
What medication is used for latent TB?
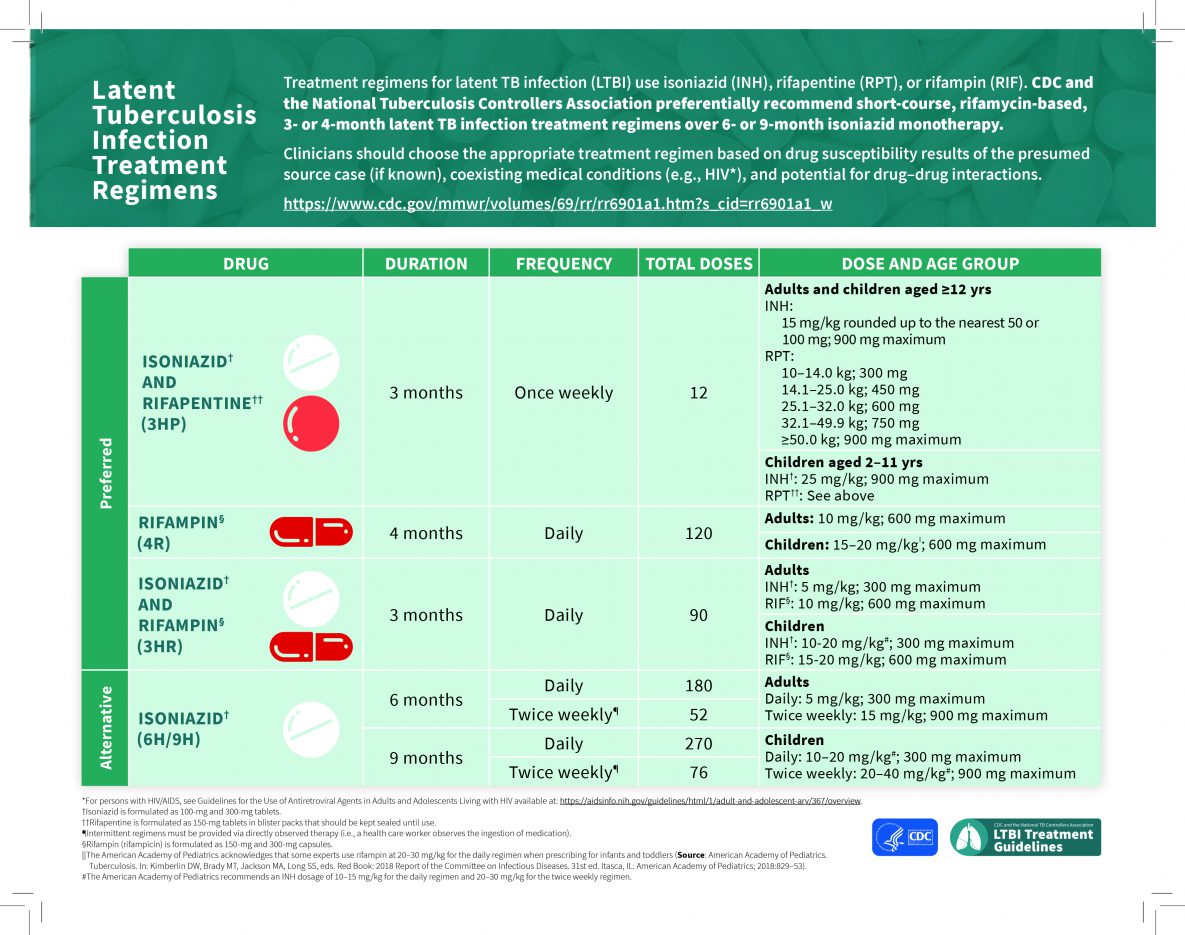
8 rows · There are several treatment regimens recommended in the United States for latent TB infection. The ...
What is the standard treatment for latent TB infection?
Nov 12, 2020 · Isoniazid (INH) is a common medicine used to treat LTBI. INH kills the "sleeping" TB germs before they have a chance to make you sick. Because the TB germs are strong, it takes many months for the medicine to kill them. INH works best if you take it every day until your doctor says it is OK to stop. Take your INH without food.
What does LTBI stand for?
For this reason, people with latent TB infection should be treated to prevent them from developing TB disease. Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
What is the standard treatment for latent TB?
Answer (1 of 2): I presume you are asking about latent tuberculosis infection which is abbreviated as LTBI. Unlike most of the common bacterial infections, tuberculosis infection and disease are different in the sense that not all “infections" result in disease. When an individual first contacts...
What is the meaning of LTBI?
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is a state of persistent immune response to stimulation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens without evidence of clinically manifested active TB. ▪ Someone has latent TB if they are infected with the TB mycobacteria but do not have signs of active TB disease.
Does LTBI need to be treatment?
For this reason, people with latent TB infection should be treated to prevent them from developing TB disease. Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
Is LTBI serious?
TB is a serious disease that kills about 1.5 million people each year worldwide (1). TB infection begins without symptoms before becoming active. This inactive carrier state is called latent TB infection (LTBI) and can persist for weeks, months or years before developing into active contagious disease.
What is the difference between LTBI and TB infection?
A person who has been exposed to TB bacteria may become infected. A person with latent TB infection (LTBI) cannot spread the bacteria to others right away. Only those who develop active TB disease can spread the bacteria to others. What is bovine TB?Mar 23, 2021
How effective is LTBI treatment?
If untreated, approximately 5%–10% of persons with LTBI progress to tuberculosis (TB) disease during their lifetime (3–5). Progression from untreated LTBI accounts for approximately 80% of U.S. TB disease cases (6). Treatment of LTBI is effective in preventing progression to TB disease (7).Feb 14, 2020
Why TB is called Koch's disease?
On March 24, 1882, Robert Koch announced his discovery that TB was caused by a bacteria in his presentation “Die Aetiologie der Tuberculose” at the Berlin Physiological Society conference. The discovery of the bacteria proved that TB was an infectious disease, not hereditary.
What is the fastest way to cure TB?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. You may begin to feel better only a few weeks after starting to take the drugs but treating TB takes much longer than other bacterial infections.Apr 8, 2020
Can I live with latent TB?
The only sign of TB infection is a positive reaction to the tuberculin skin test or TB blood test. Persons with latent TB infection are not infectious and cannot spread TB infection to others. Overall, without treatment, about 5 to 10% of infected persons will develop TB disease at some time in their lives.
What are the 3 types of tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that usually infects the lungs. It may also affect the kidneys, spine, and brain. Being infected with the TB bacterium is not the same as having active tuberculosis disease. There are 3 stages of TB—exposure, latent, and active disease.
Does chest xray show latent TB?
TB chest x-rays can only detect active TB in the lungs. This means that you may have latent TB bacteria in your body, even if you have had a clear chest x-ray.
Can latent TB come back after treatment?
Even with treatment, however, tuberculosis reinfection is becoming a problem. It's very common for people with tuberculosis to relapse during treatment. Treatment for tuberculosis symptoms can last anywhere from six months to a year, and sometimes more for drug-resistant tuberculosis.Dec 16, 2009
What is the best medicine for TB?
There are medicines you can take to prevent you from getting active TB disease. Isoniazid (INH) is a common medicine used to treat LTBI. INH kills the "sleeping" TB germs before they have a chance to make you sick. Because the TB germs are strong, it takes many months for the medicine to kill them.
What happens when you stop fighting off TB?
If your body stops fighting off the TB germs, they will "wake up" and start to grow. This can happen to anyone with LTBI at any time. When the germs grow and spread it is called "active TB disease.". People with active TB disease can get very sick and can spread TB to other people.
How to remember to take a pill?
Some ways to help you remember: 1 Keep your pills in a place where you will see them every day. 2 Ask a family member or friend to remind you every day. 3 Mark your calendar every day after you take your pill. 4 Use a pill reminder box. 5 Take your pill at the same time every day. For example, after you brush your teeth, eat breakfast, or just before you go to sleep.
Is TB still alive?
The TB germs are not hurting you now. They are "asleep" but they are still alive. The TB germs will "sleep" as long as your body can fight them off.
What is LTBI in medical terms?
Latent tuberculosis infection. Specialty. Infectious disease. Latent tuberculosis ( LTB ), also called latent tuberculosis infection ( LTBI) is when a person is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but does not have active tuberculosis. Active tuberculosis can be contagious while latent tuberculosis is not, ...
How long do you stay alert for TB?
Once a person has been diagnosed with Latent Tuberculosis (LTBI) and a medical doctor confirms no active tuberculosis, the person should remain alert to symptoms of active tuberculosis for the remainder of his or her life. Even after completing the full course of medication, there is no guarantee that the tuberculosis bacteria have all been killed. "When a person develops active TB (disease), the symptoms (cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss etc.) may be mild for many months. This can lead to delays in seeking care, and results in transmission of the bacteria to others."
What is the cutoff for a mantoux test?
guidelines, there are multiple size thresholds for declaring a positive result of latent tuberculosis from the Mantoux test: For testees from high-risk groups, such as those who are HIV positive, the cutoff is 5 mm of induration; for medium risk groups, 10 mm; for low-risk groups, 15 mm.
What is the chance of developing tuberculosis in a diabetic?
Persons with diabetes may have an 18% chance of converting to active tuberculosis. In fact, death from tuberculosis was greater in diabetic patients. Persons with HIV and latent tuberculosis have a 10% chance of developing active tuberculosis every year.
What is the phenomenon of boosting?
The phenomenon of boosting is one way of obtaining a false positive test result. Theoretically, a person's ability to develop a reaction to the TST may decrease over time – for example, a person is infected with latent TB as a child, and is administered a TST as an adult.
Why do we use preventive therapy?
There is no agreement regarding terminology: the terms preventive therapy and chemoprophylaxis have been used for decades, and are preferred in the UK because it involves giving medication to people who have no disease and are currently well: the reason for giving medication is primarily to prevent people from becoming unwell. In the U.S., physicians talk about latent tuberculosis treatment because the medication does not actually prevent infection: the person is already infected and the medication is intended to prevent existing silent infection from becoming active disease. There are no convincing reasons to prefer one term over the other.
What happens if you don't see a doctor for tuberculosis?
If a person with the above symptoms does not see a physician, ignoring the symptoms can result in lung damage, eye damage, organ damage and eventually death.
Why is latent TB important?
Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
How many people have latent TB?
In the United States, up to 13 million people may have latent TB infection. Without treatment, on average 1 in 10 people with latent TB infection will get sick with TB disease in the future. The risk is higher for people with HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the immune system.
What is a TST reaction?
People with a tuberculin skin test (TST) reaction of 5 or more millimeters who are: HIV-infected persons. Recent contacts to a patient with active TB disease. Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with old TB. Organ transplant recipients.
Can TB be treated with LTBI?
Persons with no known risk factors for TB may be considered for treatment of LTBI if they have either a positive IGRA result or if their reaction to the TST is 15 mm or larger. However, targeted TB testing programs should only be conducted among high-risk groups.
Where is TB common?
From countries where TB is common, including Mexico, the Philippines, Vietnam, India, China, Haiti, and Guatemala, or other countries with high rates of TB. (Of note, people born in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, or Western and Northern European countries are not considered at high risk for TB infection, unless they spent time in a country ...
Can TB spread to others?
People with latent TB infection do not have symptoms, and they cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if latent TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.
What is LTBI in healthcare?
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is the presence of M. tuberculosis organisms (tubercle bacilli) without symptoms or radiographic or bacteriologic evidence of TB disease. Approximately 90-95% of those infected are able to mount an immune response that halts the progression from LTBI to TB disease. However, because prevention of TB has major public health implications, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend testing populations that are at increased risk for TB infection and treating those for whom TB disease has been ruled out. Health care providers must communicate the risks and benefits of treatment to their patients and encourage adherence and treatment completion.
How is acceptance of LTBI influenced?
A patient’s acceptance of LTBI treatment is often influenced by the initial approach of the health care provider. When discussing the risks and benefits of treatment it is important to explain that
How many drugs are needed for TB?
TB infection is treated with one or two drugs, whereas TB disease initially requires four drugs.
What is the CDC's role in TB?
However, because prevention of TB has major public health implications, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend testing populations that are at increased risk for TB infection and treating those for whom TB disease has been ruled out.
What are incentives for patients?
Incentives, which are small rewards that encourage or motivate patients . Local businesses and organizations may be a resource for incentives such as grocery store vouchers, nutritional supplements, movie tickets, or restaurant coupons.
How many people will be infected with LTBI in 2020?
February 20, 2020 08:00 am Chris Crawford -- An estimated 13 million Americans are infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, most of them asymptomatic with latent tuberculosis infection. So it's fitting that the CDC this month published what it identified as the first comprehensive guidelines for the treatment of LTBI since 2000, ...
What is latent TB?
Latent TB is defined as infection with M. tuberculosis in the absence of clinical illness. Individuals with LTBI are asymptomatic but have an immune response to M. tuberculosis antigens.
When was the CDC's new guidelines published?
The new guidelines, which the CDC developed with the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association and published Feb. 14 in the agency's Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, updates clinicians and others with information about several new regimens that have been evaluated in clinical trials since then. The guidelines, which are based on ...
Does isoniazid have higher completion rates?
Sarah Coles, M.D., of Phoenix, a member of the AAFP's Commission on Health of the Public and Science, told AAFP News that the guideline reported the shorter-duration regimens had higher completion rates and less toxicity, with similar efficacy to longer monotherapy regimens with isoniazid.

Overview
Treatment
The treatment of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is essential to controlling and eliminating TB by reducing the risk that TB infection will progress to disease. Latent tuberculosis will convert to active tuberculosis in 10% of cases (or more in cases of immune compromised patients). Taking medication for latent tuberculosis is recommended by many doctors.
In the U.S., the standard treatment is nine months of isoniazid, but this regimen is not widely use…
Transmission
"TB Bacteria Are Spread Only from a Person with Active TB Disease ... In people who develop active TB of the lungs, also called pulmonary TB, the TB skin test will often be positive. In addition, they will show all the signs and symptoms of TB disease, and can pass the bacteria to others. So, if a person with TB of the lungs sneezes, coughs, talks, sings, or does anything that forces the bacteria into the air, other people nearby may breathe in TB bacteria. Statistics show that approx…
Diagnosis
There are two classes of tests commonly used to identify patients with latent tuberculosis: tuberculin skin tests and IFN-γ (Interferon-gamma) tests.
The skin tests currently include the following two:
Mantoux test Heaf test
IFN-γ tests include the following three:
Epidemiology
Tuberculosis exists in all countries in the world. Some countries have a larger number of people infected with tuberculosis than others. For each 100,000 people, Swaziland has the greatest number (627) of tuberculosis cases in the world. Second is Cambodia (560), followed in third position by Zambia (445), fourth is Djibouti (382), fifth is Indonesia (321), sixth is Mali (295), seventh is Zimbabwe (291), eighth is Kenya (291), ninth is Papua New Guinea (283) and tenth is …
Controversy
There is controversy over whether people who test positive long after infection have a significant risk of developing the disease (without re-infection). Some researchers and public health officials have warned that this test-positive population is a "source of future TB cases" even in the US and other wealthy countries, and that this "ticking time bomb" should be a focus of attention and resources.
See also
• Silent disease
Further reading
• Jasmer, R. M.; Nahid, P.; Hopewell, P. C. (2002). "Latent tuberculosis infection". New England Journal of Medicine. 347 (23): 1860–1866. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp021045. PMID 12466511.
• Mazurek, G. H.; Villarino, M. E. (2003). "Guidelines for using the QuantiFERON-TB test for diagnosing latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 52 (RR–2): 15–18.
Introduction
- Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is the presence of M. tuberculosisorganisms (tubercle bacilli) without symptoms or radiographic or bacteriologic evidence of TB disease. Approximately 90-95% of those infected are able to mount an immune response that halts the progression from LTBI to TB disease. However, because prevention of TB has major public health implications, the Center…
Communicating The Value of LTBI Treatment
- A patient’s acceptance of LTBI treatment is often influenced by the initial approach of the health care provider. When discussing the risks and benefits of treatment it is important to explain that 1. As long as TB germs are in the body, they can begin to multiply and cause disease 2. Certain individuals are at especially high risk for progression to TB disease. They include persons with r…
Identifying Barriers to Adherence
- Many variables affect a patient’s adherence to the recommended treatment regimen, including 1. Appointment hours that conflict with patient’s schedule 2. Misinformation about TB 3. Health beliefs and practices 4. Limited financial resources 5. Co-existing medical conditions 6. Medication side effects 7. Language barriers 8. Real or perceived stigma related to LTBI treatment
Strategies For Maximizing Adherence
- Partner with local health departments and community-based organizations that can provide 1. Case managementto ensure continuity of services 2. Directly observed therapy (DOT), whereby a health care worker observes the ingestion of medication; highly recommended when using intermittent regimens and for high-risk patients, such as those whose treatment has been interr…