
‘Mock’ control. Use another protein siRNA e.g. GAPDH (with no target protein siRNA) to check activation of RISC signaling pathway and also that it is not affecting overall cell function. Check the time for degradation of the mRNA and the existing protein.
Full Answer
What is Sirna Therapeutics?
The sequence-specific gene-silencing by siRNA can be used as a new therapeutic approach for treatment of a variety of diseases that are incurable by conv … siRNA therapeutics in the treatment of diseases
What is the best way to control siRNA knockout?
As a positive control for the protein of interest and a negative control for siRNA knockout. All reagents other than the siRNA should be added, this checks any effect from the transfection reagents. Use a dose response curve to optimize the amount of siRNA oligo or plasmid. To work out an optimal siRNA concentration.
How do you check if siRNA is active?
Check the sequence of the siRNA (computer programs) – BLAST search. ‘Mock’ control. Use another protein siRNA e.g. GAPDH (with no target protein siRNA) to check activation of RISC signaling pathway and also that it is not affecting overall cell function.
How do you confirm transfection with siRNA?
A small percentage of the siRNA added to the cells can be fluorescently tagged (e.g. GFP) to confirm transfection. Only a small percentage of the total siRNA should be tagged, the rest must be untagged because the tag will prevent RNA binding. Toxicity controls to check viability of cells.

What is siRNA treatment?
siRNAs are a class of dsRNAs, 21-23 nucleotides in length, which are able to silence their target genes through enzymatic cleavage of target mRNA. The sequence-specific gene-silencing by siRNA can be used as a new therapeutic approach for treatment of a variety of diseases that are incurable by conventional drugs.
How can I improve my siRNA transfection?
9 Tips for Optimal siRNA TransfectionUse the most appropriate siRNA concentration. ... Prepare a suitable siRNA stock solution. ... Transfect healthy cells. ... Check serum quality. ... Know the target gene in and out. ... Always use positive and negative controls. ... Follow up the transfection reagent protocol.More items...•
What is non targeting siRNA?
Negative control siRNAs are most often a non-targeting siRNA - designed not to target any gene - for determining the non-specific effects of siRNA delivery and for providing a baseline to compare to siRNA-treated samples.
How can we reduce the target effects of siRNA?
A second approach to reduce off-target effects is pooling of multiple siRNAs. It is important to notice that miRNA-like off-target effects are specific to individual sequences. Thus, reducing the concentration of the applied siRNAs will also reduce miRNA-like off-target effects.
How can I improve my siRNA knockdown efficiency?
Be Consistent When Conducting Experiments.Select Appropriate Order of Transfection.Use Healthy Cells at the Optimal Density.Choose the appropriate Culture Media and Culturing Conditions.Use High Quality siRNA at the Lowest Effective Concentration.More items...
What is considered a good siRNA knockdown?
Usually, 50% knockdown is considered acceptable.
What is non-targeting control?
The Sigma lenti CRISPR Non-Targeting Control is a lentiviral plasmid vector, which includes a gRNA sequence that does not target known human, mouse and rat genes. This vector is useful as a negative control in experiments using Sigma CRISPR lentiviral clones.
What is scramble siRNA?
Another negative control strategy is the “scramble” siRNA that has the same nucleotide composition, but not the same sequence, as the test siRNA. This is achieved in two ways: randomizing (also known as scrambling) the nucleotides in the siRNA or reversing the sequence of the siRNA.
How does siRNA bind to mRNA?
Once the siRNA is part of the RISC complex, the siRNA is unwound to form single stranded siRNA. Once the single stranded siRNA (part of the RISC complex) binds to its target mRNA, it induces mRNA cleavage. The mRNA is now cut and recognized as abnormal by the cell.
How do you silence genes?
To silence a gene, either one of those steps can be interrupted. By changing the structure of the DNA at the location of a specific gene, the code cannot be transcribed into a messengerRNA and therefore won't be transported to the ribosome.
Which of the following is correct for siRNA *?
Answer and Explanation: siRNA is best described as A. a short double-stranded RNA, one of whose strands can complement and inactivate a sequence mRNA.
How are siRNA processed in human cells?
After entry into the cytoplasm, siRNA is either loaded onto RISC directly or utilize a Dicer mediated process. After RISC loading, the passenger strand departs, thereby commencing the RNA interference process via target mRNA cleavage and degradation.
Why is RNAi important?
RNAi has become an important technology for manipulating cellular phenotypes, mapping genetic pathways and discovering therapeutic targets , and has therapeutic potential 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. However, owing to their large size ( ∼ 14,000 Da) and high negative charge, siRNAs do not readily enter cells 4, 5. Indeed, naked siRNAs do not enter unperturbed cells even at millimolar concentrations 4. Approaches for enhancing delivery of siRNAs to cells have included particle formation by means of cationic lipids, cholesterol, condensing polymers, antibody-protamine fusions and liposomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. However, these approaches perform best with adherent tumor cells and do not work well with primary cells or nonadherent cell types, thereby severely limiting the cell types amenable to discovery research and large-scale screening with RNAi. Consequently, there is a need for an siRNA delivery approach that targets the entire cell population of all primary and tumorigenic cell types, is noncytotoxic and is independent of siRNA sequence.
What is RNA interference?
RNA interference (RNAi) induced by short interfering RNA (siRNA) allows for discovery research and large-scale screening 1, 2, 3, 4, 5; however, owing to their size and anionic charge, siRNAs do not readily enter cells 4, 5. Current approaches do not deliver siRNAs into a high percentage of primary cells without cytotoxicity. Here we report an efficient siRNA delivery approach that uses a peptide transduction domain–double-stranded RNA-binding domain (PTD-DRBD) fusion protein. DRBDs bind to siRNAs with high avidity, masking the siRNA's negative charge and allowing PTD-mediated cellular uptake. PTD-DRBD–delivered siRNA induced rapid RNAi in a large percentage of various primary and transformed cells, including T cells, human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human embryonic stem cells. We observed no cytotoxicity, minimal off-target transcriptional changes and no induction of innate immune responses. Thus, PTD-DRBD–mediated siRNA delivery allows efficient gene silencing in difficult-to-transfect primary cell types.
What are the methods of siRNA delivery?
There are also continuing challenges with the intracellular delivery of siRNA. Common methods for delivery include transfection, electroporation, and viral-mediated delivery. The most widely applied of these is transfection, though it is not compatible with all cell types and has low in vivo efficiency.
How does siRNA work?
Mechanism of siRNA action. The method by which siRNA causes the silencing of genes is as follows: Double-stranded RNA is cleaved by the Dicer enzyme. This forms siRNA. The double-stranded siRNA enters the cell and forms the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) with other proteins. This is unwound, which forms the single-stranded siRNA.
Why is cleaving not achieved with siRNA?
For example, sometimes cleaving is not achieved due to mismatches between the siRNA and areas of the target mRNA near the cleaving site. There are other nonspecific effects when using siRNA.
What is the structure of siRNA?
It is also known as silencing RNA and short interfering RNA. It is similar to microRNA (miRNA) and the structure is short and well-defined, usually between 20 and 24 base pairs or thereabouts. Their structure has hydroxylated 3’ and phosphorylated 5’ ends. siRNA production is catalyzed by an enzyme known as the Dicer enzyme.
What are the challenges of RNAi?
RNAi intersects with other pathways, leading to the occasional triggering of these nonspecific effects. Challenges include: 1 Mammalian cells mistaking double-stranded RNA such as siRNA for viral by-products and mounting an immune response. 2 Thermodynamic properties of siRNA being chemically modified and leading to a loss of single nucleotide specificity. 3 Unintended off-targeting. This is due to the inadvertent downregulation of genes with incomplete complementarity. This leads to problems such as data interpretation issues and potential toxicity. 4 Too many siRNAs being introduced, leading to activation of the host’s innate immune responses. Evidence suggests that this is due to the activation of PKR, a dsRNA sensor, amongst other responses.
What is the enzyme that produces siRNA?
siRNA production is catalyzed by an enzyme known as the Dicer enzyme. This is a powerful tool in drug targeting and therapeutics development as it is used to modulate gene expression through transcriptional or translational repression. In principle, any gene can be silenced by a synthetic siRNA with a complementary sequence.
How many base pairs are in a siRNA?
As they are small in size at around 20 base pairs, siRNAs can pass through areas in the body where larger genetic therapies would not be able to pass.
Most recent answer
I have had significant knock down (80-90%)when I used Dharmacon transfection reagents and 20 NM siRNA on macrophages. Toxicity was minimal.
Popular Answers (1)
You could try to use a transfection reagent to get the siRNA into the cell. The electroporation could be causing the knockdown of your protein.
All Answers (8)
Maybe check if this happens in another cell line; and then check that your manufacturer hasn't sent two batches of your targeted siRNA. You could also test another scrambled control in your cells.
Most recent answer
Like Pawan said may be you ought to check the knockdown using western blot. A375 cell lines are known to be suitable transfection host and you achieve good transfection starting at about 10nM of the target gene you want to silence using HiPerfect transfection reagent .
All Answers (4)
I will suggest to check your knockdown using western blot if you have antibody available of the your target or by RT PCR rather than cell death to assess your transfection efficiency.
Most recent answer
Thanks Volker very much for very detail instruction. I used GAPDH or Actin as normalize gene. I will learn more REST2009.
All Answers (12)
I do electroporation with NIH3T3 cell lines. I dont use stable cell life. I over-expressed the gene conjugated with GFP and co-transfect with siRNA, I observed a depeletion of my target protein. It means that the siRNA works well.
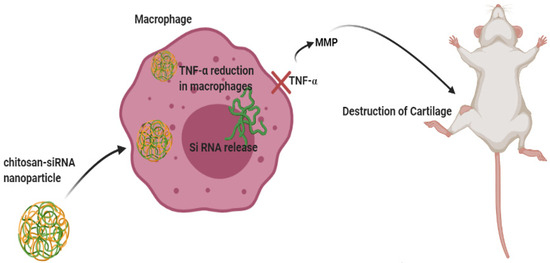
siRNA – An Overview
Mechanism of siRNA Action
- The method by which siRNA causes the silencing of genes is as follows: 1. Double-stranded RNA is cleaved by the Dicer enzyme. This forms siRNA. 2. The double-stranded siRNA enters the cell and forms the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) with other proteins. 3. This is unwound, which forms the single-stranded siRNA. 4. The strand of RNA with the ...
Challenges
- However, there are challenges associated with the use of siRNA. For example, sometimes cleaving is not achieved due to mismatches between the siRNA and areas of the target mRNA near the cleaving site. There are other nonspecific effects when using siRNA. RNAi intersects with other pathways, leading to the occasional triggering of these nonspecific effects. Challenges inc…
in Conclusion: siRNAs as Therapeutics – The Next Frontier?
- siRNAs may represent one of the next frontiers in medical science. They are currently being evaluated as to how they can be exploited in the drug development process and as therapeutic agents. If the challenges that currently exist in siRNA development and delivery can be addressed, siRNAs could be used to target virtually any gene for therapeutic intervention. The field is an exc…
Further Reading