
Procedures
What drugs can cause hypothermia? Miscellaneous causes include sepsis, multiple trauma, pancreatitis, prolonged cardiac arrest, and uremia. Hypothermia may be related to drug administration; such medications include beta-blockers, clonidine, meperidine, neuroleptics, and general anesthetic agents.
Therapy
The mechanisms of heat loss from your body include the following:
- Radiated heat. Most heat loss is due to heat radiated from unprotected surfaces of your body.
- Direct contact. If you're in direct contact with something very cold, such as cold water or the cold ground, heat is conducted away from your body. ...
- Wind. Wind removes body heat by carrying away the thin layer of warm air at the surface of your skin. ...
Nutrition
Hypothermia treatment may include warmed IV fluids, heated and humidified oxygen, peritoneal lavage (internal “washing” of the abdominal cavity), and other measures. Complications during recovery can include pneumonia, heart arrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest (a sudden stopping of the heartbeat), and death.
What drugs can cause hypothermia?
When doctors examine a person, the key symptoms and signs below indicate a diagnosis of hypothermia:
- body temperature below 95°F (35°C)
- shivering
- impaired mental state
- frostbite, which is injury to body tissues resulting from freezing
What is the normal body temperature for hypothermia?
What is treatment for severe hypothermia?
What are the signs of severe hypothermia?
What is the treatment in hypothermia?
Hypothermia treatment may include warmed IV fluids, heated and humidified oxygen, peritoneal lavage (internal "washing" of the abdominal cavity), and other measures.
What is the best first aid treatment for hypothermia?
First aid for hypothermia: Cover the person completely with foil or a space blanket, or use your own body heat to help warm him/her. Use warm compresses on the neck, chest, and groin. Give warm, sweet fluids. (Any fluids given should be nonalcoholic, as alcohol interferes with the blood's circulation.)
How does hypothermia treatment work?
How does therapeutic hypothermia help? Hypothermia counteracts neuroexcitation in brain cells by stabilizing calcium and glutamate release, reducing the degree of cell death. It also stabilizes the blood-brain barrier and suppresses the inflammatory process, reducing cerebral edema.
What causes hypothermia?
Hypothermia is caused by prolonged exposures to very cold temperatures. When exposed to cold temperatures, your body begins to lose heat faster than it's produced. Lengthy exposures will eventually use up your body's stored energy, which leads to lower body temperature.
What are the signs and symptoms of hypothermia?
Signs and symptoms of hypothermia include:Shivering.Slurred speech or mumbling.Slow, shallow breathing.Weak pulse.Clumsiness or lack of coordination.Drowsiness or very low energy.Confusion or memory loss.Loss of consciousness.More items...•
How does hypothermia affect the brain?
The basic mechanisms through which hypothermia protects the brain are clearly multifactorial and include at least the following: reduction in brain metabolic rate, effects on cerebral blood flow, reduction of the critical threshold for oxygen delivery, blockade of excitotoxic mechanisms, calcium antagonism, ...
What temperature is too low for a person?
Body temperature below 95°F (35°C) is considered abnormally low, and the condition is known as hypothermia. This happens when your body loses heat faster than it can produce heat. Hypothermia is a medical emergency, which if left untreated can lead to brain damage and cardiac failure.
Does hypothermia increase heart rate?
At temperatures below 95 F (35 C), shivering is seen. Heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure increase. As the temperature drops further, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure all decrease.
How to get warm?
Remove wet clothing and dry the person off, if needed. Warm the person's trunk first, not hands and feet. Warming extremities first can cause shock. Warm the person by wrapping them in blankets or putting dry clothing on the person. Do not immerse the person in warm water.
What to do if you can't breathe?
If the person is not breathing, start CPR immediately. Hypothermia causes respiratory rates to plunge, and a pulse might be difficult to detect. For a child, start CPR for children. For an adult, start adult CPR. Continue CPR until the person begins breathing or emergency help arrives.
How to warm up a person?
2. Restore Warmth Slowly 1 Get the person indoors. 2 Remove wet clothing and dry the person off, if needed. 3 Warm the person's trunk first, not hands and feet. Warming extremities first can cause shock. 4 Warm the person by wrapping them in blankets or putting dry clothing on the person. 5 Do not immerse the person in warm water. Rapid warming can cause heart arrhythmia. 6 If using hot water bottles or chemical hot packs, wrap them in cloth; don't apply them directly to the skin.
What is the temperature of hypothermia?
Hypothermia stages include mild, moderate, and severe. Mild hypothermia is characterized by a body temperature of 90 to 95 degrees F (32.2 to 35 degrees C) and shivering, rapid breathing, increased heart rate, and lack of coordination.
How does hypothermia happen?
Hypothermia occurs when the core body temperature—the temperature of the organs and blood in the center of the body, not the skin—drops below 95 degrees. This may happen in a number of situations, such as when someone is out in cold weather for too long or falls into icy water. People who are wet will lose body heat faster ...
How to rewarm a person from cold?
Once you have the individual sheltered from the cold and have removed any wet clothing, you will need to take the appropriate action to rewarm the body until help arrives. To do so safely: 3 . Be gentle. Avoid rubbing the person aggressively.
What is hypothermia in 2021?
Updated on June 23, 2021. Hypothermia is a medical emergency in which your body loses heat faster than it can produce it, causing a dangerous drop in the core body temperature.
What is the temperature of a person with moderate hypothermia?
Moderate hypothermia is defined as a body temperature of 82.4 to 89.9 degrees F (28 to 32.2 degrees C) with slower breathing and heart rate, dilated pupils, decreased reflexes, and low blood pressure. Severe hypothermia is a body temperature of less than 82.4 degrees F (28 degrees C) and nonreactive pupils, heart failure, difficulty breathing, ...
What is passive external rewarming?
Passive external rewarming (PER) is typically used to treat mild hypothermia. It simply involves placing the individual in an appropriately warm environment, covered in insulation, and gradually raising the core body temperature a few degrees every hour.
How to get blood out of a cold?
To do this: 2 . Move the person out of the cold, ideally to a dry, warm location. If you can't get indoors, shield the person from the cold and wind , keeping him or her in a horizontal position so that the blood can circulate more freely. Remove wet clothing.
What is the temperature of hypothermia?
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Hypothermia occurs when your body loses heat faster than it can produce heat and your body temperature falls below 95 F (35 C). Left untreated, it can be life-threatening. Hypothermia is often caused by exposure to cold weather or immersion in a cold body of water.
How do you know if you have hypothermia?
Signs and symptoms of hypothermia usually develop slowly and may include: Shivering, though this may stop as body temperature drops. Slurred speech or mumbling. Slow, shallow breathing. Weak pulse. Clumsiness or lack of coordination. Drowsiness or very low energy. Confusion or memory loss. Loss of consciousness.
What is therapeutic hypothermia?
Therapeutic hypothermia is a type of treatment. It’s sometimes used for people who have a cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest happens when the heart suddenly stops beating. Once the heart starts beating again, healthcare providers use cooling devices to lower your body temperature for a short time. It’s lowered to around 89°F to 93°F (32°C to 34°C).
How long does hypothermia last?
That’s when chilled fluids are given through an IV (intravenous) line into your bloodstream. The therapeutic hypothermia will likely last around 24 hours. The medical team will slowly rewarm you over several hours. They may set cooling blankets at gradually higher temperatures.
How long does it take for hypothermia to start after cardiac arrest?
The medical team may start the hypothermia within 4 to 6 hours after the cardiac arrest. A healthcare provider will give you medicine to help you relax (sedative). It makes you sleep and keeps you from shivering. You will not remember anything about the procedure afterward.
What is the best way to check your temperature?
Your heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs will be closely watched. Healthcare providers use special thermometers to check your internal temperature. The provider may use cooling blankets, ice packs, or cooling pads to bring the body temperature down. The goal is to cool as quickly as possible.
Can you use therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest?
Therapeutic hypothermia can help only some people who have had cardiac arrest. Some people regain consciousness right after cardiac arrest. These people often do not need this procedure. It is helpful only for people whose heartbeat returns after a sudden cardiac arrest. If the heartbeat doesn’t restart soon, it won't help.
Is hypothermia dangerous?
Therapeutic hypothermia is very helpful for some people. But it has some rare risks. Some of these risks include: Another abnormal heart rhythm, especially slow heart rates. Severe blood infection (sepsis) Blood is less able to clot. This can cause bleeding. Electrolyte and metabolic problems.
Can you use cooling blankets for hypothermia?
They may set cooling blankets at gradually higher temperatures. In some cases, they may use rewarming devices as well. Sometimes, healthcare providers may do therapeutic hypothermia at the same time as other treatments. For example, they might do heart catheterization after a cardiac arrest caused by a heart attack.
What is the treatment for hypothermia?
This treatment is known as hypothermia therapy, but it has many other names, such as “therapeutic hypothermia,” “cooling therapy,” and “neonatal cooling.”. Hypothermia therapy involves cooling the baby down to a temperature below homeostasis to allow the brain to recover from a hypoxic-ischemic injury. Typically, the target temperature is about ...
How soon after birth can you give hypothermia?
However, it must be given very shortly after birth/the oxygen-depriving incident in order to be effective (ideally within six hours). This treatment is known as hypothermia therapy, but it has many other names, ...
How much temperature should a newborn be after hypothermia?
The AMC PSO suggests that the baby’s temperature should be increased by 0.2 – 0.5 degrees Celsius, until it reaches 36.5 degrees Celsius.
How long does it take for a baby to get hypothermia?
According to the Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization (AMC PSO), hypothermia therapy should ideally be commenced within six hours of birth (under certain circumstances, this may be done within 12 hours) (2). The sooner hypothermia therapy begins, the greater the chance that the baby’s potential disabilities will be minimized.
When should a baby get hypothermia?
When should my baby get hypothermia therapy? If your baby was diagnosed with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), doctors have to begin hypothermia therapy very shortly after the oxygen deprivation occurred.
Who is the HIE Help Center?
The HIE Help Center is run by ABC Law Centers (Reiter & Walsh, P.C.), a medical malpractice firm exclusively handling cases involving HIE and other birth injuries. Our lawyers have over 100 years of combined experience with this type of law, and have been advocating for children with HIE and related disabilities since the firm’s inception in 1997.
Do hospitals have brain cooling?
Community hospitals, for example, may not have brain cooling equipment, but they should have the ability to transfer the baby to a bigger or more specialized hospital that can provide cooling. It is a good idea to inquire about what kind of care a neonatal care unit can provide when researching hospitals.
What is therapeutic hypothermia?
Therapeutic hypothermia is a procedure used to cool a person's body to a temperature that is lower than normal. The procedure is done after a cardiac arrest (when the heart stops) that happens outside of a healthcare setting.
What is used to cool a person's body?
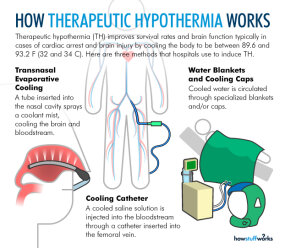
Ice packs, icy cold wet towels, or fans may be used. The ice packs are placed on the person's neck, armpits, torso, and groin. A cooling blanket may be laid over the person's body. Cool water runs through the cooling blanket. During endovascular cooling, a catheter is placed into a big vein in a person's groin.
Does shivering help with hypothermia?
Shivering increases body temperature and decreases the benefits of therapeutic hypothermia. Healthcare providers will use medicines to stop the person from shivering. Healthcare providers may also use warm air in the room to help control shivering.
What is therapeutic hypothermia?
Therapeutic Hypothermia (TH) improves neurological recovery and reduces mortality after global ischemia, such as in patients with cardiac arrest1-3, and in infants with moderate or severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy4.
What are the two methods of induced hypothermia?
In general, two methods of induced hypothermia are used currently: surface cooling and endovascular cooling. Surface cooling methods include convective air blankets, water mattresses, alcohol bathing, cooling jackets, and ice packing. Surface cooling techniques have been used for many years in the treatment of fever.
How long does hypothermia last?
Some reports suggest that to reduce cerebral edema, hypothermia duration may be needed for 48 to 72 hours after symptom onset32. Longer duration of hypothermia treatment, however, was associated with more adverse effects suggesting treatment should be limited to 24 hours49.
What is the best treatment for shivering?
In the clinical trials of hypothermia in patients after cardiac arrest, neuromuscular blockade was used to prevent and treat shivering2.
Is hypothermia a neuroprotective effect?
Therapeutic Hypothermia has proven neuroprotective effects in global cerebral ischemia. Indications for hypothermia induction include cardiac arrest and neonatal asphyxia. The two general methods of induced hypothermia are either surface cooling or endovascular cooling. Hypothermia should be induced as early as possible to achieve maximum ...
Does cooling the skin reduce heat exchange?
Cooling of the skin surface induc es vasoconstriction and reduces heat exchange in cooled patients; vasoconstriction reduces temperature control, which has lead to target temperature overshoot and lack of control during re-warming16, 20.
Is external cooling slower than endovascular cooling?
External cooling, however, is slower than endovascular cooling and requires the use of sedatives and paralytics to prevent discomfort and shivering in most cases for target temperatures below 35°C19. The use of paralytic agents renders accurate physical assessment and detection of neurologic worsening impossible.
What is the long term benefit of neonatal hypothermia?
Additional Information. Neonatal therapeutic hypothermia is a relatively new treatment option for oxygen deprivation at birth. Therapeutic hypothermia involves lowering an infant’s body temperature shortly after birth. This is done in order to reduce the chances of severe brain damage ...
Why is lowering the temperature important?
Particularly, to treat anoxia and hypoxia and related injuries. For infants who have brain damage due to oxygen deprivation, lowering the body’s temperature in a controlled setting can help prevent additional damage. This is especially important for infants experiencing conditions like hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
How many babies have hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy?
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy ( HIE) occurs in around 1 to 6 out of every 1,000 births . HIE is a lack of oxygen and blood to the brain. Without immediate treatment, infants are at risk not only of severe brain damage, but death as well.
What is the Apgar score for neonatal hypothermia?
In most instances, babies must qualify for neonatal therapeutic hypothermia treatment, which may include the following: An Apgar score of <5 after 10 minutes of birth. Need for resuscitation and oxygen after 10 minutes of birth. Infants born 36 weeks gestation and older.
Does hypothermia work on newborns?
Although there still aren’t definitive answers on how well neonatal therapeutic hypothermia works on all newborns, clinical trials have been promising. Hypothermia treatment is also used for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in adults. Many experts feel that it should become standard treatment care for infants who are deprived of oxygen.
Does hypothermia heal better in cold?
Research indicates that when people are injured , they heal better if the injury occurs in a cold environment. Based on this idea and other research, scientists and physicians developed the idea to use hypothermia in the clinical setting. Particularly, to treat anoxia and hypoxia and related injuries. For infants who have brain damage due ...
Is neonatal hypothermia good for children?
According to NIH, there are quite a few long-term benefits to neonatal therapeutic hypothermia. For instance, children who undergo treatment as infants are more likely to have a higher survival rate at 6-7 years of age. In addition, infants who receive the treatment are less likely to develop severe developmental issues such as hearing loss, vision loss and cognitive impairments. Furthermore, the rate of infant death declines with those receiving neonatal therapeutic hypothermia treatment.
