Medication
Treatments
- Exfoliating. Rouleau says that doing certain things like exfoliating will help decrease its appearance but not necessarily get rid of it completely.
- Creams and Washes. Guanche notes that creams and washes containing urea, lactic acid, or glycolic acid are your best bet for reducing the appearance of KP.
- Home Remedies. ...
Therapy
You may be more likely to experience keratosis pilaris if you have:
- Fair or light skin.
- Certain skin conditions like, eczema or ichthyosis vulgaris (a genetic condition where your dead skin cells look like fish scales).
- Asthma (a chronic disease that causes breathing problems from inflamed airways).
- A higher body weight ( obese or overweight).
Self-care
They include:
- Cryosurgery. ...
- Surgical removal and biopsy. ...
- Chemotherapy. ...
- Photodynamic therapy. ...
- Chemical peel. ...
- Dermabrasion. ...
- Immunomodulator therapy. ...
- Microtubule inhibitor .For use on the face and scalp, this medicatoin is applied topically to stablizes the damage skin and clear the lesions. ...
Nutrition
There are some important differences, however:
- Seborrheic keratoses often appear in numbers, while melanoma is usually single.
- Seborrheic keratoses tend to have texture, while melanoma tends to be smooth.
- Seborrheic keratoses are well-defined, while melanoma can have a ragged or blurry border.
- Seborrheic keratoses are uniform, while melanoma may be asymmetrical or have more than one color.
How to get rid of keratosis pilaris, According to dermatologists?
What do you need to know about keratosis pilaris?
What is the best treatment for actinic keratosis?
Is there a cure for seborrheic keratosis?

What is the main cause of keratosis pilaris?
Keratosis pilaris develops when keratin forms a scaly plug that blocks the opening of the hair follicle. Usually plugs form in many hair follicles, causing patches of rough, bumpy skin. Keratosis pilaris is caused by the buildup of keratin — a hard protein that protects skin from harmful substances and infection.
Can keratosis pilaris go away?
There is no cure for keratosis pilaris. But the symptoms can be managed. KP can improve with age and without treatment. Treatment may improve the appearance of the bumps.
How can I fix keratosis pilaris at home?
How to treat keratosis pilaris at homeKeep baths and showers short. ... Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser. ... Gently exfoliate skin with keratosis pilaris once a week. ... Moisturize your skin. ... Avoid shaving or waxing skin with keratosis pilaris.
What is the fastest way to get rid of keratosis pilaris?
Try medicated creams. Apply an over-the-counter cream that contains urea, lactic acid, alpha hydroxy acid or salicylic acid. These creams help loosen and remove dead skin cells. They also moisturize and soften dry skin.
How do I get rid of keratosis pilaris permanently?
Treatment cannot cure keratosis pilaris, so you'll need to treat your skin to keep the bumps under control. Your maintenance plan may be as simple as using the medicine twice a week instead of every day. Another option may be to switch to a non-prescription moisturizing cream.
Is Dove soap good for keratosis pilaris?
Use mild soaps like Cetaphil® bar soap, Dove® soap, or Lever 2000 antibacterial soap. Usually keratosis pilaris clears up as the person gets older.
How do you get rid of keratosis naturally?
Treating keratosis pilaris at homeExfoliate gently. When you exfoliate your skin, you remove the dead skin cells from the surface. ... Apply a product called a keratolytic. After exfoliating, apply this skin care product. ... Slather on moisturizer.
Is coconut oil good for keratosis pilaris?
Coconut Oil is known to be a very effective natural remedy in treating Keratosis Pilaris, thanks to the Lauric Acid found in the oil. Lauric Acid has anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties that is able to fight bacterial infections and/or viruses.
How to diagnose keratosis pilaris?
Your healthcare provider will typically diagnose keratosis pilaris with a simple physical examination of the skin where you have bumps. Medical testing is usually not needed to diagnose this condition. If your provider is unsure that it’s keratosis pilaris, additional tests may be done to complete your diagnosis.
What are the symptoms of keratosis pilaris?
If you do experience symptoms of keratosis pilaris, they can include: Itchy or dry skin, especially on the backs of your upper arms, legs or buttocks. Irritation of the bumps that causes them to become more red and noticeable. This is known as frictional lichenoid dermatitis.
What are the genetic traits of keratosis pilaris?
You may be more likely to experience keratosis pilaris if you have: Fair or light skin. Certain skin conditions like, eczema or ichthyosis vulgaris (a genetic condition where your dead skin cells look like fish scales).
What is a small bump on your skin?
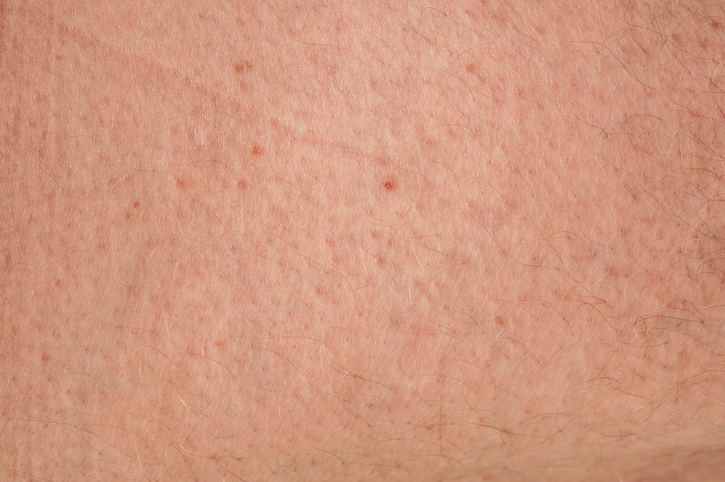
Keratosis pilaris is a benign (not harmful) skin condition that looks like small bumps. If you have this condition, you may notice small, painless bumps on your skin around the hair follicles. These bumps may have a red, brown or white color — they can also be skin-colored. You may hear keratosis pilaris called KP or even “chicken skin” because ...
Why is keratosis pilaris called chicken skin?
You may hear keratosis pilaris called KP or even “chicken skin” because of its goose bump-like appearance. It’s so common that it’s considered by many dermatologists to be a skin type instead of a medical condition. Keratosis pilaris is most commonly seen in families with a history of eczema, allergies and asthma.
Can eczema cause keratosis pilaris?
There could be a genetic factor — meaning your genes could impact your chances of developing this condition. If you have a skin condition like eczema, you’re more likely to get keratosis pilaris. Eczema is a common chronic skin condition that causes your skin to have red, itchy patches that come and go over time.
Does keratosis pilaris go away?
Keratosis pilaris is a common skin condition where small bumps develop on the arms, legs or buttocks. This condition is harmless and typically doesn’t need treatment. In fact, it usually goes away on its own over time – often fading by age 30. Treating dry skin with regular moisturizer use and a shorter shower routine can often help.
What is the best treatment for keratosis pilaris?
Most moisturizing creams used to treat keratosis pilaris contain one of the following ingredients: Urea.
How long does it take for keratosis pilaris to clear?
When treating keratosis pilaris, it helps to keep the following in mind: Clearing takes time. If you fail to see improvement after following your treatment plan for 4 to 6 weeks, tell your dermatologist. Some patients need to try a few treatments before they find one that works.
What is the best way to remove dead skin?
Your dermatologist may recommend that you gently remove dead skin with a loofah or at-home microdermabrasion kit. Your dermatologist may also prescribe a medicine that will remove dead skin cells. Medicine that can help often contains one of the following ingredients: Alpha hydroxyl acid. Glycolic acid.
Does laser treatment help with brown spots?
Another type of laser may improve your skin’s texture and reduce discoloration, including the brown spots that may appear when the bumps clear . To get the best results from the laser treatments, your dermatologist may add a few microdermabrasion sessions to your treatment plan.
Does laser help keratosis pilaris?
Lasers may work when moisturizer and medicine fail: A laser or light treatment may be used to treat keratosis pilaris. Your dermatologist may recommend one type of laser to reduce the swelling and redness.
How old do you have to be to get rid of keratosis pilaris?
Keratosis pilaris will usually clear up naturally by the time you reach 30 years old. Keep reading to learn more.
How to treat keratosis rash?
Dermatological treatments. A skin doctor, or dermatologist, may recommend a moisturizing treatment to soothe itchy, dry skin and improve the skin’s appearance from the keratosis rash. Many over-the-counter and prescription topical creams can remove dead skin cells or prevent hair follicles from being blocked, though your doctor.
What skin condition is most common in children?
eczema. ichthyosis. hay fever. obesity. women. children or teenagers. Celtic ancestry. Anyone can be susceptible to this skin condition, but it’s most common in children and teenagers. Keratosis pilaris often begins in late infancy or during adolescence.
What causes a bump on the skin?
Keratosis pilaris causes. This benign skin condition is the result of a buildup of keratin, a hair protein, in the pores. If you have keratosis pilaris, the keratin of your body hair gets clogged in the pores, blocking the opening of growing hair follicles. As a result, a small bump forms over where a hair should be.
How to stop itchy skin from flare ups?
Use humidifiers. Humidifiers add moisture to the air in a room, which can maintain the moisture in your skin and prevent itchy flare-ups.
How to get rid of dead skin on face?
Dermatologists recommend gently removing dead skin with a loofah or pumice stone, which you can purchase online. Apply hydrating lotion. Lotions with alpha hydroxy acid (AHAs) like lactic acids can hydrate dry skin and encourage cell turnover.
Where is keratosis pilaris found?
Keratosis pilaris is commonly found on the upper arms and thighs. In excess, it can extend to the forearms and lower legs. Other symptoms associated with it include: slight pinkness or redness around bumps. itchy, irritable skin. dry skin. bumps that feel like sandpaper.
Where does keratosis pilaris occur?
Keratosis pilaris most often affects the outer aspect of both upper arms. It may also occur on the thighs, buttocks and sides of the cheeks, and less often on the forearms and upper back. The distribution is symmetrical.
What is keratosis pilaris atrophicans?
Keratosis pilaris atrophicans refers to uncommon forms of keratosis pilaris in which there are scar -like follicular depressions and loss of hair. These include: Atrophoderma vermiculatum/ folliculitis ulerythematosa reticulata (pitted scarring of cheeks).
What are the spots on my skin?
The scaly spots may appear skin coloured, red (keratosis pilaris rubra) or brown ( hyperpigmented keratosis pilaris). They are not itchy or sore. Keratosis pilaris tends to be more prominent at times of low humidity, such as in the winter months.
Is keratosis pilaris common in children?
Keratosis pilaris affects up to half of normal children and up to three-quarters of children with ichthyosis vulgaris (a dry skin condition due to filaggrin gene mutations ). It is also common in children with atopic eczema.
Is keratosis pilaris autosomal dominant?
The tendency to keratosis pilaris has genetic origins, with autosomal dominant inheritance ( up to half of the children of an affected individual may display signs of keratosis pilaris to a variable degree). Keratosis pilaris-like lesions can arise as a side effect of targeted cancer therapies such as vemurafenib.
What is the best treatment for keratosis pilaris?
After applying an acid, you’ll want to follow up with an “intense hydrator,” like First Aid Beauty’s Ultra Repair Cream, which Green says is ideal for treating dry skin associated with keratosis pilaris. The cream contains colloidal oatmeal and shea butter, which offers soothing hydration to the skin.
How to treat keratosis pilaris?
This “highly effective, targeted treatment” kit includes a loofah and an exfoliating bodywash, which help to loosen keratin plugs, as well as an exfoliating body lotion that also works to reduce the appearance and feel of the rough bumps. Glycolic acid is the main ingredient in both the bodywash and body lotion, which Green says will not only slough off dead skin cells and promote cell turnover but will also help improve the skin’s overall texture and tone. She recommends using the kit once a day to achieve the best results but notes that if irritation occurs with daily use, you can switch to every other day or twice a week.
What is keratin in skin?
Keratin is a protein naturally found in the body, but it can accumulate in the opening of your pores. And when that happens, your skin gets covered in dry, rough patches and tiny bumps. KP is persistent, almost to the point of being experienced like a skin type rather than an acute condition.
Does KP cause redness on face?
Tan says less is more when treating KP on the face. “Patients routinely try to excessively exfoliate their face with harsh scrubs, making the redness and dryness even worse,” she explains. Physical scrubs are a major no-no for the more sensitive skin of your face, so look for exfoliating-acid active ingredients.
What are the signs of keratosis pilaris?
Signs and symptoms include: Painless tiny bumps, typically on the upper arms, thighs, cheeks or buttocks. Dry, rough skin in the areas with bumps. Worsening when seasonal changes cause low humidity and dry skin. Sandpaper-like bumps resembling goose flesh.
Why does keratin build up in keratosis pilaris?
It may occur in association with a genetic disease or with skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis. Dry skin tends to make keratosis pilaris worse. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
Why does keratin make my skin bumpy?
Usually plugs form in many hair follicles, causing patches of rough, bumpy skin. Keratosis pilaris is caused by the buildup of keratin — a hard protein that protects skin from harmful substances and infection.
Can keratosis pilaris be cured?
Keratosis pilaris is often considered a variant of normal skin. It can't be cured or prevented. But you can treat it with moisturizers and prescription creams to help improve the appearance of the skin. The condition usually disappears by age 30.
Is it necessary to see a doctor for keratosis pilaris?
When to see a doctor. Treatment for keratosis pilaris usually isn't necessary. But if you're concerned about your or your child's skin, consult your family doctor or a specialist in skin conditions (dermatologist).
What is the best body scrub for keratosis pilaris?
Niacinamide, amino sulfonic acid, and urea team up to exfoliate and hydrate skin—not to mention, it's lightweight. AHAs, willow bark extract, and more skin-loving ingredients work to exfoliate skin. This gentle body scrub offers both physical and chemical exfoliation which is great for treating keratosis pilaris.
What is the best lotion for keratosis?
The 8 Best Lotions for Keratosis Pilaris, According to Dermatologists. written by. Melanie Rud. Author's Instagram. Melanie Rud is a beauty editor and expert with over a decade of experience in the industry writing for various national and regional publications. Byrdie's Editorial Guidelines. Melanie Rud.
What causes bumps around hair follicles?
Greenfield explains that keratosis pilaris is a condition where dead skin—particularly keratin, a protein that's found in the skin—builds up around hair follicles instead of being naturally exfoliated away. “This causes small, rough bumps to appear around the hair follicles,” she says.
What is the best exfoliating lotion for KP?
Exfoliating lotions that contain alpha-hydroxy acids are choice for helping to combat KP, says Arch; this particular formula touts a 12% concentration of lactic acid, one of the gentlest yet most effective AHAs out there.
Why does keratin build up on skin?
It’s not quite clear why this buildup of keratin occurs, but it’s thought to be associated with genetic diseases or skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis. Dry skin also tends to intensify the symptoms of keratosis pilaris.
Can you use lotion for keratosis pilaris?
Ok, so this isn't exactly a lotion for KP, but it's still a great treatment in moderation. If you have keratosis pilaris, proceed with caution when using scrubs. Aggressive physical exfoliation can cause KP to become inflamed and ultimately worsen the condition, warns Arch.
Does dry skin cause KP?
Dry skin can further exacerbate KP, so opt for formulas that'll hydrate the skin in addition to treating it. Look for lightweight, humectant moisturizing ingredients such as hyaluronic acid and glycerin, which bind moisture to the skin without clogging pores or leaving behind a greasy residue.
