Full Answer
How long is the wastewater retained in different treatment units?
The wastewater is retained in different treatment units at a particular time to achieve the desired parameters. The HRT followed in the Homogenization Tank is 12 to 24 hours, 24 to 48 hours in aeration tanks, 72 to 120 days in Anaerobic Reactors, 5 to 12 hours in Secondary Clarifiers, 3 to 5 hour
What is hydraulic retention time in wastewater treatment plant?
This confinement is to allow the particulates in the wastewater to settle. After some time, the water that is left on top of the settled particulates (overflow) moves to another confinement or process. Now Hydraulic Retention Time is the average length of time the overflow takes to leave the confinement or the tank.
What is detention time in wastewater treatment?
with wastewater the detention time is the average amount of a time that a drop of that water will remain in the treatment tank before the tank fills and that drop of water flows out of it. This is important because as wastewater passes through a treatment tank it must stay in the tank for the necessary period of time in order to be adequately
What is the stabilization time of activated sludge in wastewater treatment?
Recall from the distribution fit in Figure No. 3 the mean SRT for an industrial wastewater plant treating complex wastewater was 13 days with a maximum value of 28 days. Also, from Table No. 2, the stabilization of activated sludge with an SRT range of 20 to 40 days is in reference to an aerobic digester.

What is retention time in wastewater?
Retention time describes the time in which a volume of wastewater is stored within the pumping installation, pump sump, pipeline, detention basin and such like. The retention time can be estimated by dividing the holding volume by the discharge flow from the holding structure.
What is a good sludge retention time?
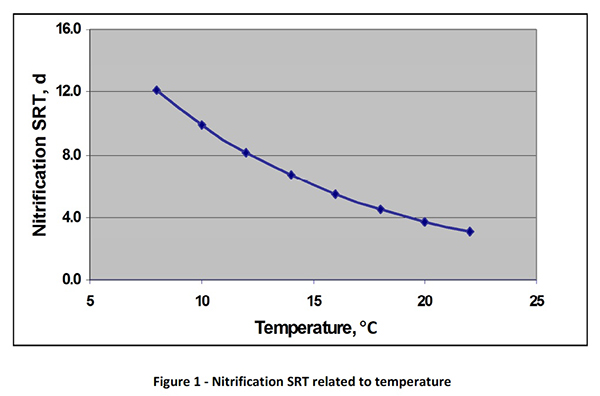
An SRT of at least 15–18 days is used for designing nitrification due to the low doubling time of nitrifiers (0.34–2 days) [11].
What is the minimum hydraulic retention time?
What is the minimum hydraulic retention time for UASB? Explanation: The hydraulic retention time should not be less than 2 hours.
Why is solid retention time important?
The solids retention time (SRT) is one important parameter for the design of WWTPs, relating to growth rate of microorganisms and to effluent concentrations. If a specific substance is degraded in dependency on the SRT, a critical value for the sludge age can be determined.
What is the meaning of retention time?
Retention time (RT) is a measure of the time taken for a solute to pass through a chromatography column. It is calculated as the time from injection to detection. The RT for a compound is not fixed as many factors can influence it even if the same GC and column are used.
What is SRT and HRT?
Summary. There are two significant retention times in an anaerobic digester. These are solids retention time (SRT) and hydraulic retention time (HRT). The SRT is the average time that bacteria (solids) are in the anaerobic digester. The HRT is the time that the wastewater or sludge is in the anaerobic digester.
How do you calculate retention time?
4:168:33Retention Time - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd the emergence of a given solute that retention time can be calculated directly from theMoreAnd the emergence of a given solute that retention time can be calculated directly from the parameters of our chromatogram. Really the linear distance on the time axis between the point of injection.
What is SVI in wastewater treatment?
Sludge Volume Index (SVI) is used to describe the settling characteristics of sludge in the aeration tank in Activated Sludge Process. It is a process control parameter to determine the recycle rate of sludge.
How do you reduce solid retention time?
The selection of an SRT has many consequences related to process performance, sludge production, and oxygen requirements. The traditional method for controlling SRT is to manually adjust the sludge wasting rate based on the food-tomicroorganism (F/M) ratio or mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) concentration.
How do you calculate retention time in a tank?
The average amount of time that liquid and soluble compounds stay in a reactor or tank. It is calculated by dividing the volume of a reactor (e.g. m3) by the influent flow rate (e.t. m3/day).
What is FM ratio wastewater?
What is an F-M ratio? Simply put, the F-M ratio is a measure of the amount of food, or BOD, that is given to the microorganisms in the aeration tank. The microorganisms are the mixed liquor volatile suspended solids, or MLVSS.
The Concept of SRT
The activated sludge process is a biological process that relies on the development of a mixed culture of microorganisms to metabolise pollutants in wastewater. It was originally developed to remove organic pollution from municipal wastewater but has been proven for nutrient removal.
Technical Enablers
Adoption of automation for wastewater treatment plants has been a slow process for several reasons. One of the main obstacles has been the inability to measure important operating parameters at a sufficient frequency to use in feedback control. Dissolved oxygen and pH were the first parameters that could be measured online.
Approaches to SRT Control
The objective of SRT control is to manage the mass balance shown in Figure 2 through adjustment of the waste activated sludge (WAS) flow rate (Qw). The calculation is straightforward: the inventory of biomass divided into the rate of sludge wasting.
Traditional Approach
The traditional method for SRT control is to maintain a constant MLSS. Manual or online samples of MLSS are analysed and a calculation is performed to determine the volume of sludge to be wasted and the wasting pump or valve is operated or adjusted accordingly.
Automated MLSS Control
A novel method for MLSS control of SRT has been utilised at an advanced wastewater plant in northern Ohio for over ten years.
Hydraulic Control
Hydraulic control is the simplest method for SRT control because it requires only a waste sludge flow measurement. MLSS is wasted directly from the aeration basin in the Garrett method. The waste sludge flow rate is calculated simply as the known volume of the aeration basin divided by the desired SRT.
Solids Control
This concept involves automation of SRT control using online TSS measurements. It is the basis for multiple commercial SRT controllers including the SIMS controller by Sanitaire, the Royce Model 7700 SRT Control System, and SRTMaster by Ekster and Associates.
How does wasting affect sludge thickening?
Click here to enlarge image. Wasting also affects sludge thickening processes not only because excessive wasting increases loads on the thickening facility , but, more importantly, because an increased daily variation in wasting biomass increases polymer consumption and reduces efficiency of all types of thickeners.
What is waste flow?
The waste flow is usually a small fraction of the influent flow; however, minimal variations of waste flow over time may have a profound effect on the performance of an activated sludge system. Inadequate wasting may cause clarifier overloading, low F/M bulking and foaming, and increased air demand for biomass endogenous respiration.
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment plants?
Wastewater treatment plants are designed to convert liquid wastes into an acceptable final effluent and to dispose of solids removed or generated during the process. In most cases, treatment is required for both suspended and dissolved contaminants.
What is biological waste treatment?
Various physical methods may be used for the removal of wastewater contaminants that are insoluble in water, such as suspended solids, oil, and grease. Ordinarily, water-soluble contaminants are chemically converted to an insoluble form to allow removal by physical methods. Essentially, biological waste treatment is this conversion ...
How is sludge dewatered?
In this section, sludge is dewatered by the gravity drainage of free water. The gravity drainage zone should increase the solids concentration of the sludge by 5-10%. If the sludge does not drain well in this zone, the sludge can squeeze out from between the belts or the belt mesh can become blinded.
Can lagoons be used for biological treatment?
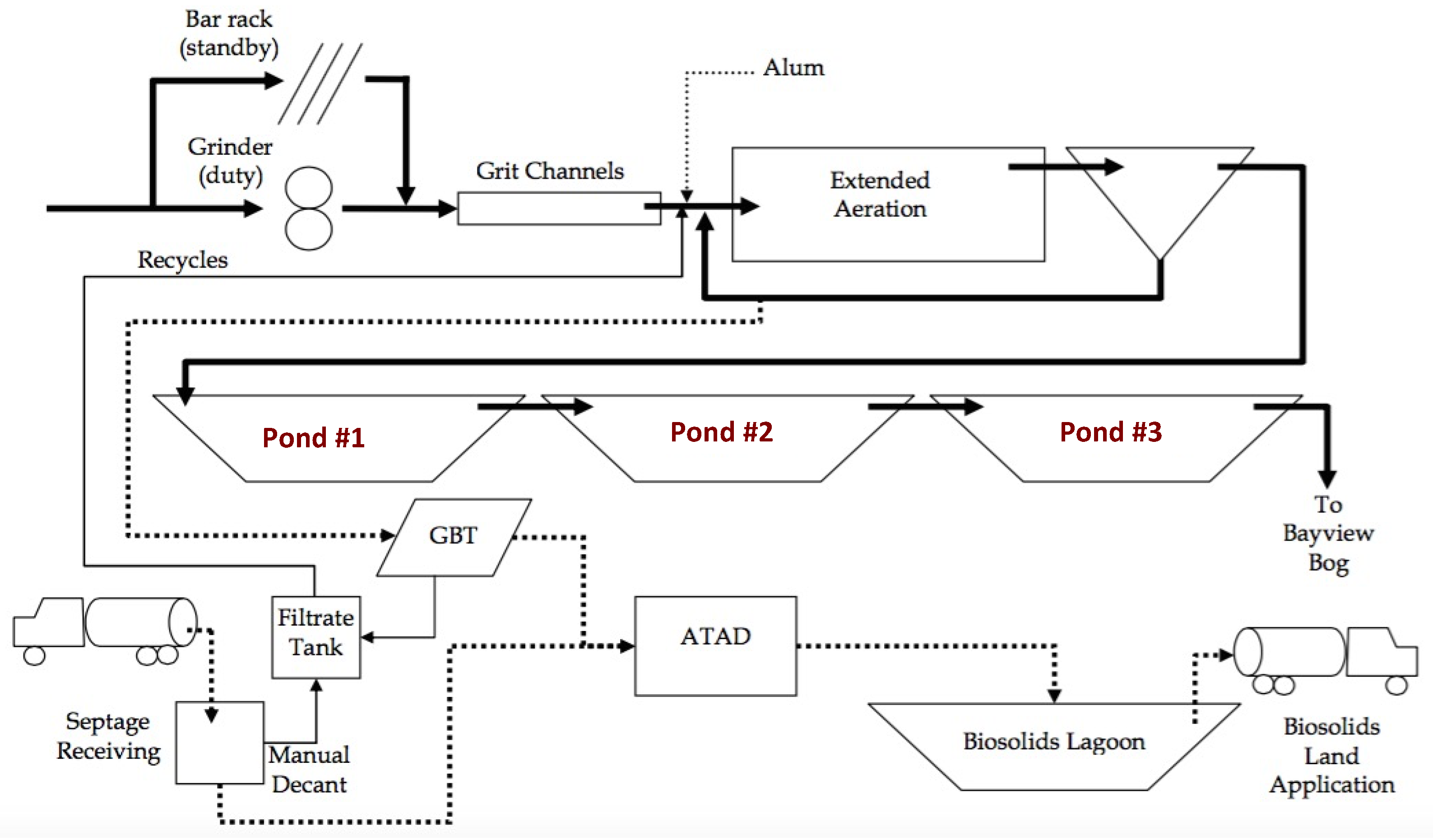
Where organic loads are low and sufficient land area is available, open lagoons may be used for biological treatment. Lagoons provide an ideal habitat for microorganisms. Natural infiltration of oxygen is sufficient for biological oxidation if the organic loading is not too high. However, mechanical aeration (Figure 37-6) is often used to increase the ability to handle a higher loading.
Does activated sludge have a low BOD?
The recirculated bacteria continue to oxidize wastewater contaminants, and if present in sufficient quantity , produce a relatively low BOD effluent water. Because the activated sludge process incorporates the return of concentrated microorganisms, it must include a process for microorganism concentration and removal.
Automation of SRT Control and Treatment Optimization
Solids Retention Time (SRT) is a critical activated sludge design and operating parameter. Automation of SRT control has many benefits, so what are the reasons that it isn’t more widely implemented? Download this white paper to find out why and to learn more about how SRT control can be optimized for the most stable results.
Looking for additional resources on SRT control in wastewater?
Webinar: Process Control Strategies for Activated Sludge Optimization YSI experts review solids control strategies in municipal wastewater applications.
GSA, MCRT, SRT, and Sludge Age Defined
I think there is confusion, sometimes, in how operators (which includes me) define the terms mean cell residence time (MCRT), solids retention time (SRT), sludge age, and, though seldom used these days (was it ever used?), Gould sludge age (GSA).
Gould Sludge Age (GSA)
The Gould sludge age represents the average number of days total suspended solids (TSS) entering the bioreactor remain under aeration. The GSA is calculated by dividing the pounds (or kg) of MLSS in the aeration tank by the pounds (or kg) of total suspended solids entering the aeration tank as shown schematically in Figure No. 1.
MCRT and SRT
Many operators refer to the mean cell residence time (MCRT), the solids retention time (SRT), and the sludge age as being one and the same and they'll use these three terms interchangeably.
MCRT & SRT Equations
The formula for calculating the mean cell residence time (MCRT) is shown in Equation No. 2. Actually, one final time, I'm showing both versions of the MCRT equation, the first with the constants removed, the second with the constants included. The solids in the clarifier are included in the calculation.
Difference Between MCRT and SRT
In Table No. 1 I shown an Excel spreadsheet using data from an industrial wastewater system where I have calculated both the MCRT and the SRT. As you can see, the SRT value is almost 32 percent lower than the MCRT value, the difference being the additional solids in the clarifier are increasing the MCRT value.
Why I Prefer SRT Over MCRT
Calculation of the SRT is easy because it uses data that is readily available and reliably produced. For the SRT the total suspended solids values you need are the MLSS, clarifier underflow TSS (the concentration in the return activated sludge or RAS) if you are wasting from the return sludge line, and the effluent TSS.
How much BOD can a pond eliminate?
The pond system can eliminate 80% to 90% of the BOD and reduce bacteria to levels comparable to other accepted oxidation types of treatment. This type of treatment system meets the needs of many small or rural communities due to low construction costs as well minimal operation and maintenance requirements.
What is the most commonly used pond in domestic wastewater treatment?
The most often used ponds in domestic wastewater treatment are the stabilization pond and facultative lagoon . The stabilization pond is designed to be aerobic throughout its depth and the facultative lagoon will be anaerobic at the bottom and aerobic at the top.
How deep should a pond be for a facultative lagoon?
Facultative lagoons are similar in design to stabilization ponds except design depth is five to eight feet. These ponds do not require primary treatment and the added depth is needed to handle the substantial increase in solids loadings. It is common for the depth near the inlets to be 10 to 12 feet.
How does a pond system stabilize organic matter?
Pond systems stabilize organic material through natural processes involving sunlight, water, nutrients, algae, atmospheric oxygen and bacterial action. Organic matter in the wastewater is broken down by aerobic bacteria and oxygen found in the pond.
What causes DO levels to decline in ponds?
Surface levels will have higher DO levels and as the depth increases it becomes more difficult for sunlight to penetrate therefore DO levels decline. Ponds use a multitude of organisms in the treatment process. Bacteria, algae, protozoa, and insects all have a part of the treatment in a pond system.
What is the purpose of stabilization ponds?
Stabilization ponds provide secondary biological treatment and are the most commonly used wastewater pond.