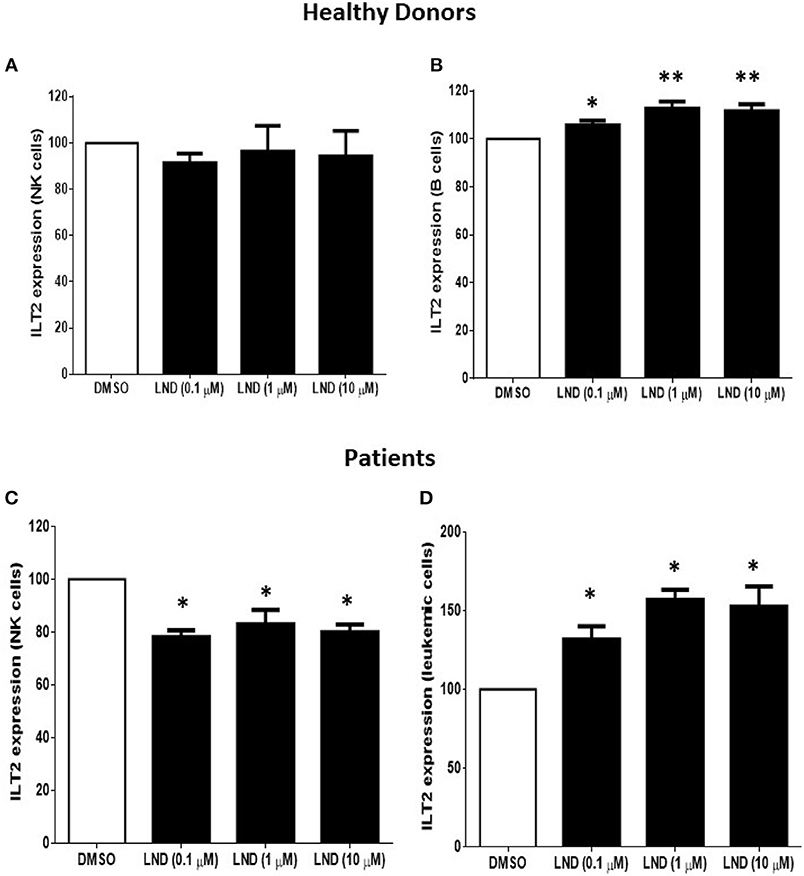
Patients with CLL are often treated with intravenous immune globulin (IVIG
Immunoglobulin therapy
Immunoglobulin therapy, also known as normal human immunoglobulin, is the use of a mixture of antibodies to treat a number of health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, Kawasaki disease, certain cases of HIV/AIDS and measles, Guillain-Barré syndrome, an…
What are the treatment options for IGHV-mutated CLL?
Nevertheless, even though novel agents might be the standard of care, CIT (chlorambucil/obinutuzumab, bendamustine/rituximab or FCR) is still an available treatment option in tn IGHV-mutated CLL patients without del(17p), TP53 mutation, or complex karyotype. 13. Treatment in Relapsed/Refractory Patients
How effective is IVIG in the treatment of CLL?
Research has shown that IVIG is effective in preventing infections in CLL patients. In a 2009 meta-analysis of nine trials, researchers assessed treatment of CLL and multiple myeloma patients with polyvalent IVIG versus a control group with primary outcomes of all-cause mortality and major infections.
What do doctors do for low-risk CLL?
If you have low-risk CLL, your doctor (usually a hematologist or oncologist) will likely advise you to “wait and watch” for symptoms. This approach is also called active surveillance. Someone with low-risk CLL may not need further treatment for many years.
How has the treatment of CLL changed over time?
These therapeutics have fundamentally changed the treatment of CLL and improved patient outcomes. An improved progression-free survival with these therapeutics over CIT in both settings, first-line and relapsed/refractory, was demonstrated in many randomized clinical trials.
What is the best treatment for CLL in 2021?
According to the American Cancer Society , doctors commonly prescribe the following medication combinations to treat CLL:acalabrutinib (Calquence) with Gazyva.alemtuzumab (Campath) with rituximab (Rituxan)bendamustine and Rituxan.chlorambucil and Rituxan.fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and Rituxan.More items...•
What does IVIG do for CLL?
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) Antibody levels can be checked with a blood test, and if they're low, antibodies from donors can be given into a vein (IV) to raise the levels and help prevent infections. These donated antibodies are called intravenous immunoglobulin or IVIG.
What is the newest treatment for CLL?
In May 2019, the FDA approved venetoclax (Venclexta) in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) to treat people with previously untreated CLL as a chemotherapy-free option. In April 2020, the FDA approved a combination therapy of rituximab (Rituxan) and ibrutinib (Imbruvica) for adult patients with chronic CLL.
Can CLL be treated with immunotherapy?
Different Treatments for CLL Several different treatment options are available for patients with newly diagnosed CLL. Many patients are treated with a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy, such as bendamustine plus rituximab, or with a targeted therapy such as ibrutinib (Imbruvica®).
Is IVIg a chemotherapy drug?
In conclusion, IVIg is a potential anticancer treatment for several reasons: (a) the bidirectional relationship between cancer and autoimmunity; (b) the apparent association between cancer regression and IVIg administration; (c) a variety of anticancer effects of IVIg observed; and (d) IVIg is considered to be a safe ...
What are the side effects of IVIg?
One of the most common side effects is headache. Other side effects include chills, fever, flushing, flu-like muscle pains or joint pains, feeling tired, having nausea, vomiting, and rash.
Can you live 20 years with CLL?
CLL has a very high incidence rate in people older than 60 years. CLL affects men more than women. If the disease has affected the B cells, the person's life expectancy can range from 10 to 20 years.
Can CLL go into remission without treatment?
While there is not yet a cure for the condition, a wide range of effective treatments are available. And some people don't need any treatment if the CLL is slow-growing or in a period of remission.
At what point does CLL require treatment?
Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (chronic lymphoid leukemia, CLL) do not need drug therapy until they become symptomatic or display evidence of rapid progression of disease, as characterized by the following: Weight loss of more than 10% over 6 months.
What is the best medicine for CLL?
Typical Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaIbrutinib (Imbruvica), alone or with rituximab (Rituxan)Acalabrutinib (Calquence), alone or with obinutuzumab (Gazyva)Venetoclax (Venclexta) and obinutuzumab.Venetoclax alone, or with rituximab.Bendamustine and rituximab (or another monoclonal antibody)More items...•
What is the success rate of immunotherapy for leukemia?
93 percent of advanced leukemia patients in remission after immunotherapy.
What is the best hospital for CLL?
Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., Mayo Clinic in Phoenix/Scottsdale, Ariz., and Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., are ranked among the Best Hospitals for cancer by U.S. News & World Report.
What is BTK inhibitor?
With the introduction of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) ibrutinib, which irreversibly inhibits Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), an essential enzyme in the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway, the era of targeted agents for CLL patients began [17,18,19] .
Is CLL treated with chemotherapy?
Until recently, CLL was treated using chemotherapy in combination with anti-CD20 antibody-based immunotherapy. Depending on age and clinical condition, patients received more or less intensive chemotherapy and were at risk of side effects commonly associated with chemotherapy.
Is acalabrutinib a BTK?
Recently, acalabrutinib, a second-generation BTKi with higher selectivity for BTK than ibrutinib [20], was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of CLL patients.
What is CLL treatment?
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is a form of blood cell cancer that can impact healthy B-cell production, which may increase the risk of infection. Patients with CLL are often treated with intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) replacement therapy in conjunction with other forms of treatment.
What test is used to determine if you have CLL?
The test results are used to stage CLL, most commonly using the Rai staging system (Figure 1). Once the stage of CLL is confirmed, treatment can be determined.
What is CLL in biology?
Understanding CLL. Leukemia is cancer that originates in blood-forming tissue characterized by the uncontrolled growth of blood cells that are produced in the bone marrow . In healthy bone marrow, blood stem cells mature over time and become either myeloid stem cells or lymphoid stem cells. Lymphoid stem cells transform into lymphoblast cells ...
Why do CLL patients have frequent infections?
Lack of proper B cell function is one reason why CLL patients experience frequent infections, which is one of many complications of the disease. While not all physicians recommend IVIG therapy to prevent these infections, it has been shown to be a successful preventive treatment.
What happens to the bone marrow when you have leukemia?
In the bone marrow of patients with leukemia, cancerous blood cells form and, in essence, crowd out the healthy blood cells, interfering with their normal function. There are several types of leukemia (Table 1) categorized according to which blood cells are affected, and whether the disease is acute or chronic.
How do you know if you have CLL?
In fact, the first sign of CLL may be an increased white blood count during routine blood work. Symptoms usually begin with frequent infections and/or fever, night sweats, fatigue and enlarged yet painless lymph nodes. There can also be pain in the left upper abdomen that may be due to an enlarged spleen. Figure 1.
Can CLL cause leukemia?
In addition, these cells remain viable and multiply, whereas normal lymphocytes die. The result is impaired antibody production, leaving the person at risk for infection. CLL is usually one of the slower progressing types of leukemia, and many people don’t experience symptoms for quite some time.
What is the first treatment for CLL?
Initial treatment of CLL. Many different drugs and drug combinations can be used as the first treatment for CLL. The options include monoclonal antibodies, other targeted drugs, chemotherapy, and different combinations of these. Some of the more commonly used drug treatments include: Other drugs or combinations of drugs may also be used.
What is the rarest complication of CLL?
If this happens, treatment is likely to be similar to that used for patients with ALL. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is another rare complication in patients who have been treated for CLL.
What is the most serious type of CLL?
One of the most serious complications of CLL is a change (transformation) of the leukemia to a high-grade or aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) called diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or to Hodgkin lymphoma. This happens in 2% to 10% of CLL cases, and is known as Richter's transformation. Treatment is often the same as it would be ...
How long does it take for chemo to lower blood count?
Chemo may not lower the number of cells until a few days after the first dose, so before the chemo is given, some of the cells may need to be removed from the blood with a procedure called leukapheresis. This treatment lowers blood counts right away.
What happens if the first line of treatment is not working?
If the initial treatment is no longer working or the disease comes back, another type of treatment often helps . If the initial response to the treatment lasted a long time (usually at least a few years), the same treatment might be used again. If the initial response wasn't long-lasting, using the same treatment isn't as likely to be helpful. The options will depend on what the first-line treatment was and how well it worked, as well as the person's overall health.
What is the best treatment for enlarged spleen?
Radiation or surgery. If the only problem is an enlarged spleen or swollen lymph nodes in one part of the body, localized treatment with low-dose radiation therapy may be used. Splenectomy (surgery to remove the spleen) is another option if the enlarged spleen is causing symptoms.
Does leukemia treatment work before chemo?
This treatment lowers blood counts right away. The effect lasts only for a short time, but it may help until the chemo has a chance to work. Leukapheresis is also sometimes used before chemo if there are very high numbers of leukemia cells (even when they aren’t causing problems) to prevent tumor lysis syndrome.
What is the best treatment for CLL?
One of the most promising future treatment options for CLL is CAR T-cell therapy. CAR T, which stands for chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, uses a person’s own immune system cells to fight cancer.
How many clinical trials are there for CLL?
These new treatments may work better for you than the ones currently available. There are currently hundreds of clinical trials ongoing for CLL.
Why are targeted therapies called targeted therapies?
These drugs are called targeted therapies because they’re directed at specific proteins that help CLL cells grow. Examples of targeted drugs for CLL include:
What is CLL in medical terms?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a slow-growing cancer of the immune system. Because it’s slow-growing, many people with CLL won’t need to start treatment for many years after their diagnosis.
What does it mean when you have a high risk CLL?
High-risk CLL describes patients with stage 3 or stage 4 cancer. This means you may have an enlarged spleen, liver, or lymph nodes. Low red blood cell counts are also common. In the highest stage, platelet counts will be low as well.
What is intermediate risk CLL?
Intermediate-risk CLL describes people with stage 1 to stage 2 CLL, according to the Rai system. People with stage 1 or 2 CLL have enlarged lymph nodes and potentially an enlarged spleen and liver, but close to normal red blood cell and platelet counts. High-risk CLL describes patients with stage 3 or stage 4 cancer.
What is low risk CLL?
Treatments for low-risk CLL. Doctors typically stage CLL using a system called the Rai system. Low-risk CLL describes people who fall in “stage 0” under the Rai system. In stage 0, the lymph nodes, spleen, and liver aren’t enlarged. Red blood cell and platelet counts are also near normal. If you have low-risk CLL, ...
Where do antibodies come from in CLL?
So, the antibodies come from B cells, and that’s why CLL is a disease of the B cells. And so, that's why they’re, as Susan mentioned, they’re not forming the proper antibodies. So, we can get these healthy antibodies from donors, and it's usually a pool of those antibodies to get enough to give you that boost.
Who said you gotta have IVIG infusions?
Okay. And Dr. Kipps here in San Diego says, “Andrew, if you want to travel,” and that’s true, and I like to travel, and we’ve seen many of our CLL friends when we do, he said, “You gotta have the IVIG infusions.”
What is the purpose of immunoglobulins?
Immunoglobulins are antibodies that help CLL patients fight infections. Understanding the process of getting healthy antibodies from donors. Discuss with your doctor if IVIG infusions are right for you.
Do you need immunoglobulin to get a boost?
You can measure the immunoglobulin levels in the body, and if they’re normal, you may not need the extra boost, especially if you’re early CLL and watching and waiting. And, again, and if patients are getting recurrent infections, that’s another reason that they might need transfusion.