How I healed my chronic idiopathic urticaria?
- Moisturize regularly with lotion.
- Use cool water when you shower.
- Apply a cold compress or an ice pack to affected areas.
- Try using over-the-counter creams such as calamine lotion.
- Wear clothing made from 100-percent cotton or 100-percent silk.
What is the best treatment for urticaria?
- Avoid aggravating factors such as avoiding excessive heat, spicy foods or alcohol.
- Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided as they often make symptoms worse.
- Medications like non-drowsy antihistamines are often used to reduce the severity of the itch. ...
How can chronic idiopathic urticaria be treated?
- H2 blockers. These are drugs that block the production of histamines that can cause hives or overproduction of stomach acids. ...
- Short-term oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone. These are especially useful for reducing the swelling around eyes, lips, or throat that can accompany hives.
- Sedating antihistamine. ...
- Immune suppressants. ...
- Monoclonal antibodies. ...
What tests conclusively diagnose idiopathic urticaria?
What are the clinical features of chronic spontaneous urticaria?
- Weals can be a few millimetres or several centimetres in diameter.
- They can be coloured white or red, usually with a red flare.
- Each weal may last a few minutes or several hours, and they may change shape before resolving.
- Weals may be round or form rings, a map-like pattern, or giant patches.

What is the treatment for CSU?
Standard management of CSU primarily involves second-generation H1 antihistamines, often at higher than usual doses and in combination with H2 antihistamines and leukotriene modifiers. Short courses of systemic glucocorticoids to control severe exacerbations may be needed.
How do you permanently cure physical urticaria?
Lifestyle and home remediesWear loose, light clothing.Avoid scratching or using harsh soaps.Soothe the affected area with a bath, fan, cool cloth, lotion or anti-itch cream.Keep a diary of when and where hives occur, what you were doing, what you were eating, and so on. ... Avoid known triggers.More items...•
What is the first-line treatment for urticaria?
Nonsedating antihistamines are the first-line treatment of urticaria and may be titrated to two to four times their normal dose, if necessary. These are recommended over older antihistamines because of their adverse effect profiles. All histamine H1 blockers appear to be effective.
Which is the best treatment for urticaria?
Antihistamines. Antihistamines are the best, first-line treatment for hives, both acute and chronic. 1 They work by suppressing histamine, a chemical produced by the immune system that triggers allergy symptoms. Newer antihistamines are non-drowsy and their effects may last for as long as 24 hours.
What is the best medicine for chronic urticaria?
Antihistamines like Benadryl and Claritin are often effective in relieving the symptoms of urticaria. Taking this type of medication at the first sign of hives can help lessen the severity of the outbreak. You can also use anti-itch lotions to help.
Is urticaria a serious disease?
Chronic urticaria (CU) is a disturbing allergic condition of the skin. Although frequently benign, it may sometimes be a red flag sign of a serious internal disease. A multitude of etiologies have been implicated in the causation of CU, including physical, infective, vasculitic, psychological and idiopathic.
What is idiopathic urticaria?
Idiopathic urticaria is the medical term for hives that seem to have no direct cause. Chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) is when the hives you've been dealing with have no known cause and last for 6 weeks or more. It's also called chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU).
Is urticaria a skin disease?
Hives (urticaria) are red, itchy welts that result from a skin reaction. The welts vary in size and appear and fade repeatedly as the reaction runs its course. The condition is considered chronic hives if the welts appear for more than six weeks and recur frequently over months or years.
What causes urticaria?
These may include environmental irritants, your immune system, and genetics. It can also be a response to a bacterial, fungal, or viral infection. Chronic idiopathic urticaria involves activation of your immune response system.
How long does it take for urticaria to reappear?
Symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria include: raised or swollen welts on your skin (hives or wheals) that appear and reappear over the course of 6 weeks. Your hives may change size, fade, and reappear. Heat, exercise, or stress may aggravate your symptoms.
What is it called when you have hives?
Diagnosis. Treatment. Diet. Outlook. Urticaria is the medical term for hives. These are itchy raised bumps or welts on your skin. Your dermatologist may call them wheals. When hives appear and reappear over the course of 6 weeks or more, they’re considered chronic. And when the cause is unknown, they’re called idiopathic.
How often is omalizumab injected?
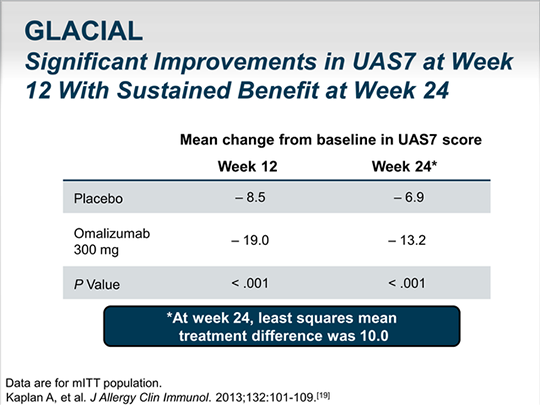
Omalizumab (Xolair) is an expensive, newer drug that has proved very effective against chronic idiopathic urticaria. It’s typically injected once per month. In one study, 83 percent of people with chronic urticaria had a complete remission after treatment with omalizumab.
What is the best medicine for hives?
fexofenadine (Allegra) desloratadine (Clarinex) levocetirizine (Xyzal) If your hives don’t clear up with OTC antihistamines, your doctor may try other types of treatment, including: H2 blockers. These are drugs that block the production of histamines that can cause hives or overproduction of stomach acids.
Is hives a symptom of urticaria?
Before classifying hives as idiopathic, your doctor will check for the presence of an allergy, autoimmunity, or infection. If none of these is the cause, it may be idiopathic urticaria. About 75 percent.
Is urticaria related to thyroid?
Chronic urticaria may be connected to the thyroid. In one study of people with chronic urticaria, 12 of 54 people. Trusted Source. , all females, had thyroid autoantibodies (anti-TPO) in their blood. Of these 12 people, 10 were found to have hypothyroidism and were treated for it.
What is it called when you have hives?
These are known as chronic hives or chronic urticaria. Sometimes you and your doctor are unable to identify what’s causing your hives to keep coming back. Often the hives can occur on different parts of the body. When this happens, the hives are called chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU). Idiopathic means “of unknown cause.”.
What is CIU in medical terms?
Idiopathic means “of unknown cause.”. Another name for CIU is chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). CIU outbreaks can appear at any time without triggers. Chronic urticaria is not contagious. The symptoms of CIU are not life-threatening, but, CIU can cause extreme discomfort and greatly impact quality of life.
How to treat CIU?
They may recommend low-impact exercises such as cycling, swimming, or yoga.
How to prevent insect bites?
Apply bug spray and wear long-sleeved tops and pants to prevent insect bites. Consider wearing a hat to protect yourself from the sun. On the other hand, the cold associated with winter (or cold conditions such as a swimming pool) can trigger a flare-up in some people.
What are the causes of CIU?
1. Stress and anxiety. Not all CIU triggers are physiological. They can also be psychological, stemming from stress or anxiety. Your mental state may play an important role in the manifestation of symptoms, so keeping your stress levels down can also keep your symptoms in check.
What causes hives in summer?
Being outside during the summer can be a minefield for CIU triggers. Pollen, insect bites, and the sun’s heat can all lead to itchy bumps on your skin. Don’t be surprised if spending time outdoors brings a sudden onset of hives. Apply bug spray and wear long-sleeved tops and pants to prevent insect bites.
Can you control CIU symptoms?
Reviewing your notes with a doctor may be able to help you identify patterns. You may never be able to control your CIU symptoms completely, but understanding the factors that may play a role in bringing on an outbreak could help you avoid certain triggers. Last medically reviewed on February 26, 2019.
Can scratching your skin cause hives?
Scratching. Although scratching your itchy skin offers temporary satisfaction, it may actually be a trigger. Scratching can lead to a vicious cycle in which you become more aware of the itch and can’t stop yourself from focusing on it. This leads to even more scratching, and an even worse case of hives. 3.
