What is interferential therapy and how does it work?
May 03, 2021 · IFT which stands for Interferential Therapy is one of the types of electrotherapy used for the management of pain. The principle of interferential therapy is to cause two medium frequency currents of slightly different frequencies to interfere with one another. For example, if circuit A carries a current with the frequency of 4000Hz and Circuit B carry a current with a …
What is Interferential current (IFC) therapy?
Oct 06, 2017 · Interferential therapy is a type of therapy which is very effective and is used in relieving pain by various physiotherapic clinics. This helps to accelerate the process of self healing and getting a patient’s body free from pain and regain healthy physical conditions. In this therapy, the interferential current is produced on the skin, of the affected body part of the …
What is inferential current therapy for muscle pain?
Apr 14, 2018 · Interferential Current stimulation is very useful in the treatment of circulatory and muscular disorders, stiffness of joints, edema, and inflammation. If you suffer from health problems such as cumulative trauma disorders, body pain, joint injuries, or are pre or post orthopedic surgery, interferential current therapy is and important option.
Does interferential therapy produce antinociception?
Interferential current therapy (ICT or sometimes shortened to IFC or IFT) is the most common form of electrical muscle stimulation. It is a noninvasive, drug-free, therapy with minimal side effects. At Loehr Health Center, ICT is used in conjunction with other modalities like chiropractic care and decompression therapy to promote healing.

What is the use of interferential therapy?
Interferential current therapy (ICT, or sometimes IFC) is the most common type of electrical muscle stimulation used to treat chronic pain resulting from surgery, injury or trauma. The end goal for using ICT as part of a physical therapy or rehab program is to relieve pain and help patients heal faster.Nov 21, 2019
Is interferential therapy effective?
Fourteen studies were included in the meta-analysis. Conclusion: Interferential current as a supplement to another intervention seems to be more effective for reducing pain than a control treatment at discharge and more effective than a placebo treatment at the 3-month follow-up.
How effective is IFC?
Frequencies produced by the IFC have been proven to stimulate endorphins, the body's natural pain killers. This can help to create a self-healing process without the need to for medications. This form of therapy is also extremely useful in reducing pain, inflammation, curing edema, and spasms.
What is the difference between interferential and tens?
How Does IFC Differ From TENS? TENS delivers low-frequency current across the surface of the skin, while IFC delivers a higher frequency current that penetrates deeper into the tissue with less discomfort.Jan 3, 2017
How does IFT reduce pain?
IFT delivers intermittent pulses to stimulate surface nerves and block the pain signal, by delivering continuous deep stimulation into the affected tissue. IFT relieves pain, increases circulation, decreases edema, and stimulates the muscles.Mar 31, 2020
Can IFT increase pain?
Learning points. Interferential therapy (IFT) may potentiate the effect of tramadol and opioids. Care must be taken in treating musculoskeletal pain with IFT if the patient is already using tramadol. IFT combined with tramadol may produce excessive pain relief.
What is IFC medical?
Interferential Current Therapy (IFC) is a noninvasive therapy indicated for the symptomatic relief from, and management of, chronic intractable pain and post-surgical and post-trauma acute pain. It provides a safe and effective alternative to pharmacological approaches to pain control.Jul 26, 2018
What is the difference between tens and IFC?
The main difference between IFC and TENS is in the use of a medium-frequency current (4,000 Hz) amplitude modulated a low frequency of 0-250 pulses per second (pps). In comparison, TENS may often use lower frequency currents, which meet greater resistance when passing through the skin as a barrier.Oct 21, 2016
When do we use IFC?
Inferential current (IFC) Developed in the 1950s, IFC is most commonly used for pain relief (Kitchen, 2001). IFC is also claimed to reduce inflammation, and assist tissue repair (including bone fractures), and reeducate muscle (especially with incontinence).Dec 1, 2019
Can TENS reduce inflammation?
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) reduces chronic hyperalgesia induced by muscle inflammation. Pain.
How do you choose between IFT and TENS?
Whereas TENS Units delivers periodic electric pulses to stimulate surface nerves and block the pain signal, IFT Physiotherapy Equipment transmits a continuous stimulation deep into the affected tissue thereby blocking the pain signals and reducing swelling and inflammation which causes pain.Aug 11, 2019
Can you do IFC with a TENS unit?
0:1111:16TENS & IFC EXPLAINED | Theory, Use, & Parameters - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's suppose you have a patient in pain. And you want to use a modality to help treat that painMoreLet's suppose you have a patient in pain. And you want to use a modality to help treat that pain which electrical stimulation modality is going to be your go-to to treat pain for pain we're pretty
What is interferential therapy?
Interferential therapy is a type of therapy which is very effective and is used in relieving pain by various physiotherapic clinics. This helps to accelerate the process of self healing and getting a patient’s body free from pain and regain healthy physical conditions. In this therapy, the interferential current is produced on the skin, ...
Where is the interferential current produced?
In this therapy, the interferential current is produced on the skin, of the affected body part of the patient, with the help of interferential device by expert physiotherapist. This interferential current penetrates into the skin and reaches the underlying living muscle tissue. This therapy involves an orthopaedic physical therapy setting.
Does current therapy help with pain?
The input of the current to the muscle produces some sensation and this sensation helps in self healing of the pain. Patients having any other problem related to pain like inflammation and swelling, if receives this therapy may achieve relief too. This therapy also helps in restoring lost movements and helps in improving it.
Does interferential therapy follow any rules?
The interferential therapy does not follow any such rules and regulations or guidelines for the patients after the treatment is done. In case of patients having any other problem in their body, must follow all the rules and guidelines as prescribed by their concerned doctors.
What is IFT therapy?
The basic principle of Interferential Therapy (IFT) is to utilise the strong physiologicaportable iftl effects of low frequency (<250pps) electrical stimulation of nerves without the associated painful and somewhat unpleasant side effects sometimes associated with low frequency stim.
Why does IFT work?
It has been suggested that IFT works in a ‘special way’ because it is ‘interferential’ as opposed to ‘normal’ stimulation. The evidence for this special effect is lacking and it is most likely that IFT is just another means by which peripheral nerves can be stimulated.
Does IFT help with oedema?
Increased local blood flow. Reduction of oedema. In addition, claims are made for its role in stimulating healing and repair. As IFT acts primarily on the excitable (nerve) tissues, the strongest effects are likely to be those which are a direct result of such stimulation (i.e. pain relief and muscle stimulation).
Can interferential therapy be used to stimulate nerves?
It is not capable of direct stimulation of nerve in the common context of such stimulation. Interferential therapy utilises two of these medium frequency currents, passed through the tissues simultaneously, where they are set up so that their paths cross & they literally interfere with each other.
Introduction of Interferential current Therapy (IFT)
The basic principle of Interferential Current Therapy (IFT) is to utilise the significant physiological effects of low frequency (<250pps) electrical stimulation of nerves without the associated painful and somewhat unpleasant side effects sometimes associated with low frequency stimulation.
PRINCIPLES OF IFT
To produce low frequency effects at sufficient intensity and at sufficient depth, patients can experience considerable discomfort in the superficial tissues (i.e. the skin). This is due to the impedance of the skin being inversely proportional to the frequency of the stimulation.
Physiological Effects of Interferential current Therapy (IFT)
Excitable tissues can be stimulated by low frequency alternating currents.
Uses of Interferential current Therapy (IFT)
Electrical stimulation for pain relief has widespread clinical use, thought the direct research evidence for the use of I/F in this role is limited. Logically one could use the higher frequencies (90-150Hz) to stimulate the pain gate mechanisms & thereby mask the pain symptoms.
Interferential current therapy contraindications
The following condition in which Interferential current therapy contraindicated as per below mentioned. :
IFT Precautions
Following precautions should taken when you applying Interferential therapy as per below :
IFT parameters
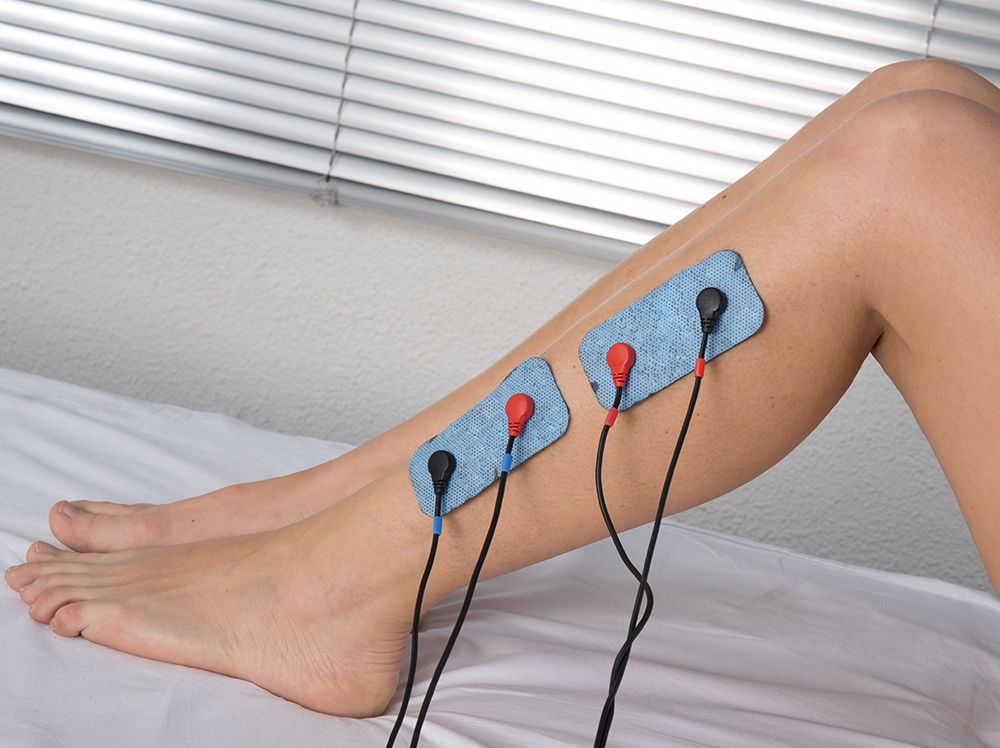
Electrode positioning should ensure adequate coverage of the area for stimulation. In some circumstances, a bipolar method is preferable if a longitudinal zone requires stimulation rather than an isolated tissue area. Placement of the electrodes should be such that a crossover effect is achieved in the desired area.
How do you know if interferential current stimulation therapy may be a treatment option for you?
You have muscle spasms, joint damage, edema, muscle strains, or sports injuries.
What is interferential therapy used for?
Interferential current therapy (ICT or sometimes shortened to IFC or IFT) is the most common form of electrical muscle stimulation. It is a noninvasive, drug-free, therapy with minimal side effects. At Loehr Health Center, ICT is used in conjunction with other modalities like chiropractic care and decompression therapy to promote healing.
What is interferential current therapy?
Interferential current therapy is a form of electrical therapy that uses a pair of electrodes containing two independent circuits, high frequency (4,000 Hz) and medium frequency (150 Hz), alternating currents.
What happens during an interferential therapy session?
You are completely clothed during your interferential therapy session. Your provider will ask you to lie on your stomach or back on a therapy table. (Depending on the area being treated, you may be asked to sit upright in a chair instead.)
How much is an interferential therapy treatment?
Loehr Health Center’s clinical team takes a multidisciplinary approach to managing and treating spinal disorders. Interferential therapy is usually part of an individualized treatment plan that includes spinal adjustments with a chiropractor. The cost of interferential therapy per treatment is $25.
What are the side effects of interferential therapy?
Interferential therapy is a non-invasive treatment with minimal side effects. You will feel your muscles contracting during interferential therapy. Patients report a buzzing or tingling sensation on the skin.
How many interferential treatments are required to resolve my condition?
The type of and frequency of treatments that are recommended to you’re you achieve your health goals depends on the severity of your condition and pain level.
What is IFT therapy?
The basic principle of Interferential Therapy (IFT) is to utilise the significant physiological effects of low frequency (<250pps) electrical stimulation of nerves without the associated painful and somewhat unpleasant side effects sometimes associated with low frequency stimulation. Recently, numerous ‘portable’ interferential devices have become easily available. Despite their size, they are perfectly capable of delivering ‘proper’ interferential therapy, though some have limited functionality and ability for the practitioner to ‘set’ all parameters. Most multifunction stimulators include all interferential modes, so the practitioner has several machine types to select from (examples below).
How effective is IFT?
IFT has been claimed to be effective as a treatment to promote the reabsorption of oedema in the tissues. Again, the evidence is very limited in this respect and the physiological mechanism by which is could be achieved as a direct effect of the IFT remains to be established. The preferable clinical option in the light of the available evidence is to use the IFT to bring about local muscle contraction(s) which combined with the local vascular changes that will result (see above) could be effective in encouraging the reabsorption of tissue fluid. The use of suction electrodes may be beneficial, but also remains unproven in this respect.
How does IFT work?
It has been suggested that IFT works in a ‘special way’ because it is ‘interferential’ as opposed to ‘normal’ stimulation. The evidence for this special effect is lacking and it is most likely that IFT is just another means by which peripheral nerves can be stimulated. It is rather a generic means of stimulation – the machine can be set up to act more like a TENS type device or can be set up to behave more like a muscle stimulator – by adjusting the stimulating (beat) frequency. It is often regarded (by patients) to be more acceptable as it generates less discomfort than some other forms of electrical stimulation.
Is iFT better than tens?
There have been numerous studies in recent years which have compared the efficacy of iFT and TENS, primarily with regard to pain relief. A significant proportion of these studies have been lab based, though some are more clinically oriented. Overall, these studies indicate that TENS generally provides higher (stronger) levels of pain relief (or some associated outcome), though IFT is generally identified as being more comfortable from the perspective of the recipient. If a patient dislikes the sensation associated with TENS, IFT would constitute a useful fallback stimulation modality on the basis of reported comfort.

Benefits
- By careful manipulation of the input currents it is possible to achieve any beat frequency that you might wish to use clinically. Modern machines usually offer frequencies of 1-150Hz, though some offer a choice of up to 250Hz or more. To a greater extent, the therapist does not have to concer…
Mechanism
- The magnitude of the low frequency interference current is (in theory) approximately equivalent to the sum of the input amplitudes. It is difficult to show categorically that this is the case in the tissues but it is reasonable to suggest that the resultant current will be stronger than either of the 2 input currents. The use of 2 pole IFT stimulation is made possible by electronic manipulation o…
Treatment
- Whichever way it is generated, the treatment effect is generated from low frequency stimulation, primarily involving the peripheral nerves. There may indeed be significant effect on tissue other than nerves, but they have not as yet been unequivocally demonstrated. Low frequency nerve stimulation is physiologically effective (as with TENS and NMES) and this is the key to IFT interv…
Usage
- Note : Care needs to be taken when setting the sweep on a machine in that with some devices, the user sets the actual base and top frequencies (e.g. 10 and 25Hz) and with other machines the user sets the base frequency and then how much needs to be added for the sweep (e.g. 10 and 15Hz). Knowing which was round your machine works is critical to effective treatment. The patt…
Examples
- There is a clear difference between these examples even though the same numbers are set. One will deliver a full range of stimulation frequencies between the set frequency levels and the other will switch from one frequency to the other. There are numerous other variations on this theme, and the trapeziodal sweep is effectively a combination of these two.
Analysis
- The only sweep pattern for which evidence appears to exist is the triangular sweep. The others are perfectly safe to use, but whether they are clinically effective or not remains to be shown.
Function
- It has been suggested that IFT works in a special way because it is interferential as opposed to normal stimulation. The evidence for this special effect is lacking and it is most likely that IFT is just another means by which peripheral nerves can be stimulated. It is rather a generic means of stimulation the machine can be set up to act more like a TENS type device or can be set up to be…
Criticism
- Selection of a wide frequency sweeps has been considered less efficient than a smaller selective range in that by treating with a frequency range of say 1-100Hz, the effective treatment frequencies can be covered, but only for a relatively small percentage of the total treatment time. Additionally, some parts of the range might be counterproductive for the primary aims of the tre…
Applications
- In addition, claims are made for its role in stimulating healing and repair and for various specialised application e.g. stress incontinence, though for the former examples (healing nad repair) there is a dearth of quality research information available.
Effects
- As IFT acts primarily on the excitable (nerve) tissues, the strongest effects are likely to be those which are a direct result of such stimulation (i.e. pain relief and muscle stimulation). The other effects are more likely to be secondary consequences of these.
Research
- Electrical stimulation for pain relief has widespread clinical use, thought the direct research evidence for the use of IFT in this role is limited. Logically one could use the higher frequencies (90-130Hz) to stimulate the pain gate mechanisms & thereby mask the pain symptoms. Alternatively, stimulation with lower frequencies (2-5Hz) can be used to activate the opioid mec…
Safety
- Whichever electrode system is employed, electrode positioning should ensure adequate coverage of the area for stimulation. Using larger electrodes will minimise patient discomfort whilst small, closely spaced electrodes increase the risk of superficial tissue irritation and possible damage / skin burn.
Advantages
- The bipolar (2 pole) application method is perfectly acceptable, and there is no physiological difference in treatment outcome despite several anecdotal stories to the contrary. Recent research evidence supports the benefit of 2 pole application (e.g. Ozcan et al 2004).
Selected publications
- Adedoyin, R. A., et al. (2002). \"Effect of interferential current stimulation in management of osteo-arthritic knee pain.\" Physiotherapy 88(8): 493-9.
Diagnosis
- Almeida, T. F., et al. (2003). \"The effect of combined therapy (ultrasound and interferential current) on pain and sleep in fibromyalgia.\" Pain 104(3): 665-72.
Selected works
- Alves-Guerreiro, J.et al. (2001). \"The effect of three electrotherapeutic modalities upon peripheral nerve conduction and mechanical pain threshold.\" Clinical Physiology 21(6): 704-711. Atamaz, F. C. et al. (2012). \"Comparison of the efficacy of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, interferential currents, and shortwave diathermy in knee osteoarthritis: a double-blind, randomiz…
Introduction & Ift Production
- The basic principle of Interferential Therapy (IFT) is to utilise the strong physiologicaportable iftl effects of low frequency (<250pps) electrical stimulation of nerves without the associated painful and somewhat unpleasant side effects sometimes associated with low frequency stim. To produce low frequency effects at sufficient intensity at depth...
Frequency Sweep
- Nerves will accommodate to a constant signal & a sweep (or gradually changing frequency) is often used to overcome this problem. The principle of using the sweep is that the machine is set to automatically vary the effective stimulation frequency using either pre-set or user set sweep ranges. The sweep range employed should be appropriate to the desired physiological effects (s…
Physiological Effects & Clinical Applications
- It has been suggested that IFT works in a ‘special way’ because it is ‘interferential’ as opposed to ‘normal’ stimulation. The evidence for this special effect is lacking and it is most likely that IFT is just another means by which peripheral nerves can be stimulated. It is rather a generic means of stimulation – the machine can be set up to act more like a TENS type device or can be set up to …
Treatment Parameters
- Stimulation can be applied using pad electrodes and sponge covers (which when wet provide a reasonable conductive part), though electroconductive get is an effective alternative. The sponges should be thoroughly wet to ensure even current distribution. Self adhesive pad electrodes are also available (similar to the newer TENS electrodes) and make the IFT application easier in the …