What medications affect INR?
- St. John's wort.
- carbamazepine (Tegretol, Tegretol XR, Equetro, Carbatrol)
- rifampin, bosentan (Tracleer)
- prednisone.
What is the treatment for elevated INR?
The treatment options for patients who have been over-anticoagulated are:
- Dose omission;
- Oral phytomenadione (vitamin K 1 );
- Intravenous phytomenadione;
- Fresh frozen plasma (FFP);
- Prothrombin complex concentrates (PCC).
How to treat a patient whose INR is too high?
- Increase or decrease oral Vitamin K administration based on the clinical situation.
- Parenteral Vitamin K should only be used for life-threatening bleeding and is therefore not appropriate for outpatient use.
- Use the recommendations for the next lower INR range in the following situations:
How to correct elevated INR?
- Most cirrhotics are in a state of rebalanced hemostasis, due to similar reductions in pro- and anti-coagulant proteins. ...
- INR measures the level of clotting factors only, not the overall balance of coagulation. ...
- Responding to an elevated INR by transfusing FFP is a misguided practice which should be abandoned. ...
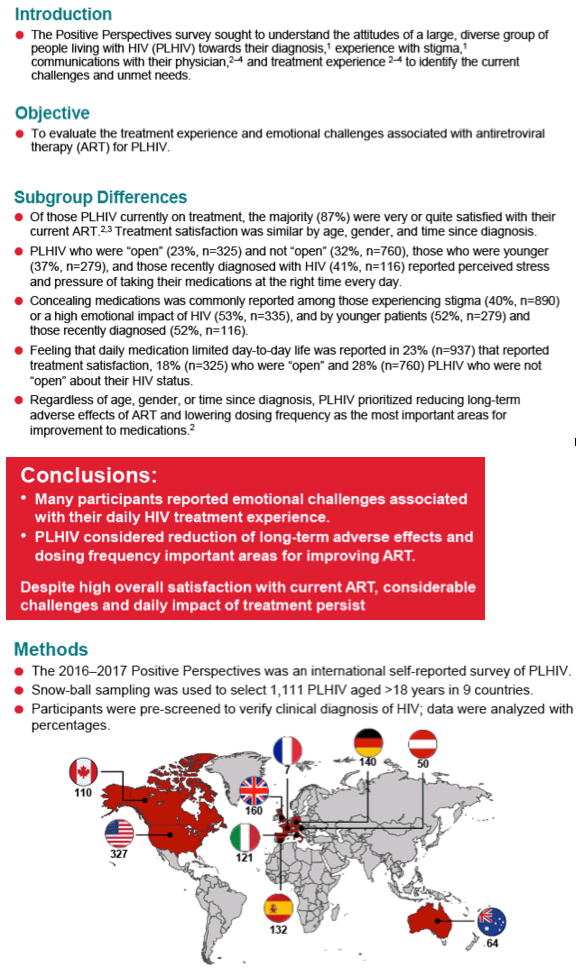
What does INR mean?
An INR (international normalized ratio) is a type of calculation based on PT test results. Prothrombin is a protein made by the liver. It is one of several substances known as clotting (coagulation) factors.
What is the treatment for a high INR?
If your INR is between 4 and 10, you might take some vitamin K in addition to skipping your medication for a few days. If your INR is higher than 10, you'll probably take vitamin K. You'll also want to stop taking warfarin and get frequent INR checks to make sure it's improving.
What happens if INR level is too high?
The higher your PT or INR, the longer your blood takes to clot. An elevated PT or INR means your blood is taking longer to clot than your healthcare provider believes is healthy for you. When your PT or INR is too high, you have an increased risk of bleeding.
What does INR therapeutic mean?
International normalized ratio (INR) is the preferred test of choice for patients taking vitamin K antagonists (VKA). It can also be used to assess the risk of bleeding or the coagulation status of the patients.
Can a high INR cause a stroke?
Elevated International Normalized Ratio Is Associated With Ruptured Aneurysms | Stroke.
What causes high INR?
A high INR level can happen when you take warfarin (Coumadin). Warfarin helps prevent blood clots. To do this, it slows the amount of time it takes for your blood to clot. This raises your INR level.
What are the symptoms if your blood is too thin?
Other signs of thin blood include nosebleeds and abnormally heavy menstrual flow. Thin blood can also cause bruises to appear under the skin. A minor bump can cause the tiny blood vessels under the skin to bleed. This can result in purpura, which are small purple, red, or brown bruises.
Does drinking water affect INR levels?
What you eat and drink can also affect your INR. The more consistent you are in what you eat and drink, the easier it can be to regulate your dose of Warfarin and keep your INRs in range.
Does thin blood make you tired?
Aside from bleeding-related issues, there are several side effects that have been linked to blood thinners, such as nausea and low counts of cells in your blood. Low blood cell count can cause fatigue, weakness, dizziness and shortness of breath. Be careful mixing medications.
What are the effects of INR?
Multiple factors such as vitamin K consumption, drug interactions, herbs interactions, disease states, and alcohol intake affect international normalized ratio (INR) values and thus warfarin dosing. These variables have been described in general and for all patients in the literature.
What is normal INR level?
What is a normal PT/INR range? Your test result will show different ranges for PT and INRs The normal ranges for clotting are: 11 to 13.5 seconds. INR of 0.8 to 1.1. INR of 2.0 to 3.0 is a general therapeutic range for people taking warfarin.
Why INR test is done?
An INR test measures the time for the blood to clot. It is also known as prothrombin time, or PT. It is used to monitor blood-thinning medicines, which are also known as anticoagulants. The INR, or international normalised ratio, can also be used to check if you have a blood clotting problem.
What Increases My Risk For An Elevated INR?
1. Too much anticoagulant medicine, a type of blood thinner that helps prevent clots 2. Other medicines, such as aspirin, NSAIDs, and some antibiot...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of An Elevated INR?
You may have small cuts that bleed more than normal, and for longer than normal. You may bruise easily, have frequent nosebleeds, or notice your gu...
How Is An Elevated INR Treated?
Treatment depends on whether you currently have bleeding and how severe it is. If you take an anticoagulant medicine, your healthcare provider may...
How Can I Prevent An Elevated INR?
1. Have your INR measured regularly. Your healthcare provider may want your INR to be measured every few days until it is stable, and then only onc...
How Can I Decrease My Risk of bleeding?
1. Avoid activities that may cause bleeding or bruising. 2. Brush and shave gently. Use a soft toothbrush and an electric razor to avoid bleeding....
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. Your menstrual period is heavier than normal. 2. You see blood in your urine. 3. Your bowel movement is bloody or black. 4. You bruise or bleed...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care Or Call 911?
1. You throw up blood, or your vomit looks like coffee grounds. 2. You have any kind of bleeding that does not stop in 15 minutes. 3. Your leg feel...
How to test for INR?
It is recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institutes (2017) that the blood specimens for INR/PT testing in the laboratory setting should be collected from venous blood and it is directly obtained into a tube with a light blue top. The tube contains an anticoagulant. The acceptable anticoagulant is the concentration of sodium citrate 3.2%. The tubes must be filled to within 90% of the full collection volume. The tube should be then inverted a few times, gently and as soon as possible, for proper mixing with the anticoagulant. The total time between sample collection and testing should not exceed 24 hours.
What is the target INR for a mitral valve?
For patients with a mechanical mitral prosthetic valve (including On-X valve) or mechanical tricuspid prosthetic valve, the target INR is 3.
What is the INR for VKA?
International normalized ratio (INR) is the preferred test of choice for patients taking vitamin K antagonists (VKA). It can also be used to assess the risk of bleeding or the coagulation status of the patients. Patients taking oral anticoagulants are required to monitor INR to adjust the VKA doses because these vary between patients. The INR is derived from prothrombin time (PT) which is calculated as a ratio of the patient’s PT to a control PT standardized for the potency of the thromboplastin reagent developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) using the following formula:
What is the INR range for a patient on anticoagulation?
For normal patients who are not on anticoagulation, the INR is usually 1.0 regardless of the ISI or the particular performing laboratory. [8]For patients who are on anticoagulant therapy, the therapeutic INR ranges between 2.0 to 3.0. INR levels above 4.9 are considered critical values and increase the risk of bleeding. The therapeutic INR range differs in a patient with prosthetic valve:
What is the target INR for a bileaflet?
For patients with a bileaflet (other than On-X) or current generation, single-tilting disk, mechanical, aortic, prosthetic valve with no other risk factors for thromboembolism, the target INR is 2.5.
How long does it take to get an INR after a valve surgery?
For patients with an On-X mechanical bileaflet aortic valve with no other risk factors for thromboembolism, the INR goal is 2 to 3 for the first three months after valve surgery; and after three months the goal is 1.5 to 2.
Why is warfarin adapted to INR?
The dose of warfarin is adapted based on INR scores so that it remains in the therapeutic range to prevent thrombosis from subtherapeutic INR or hemorrhagic complications from supratherapeutic INR. The anticoagulant effect of warfarin indicated by an INR in the target range also guides us when to discontinue heparin.
Why is INR important?
Regardless of which treatment is used, it is important to increase the frequency of INR monitoring until it returns to the desired range.
What is the aim of treatment for haemorrhage?
The aim of treatment should be to arrest the haemorrhage as quickly as possible and stabilise the patient, thereby limiting further harm.
What is a thromboprophylaxis med?
They are used for several indications, including thromboprophylaxis for patients with atrial fibrillation, or who have undergone a mechanical heart valve replacement or had deep vein thrombosis (DVT). They are also used to treat current DVTs or pulmonary emboli.
Do pharmacists need to refer patients for warfarin reversal?
Nonetheless, pharmacists may need to refer patients for treatment to reverse over-anticoagulation, so a clear understanding of how such patients are managed is essential. It also helps to understand the subsequent care of patients who have undergone warfarin reversal treatment.
Does warfarin help with pulmonary emboli?
They are also used to treat current DVTs or pulmonary emboli. Appropriate management of warfarin therapy requires monitoring of patients’ international normalised ratios (INRs). While pharmacists often monitor their patients’ INRs, it is usually doctors who manage patients who have become over- anticoagulated.
Can warfarin be reversed?
Clinicians also consider how quickly and to what extent the anticoagulation needs to be reversed. Any requirement for warfarin reversal therapy can serve as an opportunity to review whether warfarin treatment is still necessary for the patient .
How to keep INR stable?
Eat the same amount of vitamin K daily to keep your INR stable. Vitamin K changes how your blood clots and affects your INR. Vitamin K is found in green leafy vegetables, broccoli, grapes, and other foods. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about what to eat when you have an elevated INR.
What is elevated INR?
What is an elevated INR? The INR, or International Normalized Ratio, is a measure of how long it takes your blood to clot. A prothrombin time (PT) is a another blood test done to help measure your INR. The higher your PT or INR, the longer your blood takes to clot.
How to avoid bleeding from a syringe?
Avoid activities that may cause bleeding or bruising. Brush and shave gently. Use a soft toothbrush and an electric razor to avoid bleeding. Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers if you take anticoagulant medicine or have a bleeding disorder.
What is the best treatment for a clot?
Blood components may be given during a transfusion to help stop your bleeding. Blood components are the parts of blood that help it to clot. Examples are clotting factors, platelets, and plasma.
Does alcohol increase INR?
Limit alcohol. Alcohol increases your INR. Ask your healthcare provider how much alcohol is safe for you.
What is the INR of a patient?
The INR is another way of measuring the blood-clotting time and it is easier to determine than the PT. < Previous. Just Diagnosed Main. Next >.
What does it mean when INR is 1.0?
A normal INR is 1.0. Each increase of 0.1 means the blood is slightly thinner (it takes longer to clot). INR is related to the prothrombin time (PT). If there is serious liver disease and cirrhosis, the liver may not produce the proper amount of proteins and then the blood is not able to clot as it should. When your provider is evaluating the function of your liver, a high INR usually means that the liver is not working as well as it could because it is not making the blood clot normally.
What does INR stand for?
INR stands for international normalized ratio and is measured with a blood test called PT-INR. PT stands for prothrombin time. The test measures how much time it takes for your blood to clot and will determine if you’re receiving the right dose of warfarin.
How often is testing needed?
Testing needs depend on how stable a patient’s INR is over time. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), patients should be tested at least once a month, but some patients will require testing as often as twice a week. INR tests can be done at a lab or clinic but can also be done at home for some patients.
What can I do to help keep my INR level where it should be?
First, always listen closely to your doctor’s instructions and take your medication exactly as prescribed. If you miss any doses, you should contact your healthcare provider and ask about how to safely restart it.
Looking forward
Starting a new medication can be challenging and warfarin is no exception. If you have questions or concerns about taking warfarin, be sure to contact your healthcare provider. In addition, pharmacists at either your local hospital or retail pharmacy are an excellent resource.
What are the INR findings?
The INR’s scientific findings have been published in multiple, peer-reviewed medical journals, including Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, CNS Drugs, BMC Neurology, Current Alzheimer Research , Clinical Therapeutics , Drug Discovery Today, and Current Medical Research and Opinion . INR publications, findings, and research have advanced the science of neurology, dementia, and spine medicine, and have been cited and discussed by physicians and scientists from academic centers around the world. There have been hundreds of scientific citations to INR publications, including in Nature Clinical Practice Neurology and F1000 Biology.
What is the phone number for INR?
Consultation and treatment are by appointment only. Phone or in-office consultations can be scheduled by calling the INR at +1 (561) 353-9707, Monday through Friday, 9 AM to 6 PM Eastern Time.
What is the INR number for stroke in Florida?
Please call the INR in Florida +1 (561) 353-9707 for further information.
What is the drug used for TNF?
The drug utilized was etanercept, a therapeutic that selectively binds and neutralizes an inflammatory immune molecule that may remain elevated for years following stroke. The anti-TNF fusion protein was administered utilizing a novel delivery method, invented by Edward Tobinick M.D., lead author of the study.
Does INR use etanercept?
Please note: INR medical providers utilize etanercept for a limited number of off-label indications. INR medical providers do not use etanercept for treating Parkinson’s disease, brain tumor, or carpal tunnel syndrome. Individual treatment recommendations are only made following physician evaluation, including history, physical examination, and review of imaging studies, if available.
Does INR accept telephone inquiries?
The INR welcomes telephone inquiries from physicians and family members. In particular, the IN R encourages telephone inquiry and discussion with an INR medical provider for those patients referred from locations at a geographic distance from Boca Raton, Florida, prior to appointment scheduling. This is recommended especially for those patients who will be flying across country or from overseas for treatment at the INR, due to the special nature of the services provided at the INR, and the unique experience which the INR has performing anti-TNF treatment for neurological disorders.
Is TNF good for stroke recovery?
These published results, and more than 8 years of clinical experience, suggest that excess TNF plays an important role in post-stroke chronic disability and establish the promise that the INR’s patented anti-TNF treatment presents for stroke recovery and stroke rehabilitation. Results can vary, and more than one dose may be necessary for optimal benefit, please see the Terms of Use , but these results represent a new breakthrough in the understanding of the neurological basis of chronic brain dysfunction following stroke.
Why do we use INR?
Because the clotting ability of blood will vary depending on temperature and humidity etc. a pair of tests that produces something called the INR (International Normalized Ratio) is calculated.
What does it mean when INR is low?
A low INR (meaning near 1.0) therefore means you have unthinned blood and normal levels of clotting factors in your blood. If the INR is less than about 0.8 you have abnormal amounts of clotting factors.
What is the INR of 1.0?
Of course it's 1.0 if you're not taking warfarin! 1.0 is the INR for normal unthinned blood. If your doctor wants your INR in the range 2.0 to 4.0, he needs to give you warfarin. (Other thinners don't impact the INR number, because they work in a different way.)
Why is blood thinning used?
The idea of blood thinning treatment to make the INR higher than normal (e.gg. 2.0) is to prevent clotting which can happen in stroke patients, or patients with Deep Vein Thrombosis or heart flow problems.
How long does it take for INR to return to normal?
Remember that INR responds 36 hours AFTER you take your warfarin or food containing vitamin K, and the effect lasts for about 36 hours, so you should look at the 3 to 4 days before your test for diet changes ... like spinach salads!
What is an antivert?
Antivert is essentially an antihistamine / anti-nauseant, like Gravol (dramamine).
Can you adjust your warfarin dose?
Speak with your doctor. He may have to adjust your warfarin dose. Never adjust your dose yourself.