What does MBR stand for in wastewater?
SUMMARY about membrane bioreactors
- Reduction in equipment cost
- Reduction in space requirements
- Improve disinfection and gets a better-clarified water
- Product removes 95% to 99% of BOD, COD, Microorganism, and nutrients from effluent
- Life-time > 10 years
What is a MBR and how it works?
The pathway functions by ultimately activating enzymes that break down excess collagen. The pathway also stops further production of fibrotic collagens. The team conducted its studies by using cells collected from human lungs. Team members also constructed tissue cores from fibrotic lungs donated from patients with lung fibrosis.
What are the biggest problems in wastewater treatment?
- Increasing/expanding regulations. Concerns over increasing regulations consistently ranked near the top of the list for every geographical region, pushing the topic into the No. ...
- Technology changes. Information technologies jumped to the No. ...
- Aging workforce. In the No. ...
- Water scarcity. ...
How are SBR, MBR and MBBR sewage treatment plants different?
These are classified on the basis of these features:-
- Size of membrane
- Mechanism
- Membrane material and configuration
- Driving forces used for separation.
What does MBR stand for in wastewater treatment?
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology has emerged as a wastewater treatment technology of choice over the activated sludge process (ASP), which has been the conventional municipal wastewater technology over the last century.
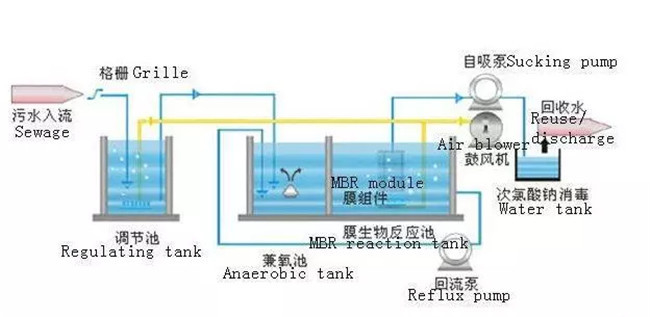
How does an MBR work?
Working Principle Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) combine conventional biological treatment (e.g. activated sludge) processes with membrane filtration to provide an advanced level of organic and suspended solids removal.
How does MBR STP work?
Overview. Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) is a process that combines a membrane ultra / micro filtration process and activated sludge process. (The MBR process is used in place of the secondary sedimentation tank and sand filter used for tertiary treatment in the conventional activated sludge process.)
What is MBR and SBR?
SBR technology relies on gravity settling (or phase separation), while MBR technology uses the membrane as a physical barrier for separation. On the surface this may seem like a subtle difference, however, by using a physical barrier for separation, MBR technology provides numerous advantages.
What is MBR water?
'Membrane bioreactor' (MBR) is generally a term used to define wastewater treatment processes where a perm-selective membrane, eg microfiltration or ultrafiltration, is integrated with a biological process − specifically a suspended growth bioreactor.
What is MBR and PBR?
The partition boot record is the first block of any bootable partition. It is also sometimes referred to as the Volume Boot Record (VBR). The MBR (or the GRUB chainloader) loads the PBR into memory and transfers control to it.
What is difference between MBR and MBBR?
MBR can effectively improve sludge load, while MBBR belongs to biofilm process, both of which have good effect on organic pollutant treatment, including COD, BOD and ammonia nitrogen. MBR has obvious effects in treating SS, but it is a problem that it is easy to block the membrane.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of MBR?
Specific advantages and disadvantagesAdvantagesDisadvantagesHigh effluent qualityStress on sludge in external MBRHigh volumetric load possibleMembrane pollutionHigh rate of degradationCost pricePossible to convert from existing conventional active sludge purification1 more row
What is SBR treatment?
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a fill-and- draw activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. In this system, wastewater is added to a single “batch” reactor, treated to remove undesirable components, and then discharged.
What is the difference between SBR and MBBR STP?
The technology used by SBR is phase separation that is gravity setting method, while MBR uses the membrane – and the use of a physical barrier for separation gives more importance to this process as it increases the advantages.
What type of reactor is used for SBR?
The SBR process utilizes a fill-and-draw reactor in which cBOD oxidation, nitrification, denitrification, and settling are accomplished in a single reactor (Figure 12). The reactor is operated in six or more stages, which accomplish in time what an MLE process does in space.
Why is MBR used in hospitals?
This is because the membrane technology used in MBR is more efficient at removing pathological microorganism compared with other wastewater treatment systems.
Why is membrane bioreactor used?
Membrane bioreactor technology presents a more efficient system at removing pathological microorganism compared with existing wastewater treatment systems. This is why it’s being adopted by the commercial sectors where bio-waste is a problem- like hospitals and pharma sectors.
What is the term for thin films of material that allow certain substances to pass through them?
Membranes are thin barriers or films of material that allow certain substances to pass through them. Nature is full of membranes and our skin is a great example. Our skin is called a semi-permeable membrane. Semi-permeable membranes allow certain substances to pass through but keep others out.
What is reverse osmosis?
Most of us have heard of reverse osmosis as a treatment for potable or drinking water systems in our homes. The smaller the pore size and the dirtier the water the more energy it takes to pull or push water through a membrane and deliver treated water. The term membrane bioreactor or MBR is used in wastewater treatment and defines a combination ...
What is a semi-permeable membrane?
Semi-permeable membranes allow certain substances to pass through but keep others out. In the wastewater industry we deal with semi-permeable membranes that are synthetic, very thin (100-500 microns thick), and are made from various substances such as polymers, ceramics or other porous materials.
What is MBR water treatment?
MBR water treatment is a proven technology set to become a standard in the management of municipal and industrial wastewater worldwide to step towards United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
What is membrane bioreactor?
What is a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)? Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) is a modern, cost-effective and most efficient wastewater treatment process, which combines a filtration membrane technology for solid-liquid separation together with traditional activated sludge process.
What is MBR, Membrane Bioreactor?
The Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) is a combination of membrane separation and biological technology. Water can enter small pores and activated sludge trapped in the tank, so this can greatly increase the system’s ability to degrade pollutants. cod bod can be very bad and suspended solids, bacterial virus (99.9%), etc. can be removed.
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Process
The membrane bioreactor process consists of a suspended growth biological reactor combined with ultrafilter membrane modules. during this process, the ultrafilter membrane directly separates solids from mixed liquid in biological reactors.
Advantages of MBR, Membrane Bioreactor
1. Permanently hydrophilic modification, excellent Anti-oxidation. 2. High Intensive strength (≥200N), High Anti-peeling strength, no broken and peeling during normal operation, can withstand high frequent backwash. 3.Large Flux,pure water flux up to 1000L/m2.h, design flux 10-25L/m2.h 4.
MBR (Membrane Bioreactor) Design
The membrane bioreactor design in MBR system wastewater treatment syndicates a step of biological treatment mostly activated sludge through a membrane step which is ultrafiltration of low or ultrafiltration. Membrane bioreactor is formulated for meeting the stress of municipal and industrial sewage treatment.
Technology Relates to MBR or Membrane Bioreactor
The hollow fiber membrane bioreactor features a fibrous shape and a self-supporting membrane.
About Oxymembrane
Oxymembrane is a professional MBR & UF filter membrane manufacturer. we’ve been specializing in research & development, manufacture, and applications of Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane hollow fiber technology for water & wastewater.
What We Have Done
We have owned patents of UF membrane includes Embedded-reinforced PVDF, PVDF, Alloy-PVC, PAN, and PS/PES with different filter precision & structures. we’ve launched several series products, like Membrane Bio-reactor (MBR) series, standard UF series, and Gravity UF series for various applications.
What is MBBR in wastewater treatment?
Because of the many benefits it offers, MBBR has become a popular mode of biological wastewater treatment.
What is MBBR process?
As with other biological treatment processes, MBBR is often part of a multi-step system for wastewater treatment, with other processes focused on different aspects of purification. That is why an MBBR process flow diagram will often include other steps, such as grit removal and disinfection.
What is MBBR aeration?
MBBR aeration tanks are open at the top, exposing the water to the open air, which makes this an aerobic process of filtration. Media: The basin is full of thousands of small plastic chips, called media or carriers. These media may occupy as much as 50 to 70% of the tank.
What is MBBR in biology?
MBBR allows nature to take its course, which minimizes the role of the operator. It is worth noting that operators must be knowledgeable about the process so they can ensure everything is working properly at the molecular level. However, the process itself does not require very many steps.
What is activated sludge?
With this traditional process, wastewater enters an aeration tank that contains high levels of oxygen. This oxygen aids in the process of microbial growth and decomposition of organic waste. The water then moves onto a settling tank, where the remaining waste in the water will separate from the water, leaving it cleaner.
When was MBBR developed?
Norwegian researchers developed MBBR technology in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The goal of MBBR was to compensate for some of the issues that characterize other biological wastewater treatment methods, and it did so effectively. MBBR combines many of the strengths of biological processes, specifically anactivated sludge process ...
How efficient is MBBR?
Efficient: One of the most significant advantages of MBBR is its impressive level of efficiency. An MBBR system can work much more quickly than alternative methods to treat the water. The hydraulic retention time (HRT) for BOD and nitrogen removal with an MBBR is around three to four hours.
Why use MBR membranes?
For new installations, the use of MBR systems allows for higher wastewater flow or improved treatment performance in a smaller space than a conventional design, i.e., a facility using secon-dary clarifiers and sand filters. Historically, membranes have been used for smaller-flow sys-tems due to the high capital cost of the equipment and high operation and maintenance (O&M) costs. Today however, they are receiving increased use in larger systems. MBR systems are also well suited for some industrial and commercial applications. The high-quality efflu-ent produced by MBRs makes them particularly applicable to reuse applications and for surface water discharge applications requiring extensive nutrient (nitrogen and phosphorus) removal.
How does a MBR work?
The advantage of the vacuum is that it is gentler to the membranes; the advantage of the pressure is that throughput can be controlled. All systems also include techniques for continually cleaning the system to maintain membrane life and keep the system operational for as long as possible. All the principal membrane systems used in MBRs use an air scour technique to reduce buildup of material on the membranes. This is done by blowing air around the membranes out of the manifolds. The GE/Zenon systems use air scour, as well as a back-pulsing technique, in which permeate is occasionally pumped back into the membranes to keep the pores cleared out. Back-pulsing is typically done on a timer, with the time of pulsing accounting for 1 to 5 percent of the total operating time.
What is the permeate from an MBR?
The permeate from an MBR has low levels of suspended solids, meaning the levels of bacteria, BOD, nitrogen, and phosphorus are also low. Disinfection is easy and might not be required, depending on permit requirements..
What information is needed for MBR?
Designers of MBR systems require only basic information about the wastewater characteristics, (e.g., influent characteristics, effluent require-ments, flow data) to design an MBR system. Depending on effluent requirements, certain supplementary options can be included with the MBR system. For example, chemical addition (at various places in the treatment chain, including: before the primary settling tank; before the sec-ondary settling tank [clarifier]; and before the MBR or final filters) for phosphorus removal can be included in an MBR system if needed to achieve low phosphorus concentrations in the effluent.
What are the advantages of MBR systems?
The advantages of MBR systems over conven-tional biological systems include better effluent quality, smaller space requirements, and ease of automation. Specifically, MBRs operate at higher volumetric loading rates which result in lower hydraulic retention times. The low reten-tion times mean that less space is required compared to a conventional system. MBRs have often been operated with longer solids residence times (SRTs), which results in lower sludge pro-duction; but this is not a requirement, and more conventional SRTs have been used (Crawford et al. 2000). The effluent from MBRs contains low concentrations of bacteria, total suspended solids (TSS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and phosphorus. This facilitates high-level disinfec-tion. Effluents are readily discharged to surface streams or can be sold for reuse, such as irrig-tion.
How long is a Zenon membrane warranty?
For municipal wastewater treatment, longer guarantees might be more readily available com-pared to those available for industrial systems. Zenon offers a 10-year guarantee; others range from 3 to 5 years. Some guarantees include cost prorating if replacement is needed after a certain service time. Guarantees are typically negotiated during the purchasing process. Some manufac-turers’ guarantees are tied directly to screen size: longer membrane warranties are granted when smaller screens are used (Wallis-Lage et al. 2006). Appropriate membrane life guarantees can be secured using appropriate membrane pro-curement strategies (Crawford et al. 2002).
