Is the Merci device a better alternative to traditional stroke treatment?
The Merci device is a tool your doctor may use to help treat a recent stroke. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is suddenly interrupted. Brain cells rely on a constant blood supply, so interrupting this supply, even for a few …
How does a MERCI Retriever treat an ischemic stroke?
Jan 20, 2014 · The bottom line: the MERCI device may be a better alternative than traditional stroke treatments for patients who are outside the time window and are prone to hemorrhaging. The MERCI device can be administered within 8 hours of symptom onset. The MERCI device is becoming an international phenomenon.
What is the history of the Merci device?
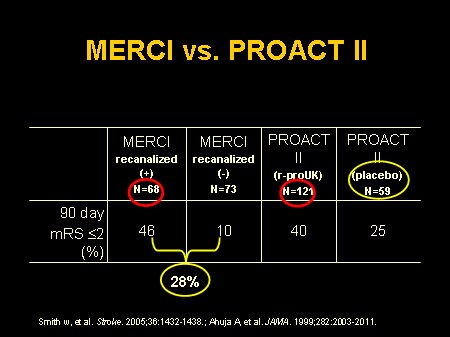
Sep 25, 2012 · The Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) and multi-MERCI trials, designed to test the safety and efficacy of the first and second generations of the retriever devices, showed similar results. 9,15 Both trials were prospective, multicenter single-arm studies of patient populations, up to 8 hours after symptom onset, with occlusion of major cerebral …
What was the purpose of the Merci trials?
Apr 06, 2006 · Technically, it works. And remarkably so. The Merci Retriever is a mechanical embolectomy device designed to reopen occluded vessels by extracting occlusive thrombi from the cerebral vasculature. In the Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) trial (parts I and II combined), among 151 patients enrolled in the intention-to-treat group; partial or …
What are 3 possible treatments of an ischemic stroke?
Treating ischaemic strokesThrombolysis – "clot buster" medicine. ... Thrombectomy. ... Aspirin and other antiplatelets. ... Anticoagulants. ... Blood pressure medicines. ... Statins. ... Carotid endarterectomy.
What is a coil retriever?
The coil retrievers are composed of Nitinol shape-memory wire and delivered through a microcatheter across the target clot. As the device is extruded from delivery catheter, it immediately reassumes its native coil form.
What is stroke treatment called?
Emergency IV medication. An IV injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) — also called alteplase (Activase) or tenecteplase (TNKase) — is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke. An injection of TPA is usually given through a vein in the arm within the first three hours.Jan 20, 2022
What is penumbra in stroke?
“Penumbra” is the term used for the reversibly injured brain tissue around ischemic core; which is the pharmacological target for acute ischemic stroke treatment (Astrup et al. 1981a). The goal to treat ischemic stroke is to salvage the penumbra as much and early as possible.
Is penumbra a stent retriever?
Certain lots of Penumbra's 3D revascularization device, a stent retriever used to remove thrombus in the setting of acute ischemic stroke, have been recalled due to risk of breakage or separation of the delivery wire, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced Friday.Jul 21, 2017
Can stroke be cured permanently?
The short answer is yes, stroke can be cured — but it occurs in two stages. First, doctors administer specific treatment to restore normal blood flow in the brain. Then, the patient participates in rehabilitation to cure the secondary effects.Sep 28, 2020
What are the 3 types of strokes?
These types are: Ischemic Stroke. Hemorrhagic Stroke. Transient Ischemic Attack (Mini-Stroke)Aug 13, 2020
Can you fully recover from a hemorrhagic stroke?
Is rehabilitation always successful? According to the National Stroke Association, 10 percent of people who have a stroke recover almost completely, with 25 percent recovering with minor impairments. Another 40 percent experience moderate to severe impairments that require special care.
What is the purpose of Merci?
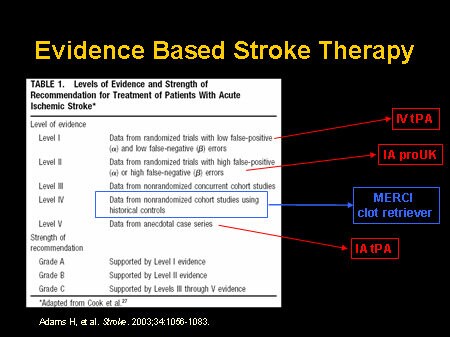
The purpose of the MERCI trials was to investigate the safety and efficacy of the MERCI device in a non-randomized, multi-center trial at 25 United States centers. The primary outcomes measured were recanalization (ability to restore blood flow in previously occluded vessel) in large cerebral vessels and safety.
When was the first mechanical thrombectomy device invented?
Dr. Y. Pierre Gobin of Weill Cornell Medical College understood this axiom in 1995 when he began developing the first mechanical thrombectomy device, now FDA-approved, for treatment of acute stroke.
Who invented the mechanical embolus?
The first Mechanical Embolus Removal for Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) device was conceived by Drs. Pierre Gobin and Jeffrey Wensel. With scant success using clot-busters, Gobin was the Initiator driven to try something new. “Frustrated, I thought that we should have a device that would just remove the clot, that should be faster and have less risk of hemorrhage than thrombolytics,” said Gobin. Gobin was attempting to use a clot-busting medication termed urokinase which “could not reopen the occlusion despite a two-hour infusion.” Learning from past failures, he immediately went back to the drawing board and by 1996, animal trials were performed. Gobin’s artistic gift of design was finally coalescing with his magnificent knowledge of science.
What is the purpose of the Merci study?
Background and Purpose— To report the result of the Mechanical Embo lus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) 1 study, a phase 1 trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of mechanical embolectomy in the cerebral vasculature.
When was the Merci 1 study done?
The study was performed in 7 US centers between May 16, 2001 and October 17, 2002, and the protocol was approved by the FDA under an international device exemption study, and by the institutional review boards at each center.
What is a merci retriever?
The Merci Retriever uses superelastic technology, ie, the superelastic property of memory shaped nitinol (nickel titanium). The Merci Retriever is a tapered wire with 5 helical loops of decreasing diameter (from 2.8 mm to 1.1 mm) at its distal end. The Merci Retriever is advanced through the microcatheter in its straight configuration and resumes its pre-imposed helical shape once it is delivered into the occluded intracranial artery in order to ensnare the thrombus.
What is a merci retriever?
In 2004, the Merci retriever system was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration as the first mechanical thrombectomy device for removing clot in AIS patients. The Merci retriever has undergone considerable redesigns throughout its existence. The first generation of the retriever device (X5 and X6) boasted a corkscrew appearance due to the helical tapered fashion in which the nitinol was coiled. It was further revised and reiterated for the second generation (L4, L5, and L6) to include arcading filaments that were attached to a nontapering helical nitinol coil. The L-generation helical coil was designed in a 90-degree angle with respect to the proximal catheter. The third generation (V 2.0, V 2.5, and V 3.0) is a hybrid design of a nontapered, nonangulated filamented helical coil that was provided in soft and firm versions. The current generation is based on flexible nitinol wire that assumes a helical shape once it emerges from the tip of a microcatheter ( figure 1 ). The helical coil loops are attached to a wire pusher and delivered through a microcatheter (18L). The system is usually used in conjunction with an 8- or 9-French balloon guide catheter. Inflating the silicone balloon at the distal end of the guide catheter temporarily arrests the antegrade flow in the carotid or the vertebral arteries and also allows for aspiration during the clot retrieval process.#N#10#N#Figure 2 demonstrates an occluded right carotid terminus treated successfully with the Merci clot retrieval device.
What is mechanical thrombectomy?
Background: Mechanical thrombectomy is a promising adjuvant or stand-alone therapy for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) caused by occlusion of a large vessel in patients beyond the systemic thrombolysis therapeutic window . This review focuses on the clinical and angiographic outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy with use of the Merci retriever device.
What percentage of stroke patients have a vascular occlusion?
Nearly 75% of patients with a severe stroke, exceeding 10 on the NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS), treated with IV-tPA continue to have persisting vascular occlusions, with only 8% likelihood of significant clinical improvement.#N#11#N#,#N#–#N#,#N#13#N#In contrast, treatment mechanical thrombectomy devices lead to higher rates of revascularization.#N#8#N#,#N#14#N#,#N#15#N#It is important to note that the correlation between revascularization and good clinical outcomes has been repeatedly demonstrated.#N#16#N#,#N#17#N#Given the lack of randomized control clinical efficacy trials comparing the Merci retriever to standard of care, the limited data on single-arm prospective trials, and the American Stroke Association guidelines, the level of evidence is considered less well established (Class II, level of evidence B).#N#18#N#Here we summarize the more significant studies involving the Merci retriever.
What is the best medicine for a stroke?
If you get to the hospital within 3 hours of the first symptoms of an ischemic stroke, you may get a type of medicine called a thrombolytic (a “clot-busting” drug) to break up blood clots. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a thrombolytic. tPA improves the chances of recovering from a stroke.
What do you need to do after a stroke?
After a stroke, you may need rehabilitation ( rehab) to help you recover. Before you are discharged from the hospital, social workers can help you find care services and caregiver support to continue your long-term recovery.
What is the best way to get to the hospital for a stroke?
Stroke Treatment. Calling 9-1-1 at the first symptom of stroke can help you get to the hospital in time for lifesaving stroke care. Your stroke treatment begins the moment emergency medical services (EMS) arrives to take you to the hospital. Once at the hospital, you may receive emergency care, treatment to prevent another stroke, ...
Why do people go to the hospital for stroke?
Stroke patients who are taken to the hospital in an ambulance may get diagnosed and treated more quickly than people who do not arrive in an ambulance. 1 This is because emergency treatment starts on the way to the hospital. The emergency workers may take you to a specialized stroke center to ensure that you receive the quickest possible diagnosis ...
What type of doctor treats strokes?
Brain scans will show what type of stroke you had. You may also work with a neurologist who treats brain disorders, a neurosurgeon that performs surgery on the brain, or a specialist in another area of medicine.
How many days after TIA can you get a stroke?
The risk of stroke within 90 days of a TIA may be as high as 17%, with the greatest risk during the first week. 6. That’s why it’s important to treat the underlying causes of stroke, including heart disease, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation (fast, irregular heartbeat), high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Do not drive to the hospital for a stroke?
Do not drive to the hospital or let someone else drive you. The key to stroke treatment and recovery is getting to the hospital quickly. Yet 1 in 3 stroke patients never calls 9-1-1. 1 Calling an ambulance means that medical staff can begin life-saving treatment on the way to the emergency room.
What is the best way to prevent stroke?
It’ll likely include a combination of exercise, a healthier diet, and medications such as aspirin. If you smoke, quitting smoking is an important lifestyle change for stroke prevention.
What is the procedure for a large stroke?
Decompressive craniotomy. A large stroke can lead to serious swelling in the brain. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary if drugs don’t adequately relieve the swelling. Decompressive craniectomy aims to relieve the buildup of pressure inside your skull before it becomes dangerous.
Why does hemorrhagic stroke cause swelling?
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a brain aneurysm bursts or a weakened blood vessel leaks. This causes blood to leak into your brain, creating swelling and pressure. Unlike ischemic strokes, treatment for hemorrhagic strokes doesn’t involve blood thinners. This is because thinning your blood would cause the bleeding in your brain to become worse.
How long does it take for a stroke to start?
They occur when a blood clot blocks blood flow to your brain. Medication treatment for this type of stroke must start within 4.5 hours of the event, according to 2018 guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Stroke Association (ASA).
What is the procedure for a blocked carotid artery?
Carotid endarterectomy. This procedure is often performed on people who’ve had an ischemic stroke due to a blocked carotid artery. The carotid arteries are the major blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain.
How does a stroke affect you?
How a stroke affects you depends on the location in your brain where the stroke occurs. Evaluation and treatment for a stroke should begin as soon as possible. The quicker emergency treatment begins, the greater the chance of preventing lasting damage. Treatment depends on the type of stroke you’re having.
What happens when the brain is cut off?
A stroke occurs when the blood flow to a specific part of your brain is cut off. When this happens, the cells don’t get oxygen and begin to die, causing numerous symptoms. The most common symptoms are changes in speech and numbness or weakness of the face, legs, or arms.
How is ischemic stroke treated?
Ischemic stroke is treated by removing obstruction and restoring blood flow to the brain. The only U. S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved medication for ischemic stroke is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which must be administered within a three-hour window from the onset of symptoms to work best.
What is a merci retriever?
The Merci Retriever, approved in 2004 by the FDA, is a corkscrew- shaped device used to help remove blood clots from the arteries of stroke patients. A small incision is made in the patient’s groin, into which a small catheter is fed until it reaches the arteries in the neck.
How is a microcatheter used in stroke?
Microcatheter-based surgical interventions for stroke may include the use of a small micro catheter , delivered through a larger guiding catheter inserted at the groin through a small incision. A microguidewire is used to navigate the microcatheter to the site of obstruction in the brain. Thrombolytic medication, such as tPA, can then be administered directly to the occluding thrombus. This kind of treatment, which delivers thrombolytic medication intraarterially, is more specific than IV (intravenous) tPA and consequently may require significantly lesser dosages of medication. The time limit to implement this type of intervention is also significantly (double) longer than that for IV TPA. Generally, only Comprehensive Stroke Care Centers offer this type of treatment.
What is the most common type of ischemic stroke?
Ischemic Stroke. Thrombotic (cerebral thrombosis) is the most common type of ischemic stroke. A blood clot forms inside a diseased or damaged artery in the brain resulting from atherosclerosis (cholesterol-containing deposits called plaque), blocking blood flow. Embolic (cerebral embolism) is caused when a clot or a small piece ...
What is the cause of a stroke?
The interruption of blood flow can be caused by a blockage, leading to the more common ischemic stroke, or by bleeding in the brain, leading to the more deadly hemorrhagic stroke.
What is TIA in medical terms?
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) This is a warning sign of a possible future stroke and is treated as a neurological emergency. Common temporary symptoms include difficulty speaking or understanding others, loss or blurring of vision in one eye and loss of strength or numbness in an arm or leg.
How many strokes are ischemic?
Ischemic stroke constitutes an estimated 87 percent of all stroke cases. Stroke often occurs with little or no warning, and the results can be devastating. It is crucial that proper blood flow and oxygen be restored to the brain as soon as possible.
