of narcolepsy.
Resources
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/narcolepsy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20375503#:~:text=Selective%20serotonin%20reuptake%20inhibitors%20 (SSRIs,hypnagogic%20hallucinations%20and%20sleep%20paralysis.

What Is Narcolepsy?
Types
How Common Is Narcolepsy?
Symptoms
Specialist to consult
What Are The Effects of Narcolepsy?
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatments