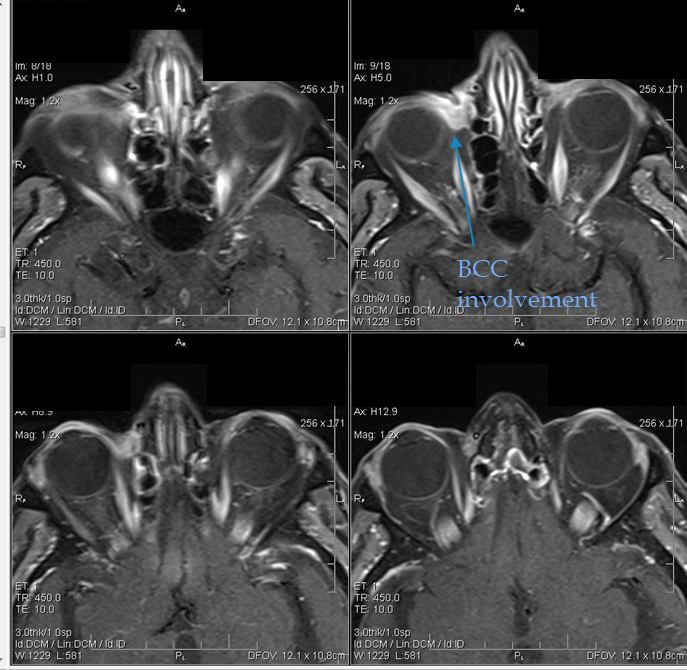
What are the common treatments for cancer?
- Abstract. In current clinical practice, tumor response assessment is usually based on tumor size change on serial computerized tomography (CT) scan images.
- Introduction. ...
- Results. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Methods. ...
- Data availability. ...
- Materials availability. ...
- Code availability. ...
- Acknowledgements. ...
- Author information. ...
What is the newest treatment for cancer?
While the cancer in the colon is often treatable by surgical resection, diffuse liver metastases are much less amenable to surgical treatment. The cancer is either distributed in a way that it can't be operated on safely, or the size of the lesions make it impossible."
What is mapping for cancer?
Mapping Cancer Markers aims to identify chemical markers associated with various types of cancer. This will help researchers detect cancer earlier and design more personalized cancer care by determining an individual's susceptibility to developing cancer and suggest the best treatment for them.
What to expect from cancer treatments?
Symptoms of this include:
- fever that doesn’t respond to aspirin or other fever reducers
- confusion
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- shortness of breath

Why is Gene mapping important in cancer research?
The project help to crystalize our understanding of the structure of DNA, genes and chromosomes. It has also led to a better understanding of how mutations in our genes can lead to disease, including cancer.
What are the three modes of treatment for cancers?
The most common treatments are surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
How do you calm down after cancer diagnosis?
AdvertisementKeep the lines of communication open. Maintain honest, two-way communication with your loved ones, doctors and others after your cancer diagnosis. ... Maintain a healthy lifestyle. This can improve your energy level. ... Let friends and family help you. ... Review your goals and priorities. ... Fight stigmas.
What is are the goal's of chemotherapy cancer treatment?
The three goals of chemotherapy for cancer are to cure, control or relieve suffering. More than 100 chemotherapy drugs are used to treat many types of cancer.
Which is harder on the body chemo or radiation?
Since radiation therapy is focused on one area of your body, you may experience fewer side effects than with chemotherapy. However, it may still affect healthy cells in your body.
What is the alternative to chemotherapy?
Alternative therapies to chemotherapy include photodynamic therapy, laser therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and hormone therapy. Individuals should discuss possible treatments with medical professionals to establish which treatment may be most beneficial for them.
Which cancer has highest recurrence rate?
Some cancers are difficult to treat and have high rates of recurrence. Glioblastoma, for example, recurs in nearly all patients, despite treatment. The rate of recurrence among patients with ovarian cancer is also high at 85%....Related Articles.Cancer TypeRecurrence RateGlioblastoma2Nearly 100%18 more rows•Nov 30, 2018
Why are cancer patients so mean?
Cancer patients simply want to be their old selves, Spiegel says, so they often can fail to make their new needs clear to their loved ones and caregivers, which can lead to frustration and anger.
When are you considered a cancer survivor?
One who remains alive and continues to function during and after overcoming a serious hardship or life-threatening disease. In cancer, a person is considered to be a survivor from the time of diagnosis until the end of life.
Can cancer spread while on chemo?
While chemotherapy is one of the oldest and most successful ways of treating cancer, it doesn't always work. So, yes, cancer can spread during chemotherapy. Spreading could mean the tumor keeps growing, or that the original tumor shrinks, but cancer metastasizes, forming tumors in other areas of the body.
How much should a tumor shrink after chemo?
With chemotherapy, the tumor might shrink, but will still remain at the next imaging. That's an important concept for some people to understand about chemotherapy. In clinical trials for solid tumors, the tumor is said to have responded if it shrinks by more than 30 percent.
How many rounds of chemo is normal?
During a course of treatment, you usually have around 4 to 8 cycles of treatment. A cycle is the time between one round of treatment until the start of the next. After each round of treatment you have a break, to allow your body to recover.
What is the term for the analysis of tumors?
Alterations found in only a small number of tumor cells in a sample were considered to have likely occurred later in a cancer’s evolution. “Genomic analysis of tumors is sometimes referred to as molecular archaeology,” said Jerry Li, M.D., Ph.D., of NCI’s Division of Cancer Biology, who was not involved with the study.
What tumors have copy number gains?
For some brain tumors, such as glioblastoma and medulloblastoma, copy-number gains associated with cancer development occurred very early in molecular time. In contrast, for cancers such as lung cancer, kidney cancer, and melanoma, the researchers saw copy-number gains developing toward the end of carcinogenesis.
What is the term for the time lag between cancer and ovarian cancer?
Several cancer types studied showed a long time lag between when mutations in driver genes arose and when cancer was diagnosed—a period called cancer latency. For example, this latency was more than a decade for ovarian cancer, which is often diagnosed at a late stage.
Can genetic mutations turn a cell cancerous?
A single genetic alteration is rarely enough to turn a cell cancerous. In most cases, incremental damage to the DNA of a cell and the cells that arise from it builds up over years or decades, to the point where those cells gain the ability to grow unchecked—or, in the case of metastatic cancer, to spread to other parts of the body. ...
When is sentinel node mapping and biopsy recommended?
When lymph node involvement is unconfirmed prior to surgery, sentinel node mapping and biopsy may be recommended as a less invasive alternative to axillary dissection for obtaining information about how far a patient’s breast cancer has spread.
What is a sentinel node biopsy?
Sentinel node mapping and biopsy is a technique that may be performed in conjunction with breast cancer surgery, such as a mastectomy, in order to assess the lymph nodes in the underarm area (axillary lymph nodes) for evidence of cancer.
What is the lymph node closest to breast cancer?
The axillary lymph node located closest to the breast cancer tumor is known as the “sentinel node.”. Because this lymph node handles drainage from the breast, it is usually the first area where breast cancer cells metastasize. When lymph node involvement is unconfirmed prior to surgery, sentinel node mapping and biopsy may be recommended as ...
What is the pathologist's job to examine lymph nodes?
A pathologist examines the sentinel node under a microscope for evidence of cancer. If cancerous cells are not found in the sentinel node, lymph node involvement is unlikely, but if the sentinel node tests positive, further evaluation or treatment is usually recommended.
Why are drugs used in cancer treatment?
They’re tailored to attack certain mutations in cancer cells and kill the cells or help other treatments work better. The drugs often target cancer cells’ ability to grow unchecked, but some are designed to stop certain survival techniques cancers use to adapt to threats, such as creating new blood supplies.
How does the Project help us understand cancer?
The project help to crystalize our understanding of the structure of DNA, genes and chromosomes. It has also led to a better understanding of how mutations in our genes can lead to disease, including cancer. Below are five ways these discoveries have helped scientists and doctors better understand cancer and how to treat it.
What are tumor suppressor genes?
Tumor suppressor genes: These genes regulate when cells stop growing. They also shut down defective cells or those that grow too fast and sometimes repair damage in DNA. When tumor suppressor cells mutate, damaged cells may be allowed to grow and potentially form cancers. Common tumor suppressor cells found in cancers include: 1 TP53 or P53, found in about half of all cancers 2 BRCA1 and BRCA2, found in about 10 percent of breast cancers and in reproductive cancers, pancreatic cancer and other cancers
What are some examples of oncogenes?
Examples of common oncogenes include: EGFR, found in pancreatic, head and neck and colorectal cancers. HER 2, found in breast cancer. Tumor suppressor genes: These genes regulate when cells stop growing.
How did the Human Genome Project help scientists?
The Human Genome Project not only confirmed those theories; it helped identify specific mutations and improve our understanding of why they may lead to cancer.
Why do we need a biopsy?
Many cancer diagnoses require a biopsy to look for cancer cells and help determine the stage of the disease. Most biopsies are surgical procedures that remove a piece of a tumor that is then sent to a lab for examination. But what if doctors could perform biopsies without surgery?
Can gene mutations slow tumor growth?
Still, identifying gene mutations in tumors does not guarantee a targeted therapy drug can be developed for that mutation, or that the drug will help slow a tumor’s growth, because: Tumors often have multiple mutations, making it difficult to identify those that are driving a tumor's growth.
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer in Germany, and the second and third most commonly diagnosed cancer in women and men, respectively. In this context, evidence-based guidelines positively impact the quality of treatment processes for cancer patients.
MeSH terms
Funding The research reported in this publication was supported by the West German Cancer Center and the Institute of Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology in Essen, Germany. This study was performed free of charge and for noncommercial purposes.
How long does it take for a doctor to review a cancer case?
It may take several minutes for the doctors to thoroughly review your case before they speak with you. After this visit you may be scheduled to start the radiation process, or you may be asked to return for a follow-up visit depending on the type of cancer and your individual treatment plans.
What is the first visit to radiation oncology?
Your first visit to radiation oncology is a consultation with the radiation oncologist and your care team including a resident physician and a registered nurse. You will not receive a radiation treatment at this visit . Plan to be in the clinic for two or more hours. This is an important visit to learn about your medical history and treatment needs. For most patients the visit will include:
What is a sim appointment?
For most types of treatment, a simulation (SIM) appointment will be scheduled. The purpose of this visit is to outline or map the exact area to be treated.
What is the FDA testing for cancer?
FDA Approves Two Genomic Profiling Tests for Cancer. Tests can identify different cancer-associated genetic alterations. Some tests, called whole-exome sequencing, look at all the genes in your cancer. Others, called whole-genome sequencing, look at all the DNA (both genes and outside of genes) in your cancer.
What type of cancer is a biomarker?
Biomarker testing is also done routinely to select treatment for people who are diagnosed with certain types of cancer—including non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer.
What are biomarkers used for?
Most biomarker tests used to select cancer treatment look for genetic markers. But some look for proteins or other kinds of markers. Some tests check for one certain biomarker. Others check for many biomarkers at the same time and may be called multigene test s or panel tests.
Why are biomarkers not helpful?
One other reason biomarker tests might not help is because the biomarkers in your cancer can change over time.
What is biomarker testing?
Biomarker testing is a way to look for genes, proteins, and other substances (called biomarkers or tumor markers) that can provide information about cancer. Each person’s cancer has a unique pattern of biomarkers. Some biomarkers affect how certain cancer treatments work. Biomarker testing may help you and your doctor choose a cancer treatment ...
Why isn't my cancer test working?
There could be several different reasons why they may not help you. One reason is that the test might not find a biomarker in your cancer that matches with an available therapy. Even if your cancer has a biomarker that matches an available treatment , the therapy may not work for you.
What is precision medicine?
For cancer treatment, precision medicine means using biomarker and other tests to select treatments that are most likely to help you, while at the same time sparing you from getting treatments that are not likely to help.
What is a mapping arteriogram?
Mapping arteriogram is done to plan for your Y-90 SIRT treatment. This mapping study will inform us on the anatomy of the liver, i.e. identify the arteries that are responsible for specifically bringing blood flow to the liver tumors and ensuring that the lungs will not be impacted negatively by the treatment with Y-90 SIRT.
Why is it important to treat liver cancer?
The liver is the most common site for the spread of this cancer which is why it is so important to treat the cancer there to prevent further spread beyond the liver. Patients with colorectal liver cancer whose liver metastases cannot be removed by surgery are ...
What is the liver in radiation therapy?
Radioembolization combines the localized delivery of radiation therapy in the form of tiny beads and embolization to treat patients with liver cancer. The liver is unique because it has two blood supplies—the hepatic artery and the portal vein. The normal liver receives about 75 percent of its blood supply through the portal vein ...
How long does a radioactive microsphere stay in the artery?
After the catheter has been advanced into the artery that supplies the blood flow to the tumor (s), the radioactive microspheres are injected into the artery before reaching the tumor (s) where they will lodge and emit radiation for about two weeks.
How long does it take for a tumor to decay?
The whole procedure may take around 60–90 minutes.
Where is the catheter inserted for liver surgery?
Using live imaging, a catheter is then inserted through the incision and guided to the hepatic artery that feeds the liver tumors.
Can liver cancer be treated with radiation?
This typically happens after one treatment but treatments can be repeated if necessary to achieve complete tumor destruction. The targeted nature and high level of precision of this therapy enable doctors to deliver more radiation to the liver tumors than would be possible using conventional external beam radiotherapy.