Humanistic therapies include a number of approaches. Three of the most common are Gestalt therapy, client-centered therapy, and existential therapy. In Gestalt therapy, your personal experiences are key, along with describing what you’re going through in your own words.
Full Answer
What is humanistic therapy?
Humanistic therapy is used to treat depression, anxiety, panic disorders, personality disorders, schizophrenia, addiction, and relationship issues, including family relationships.
What philosophers have influenced humanistic therapy?
humanistic therapy: therapeutic orientation aimed at helping people become more self-aware and accepting of themselves lobotomy: a form of psychosurgery in which parts of the frontal lobe of the brain are destroyed or their connections to other parts of the brain severed
What is the treatment modality for Social Work?
Feb 21, 2019 · Humanistic therapy is a type of mental health treatment that centers around your unique experience and perspective. Humanistic therapists offer empathy, genuine concern for you and your experience,...
What is the difference between humanistic and integrative Counselling?
The relationship between therapist and client is significant in creating conditions for growth, become a fully functioning person and achieve self-actualization. There are a wide range of …
What is humanistic therapy used to treat?
Humanistic therapy is used to treat depression, anxiety, panic disorders, personality disorders, schizophrenia, addiction, and relationship issues, including family relationships.
What is an example of humanistic therapy?
For example, you might explore the belief that your opinions don't matter to your partner. Therapists help create the “here and now” atmosphere by asking what you're currently aware of or how certain emotions make you feel. You might use a range of techniques to do this, including: role-playing.Feb 21, 2019
What type of therapy is humanistic therapy?
Humanistic therapy describes a range of different types of therapy that focus on a person as an individual with unique potential and abilities. Instead of concentrating on what is wrong with people, this type of therapy is more focused on helping them overcome their difficulties through personal growth.Oct 7, 2021
What is humanistic approach in Counselling?
Humanistic therapies focus on self-development, growth and responsibilities to help individuals recognise their strengths, creativity and choice. By working with a humanistic counsellor, you are supported in identifying and overcoming any blocks that are preventing you from achieving your full potential.
What are the 3 basic tenets of humanistic therapy?
The discussions revolved around the topics they believed would become the core tenets of this new approach to psychology: Self-actualization, creativity, health, individuality, intrinsic nature, self, being, becoming, and meaning.Mar 8, 2018
How does humanistic therapy treat PTSD?
The humanistic-existential approach to PTSD may not focus primarily on symptom, or even on the traumatic event itself. It may rather emphasize the exploration of the lived experience of the individual and, most importantly, of its existential meaning.
What are the main tenets of humanistic psychology?
The key principles of humanistic psychology include human capacity for self-actualization, self-direction, and choice. Carl Rogers identified five principles of a fully functioning person as open, present, trusting, creative, and fulfilled.
What is the difference between humanistic therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy?
Building a strong therapeutic relationship with a client through genuineness, warmth, empathy, and unconditional positive regard (humanistic approach), while helping clients restructure their thoughts and modify responding behavior (cognitive/behavioral approach), may accelerate client change.
Why is humanistic psychology important?
So it makes sense that the goal of humanistic therapy is to help people become more self-aware and accepting of themselves.
What is Rogerian therapy?
Psychologist Carl Rogers developed a therapeutic orientation known as Rogerian, or client-centered therapy (also sometimes called person-centered therapy or PCT). Note the change from patients to clients. Rogers (1951) felt that the term patient suggested the person seeking help was sick and looking for a cure.
What is MBCT in psychology?
In MBCT, rather than reducing one’s general stress to address a specific problem, attention is focused on one’s thoughts and their associated emotions. For example, MBCT helps prevent relapses in depression by encouraging patients to evaluate their own thoughts objectively and without value judgment (Baer, 2003).
What is evidence based therapy?
A buzzword in therapy today is evidence-based practice. However, it’s not a novel concept but one that has been used in medicine for at least two decades. Evidence-based practice is used to reduce errors in treatment selection by making clinical decisions based on research (Sackett & Rosenberg, 1995). In any case, evidence-based treatment is on the rise in the field of psychology. So what is it, and why does it matter? In an effort to determine which treatment methodologies are evidenced-based, professional organizations such as the American Psychological Association (APA) have recommended that specific psychological treatments be used to treat certain psychological disorders (Chambless & Ollendick, 2001). According to the APA (2005), “Evidence-based practice in psychology (EBPP) is the integration of the best available research with clinical expertise in the context of patient characteristics, culture, and preferences” (p. 1).
Why are substance abuse disorders so difficult to treat?
Addiction and substance abuse disorders are difficult to treat because chronic substance use can permanently alter the neural structure in the prefrontal cortex, an area of the brain associated with decision-making and judgment, thus driving a person to use drugs and/or alcohol (Muñoz-Cuevas, Athilingam, Piscopo, & Wilbrecht, 2013). This helps explain why relapse rates tend to be high. About 40%–60% of individuals relapse, which means they return to abusing drugs and/or alcohol after a period of improvement (National Institute on Drug Abuse [NIDA], 2008).
How does psychotherapy help?
Psychotherapy can help reduce a person’s anxiety, depression, and maladaptive behaviors. Through psychotherapy, individuals can learn to engage in healthy behaviors designed to help them better express emotions, improve relationships, think more positively, and perform more effectively at work or school.
What does Donna tell her therapist about her dog?
Donna tells her therapist that she came home from work in a bad mood and kicked her dog. Her humanistic therapist does not judge her for this action, but rather asks Donna to discuss what she was feeling at that time. The therapist is using ________.
What is humanistic therapy?
Takeaway. Humanistic therapy is a mental health approach that emphasizes the importance of being your true self in order to lead the most fulfilling life. It’s based on the principle that everyone has their own unique way of looking at the world. This view can impact your choices and actions. Humanistic therapy also involves a core belief ...
How do humanistic therapists work?
Humanistic therapists work from the idea that you are the expert in your difficulties. They’ll support the direction you take each session, trusting you to know what you need to talk about in order to work through the things bringing you to therapy.
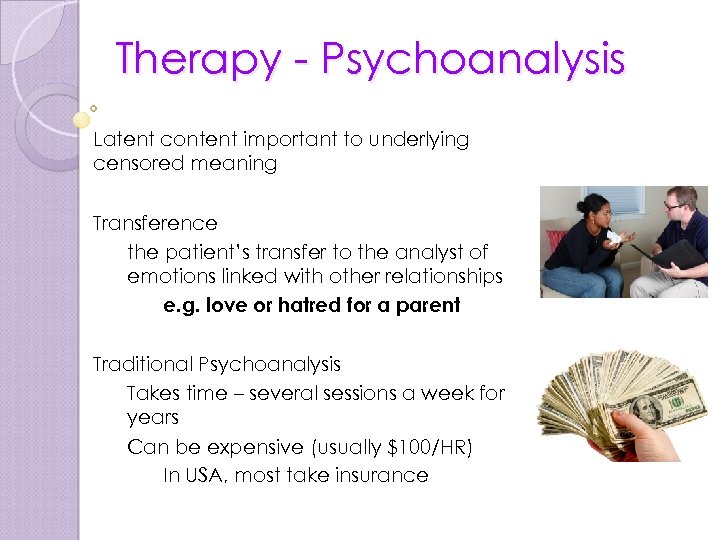
What is Gestalt therapy?
Gestalt therapy. In Gestalt therapy, your personal experiences are key, along with describing what you’re going through in your own words. It’s based on an underlying theory that unresolved conflicts with others — including family members or romantic partners — lead to distress.
Do therapists take insurance?
When looking for a therapist, you also want to take note of how much each potential therapist charges per session. Some therapists take insurance, but others don’t. And some may offer a sliding scale program that allows you to pay what you can. Learn more about how to find affordable therapy.
What is existential therapy?
Like other humanistic approaches, existential therapy is mainly concerned with the issues you currently face, rather than things from your past. But it does consider how your thoughts — conscious or unconscious — impact your mental health and goals.
Is cognitive behavioral therapy effective for anxiety?
coping with chronic health issues. However, it wasn’t quite as effective as cognitive behavioral therapy for addressing anxiety and panic disorder. Whether a humanistic approach fits your needs can depend on what you want to get out of therapy.
What is an effective treatment modality?
An effective treatment modality is one that adopts techniques and philosophies that are designed to encourage the client to create a healthy quality of life. The Existential/Humanistic model, like many other models, emphasizes the importance of several of these techniques and strategies with a particular focus on the importance of developing a sense of meaning and purpose in people’s lives.
How to treat PTSD?
Common Mental Health techniques used for treating PTSD include Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT), Exposure Therapy, Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and psychotropic medications such as anti-anxiety and antidepressants. These treatments are, for the most part, cost effective, short-term approaches that essentially teach the RCV to accommodate the trauma into their lives and focus on developing strategies that are tailored to reducing the symptoms of anxiety and depression associated with PTSD. These approaches devote little if any attention to helping the RCV confront the trauma that she/he experienced while in combat. While most MHPs would agree that CBT and the use of medication has had some success reducing symptoms of PTSD such as anxiety, the psychological impact of combat still remains unresolved. What is often not discussed during psychological counseling sessions is the psychological impact that trauma has on a RCV’s sense of self in terms of how they view their sense of meaning and purpose.
What mental health issues do veterans have?
Mental Health Professionals have focused on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and medication as sufficient treatment . This article suggests that while this may be a useful treatment modality for addressing symptoms it does not adequately help veterans to resolve the full trauma of combat.
What are the challenges of returning combat veterans?
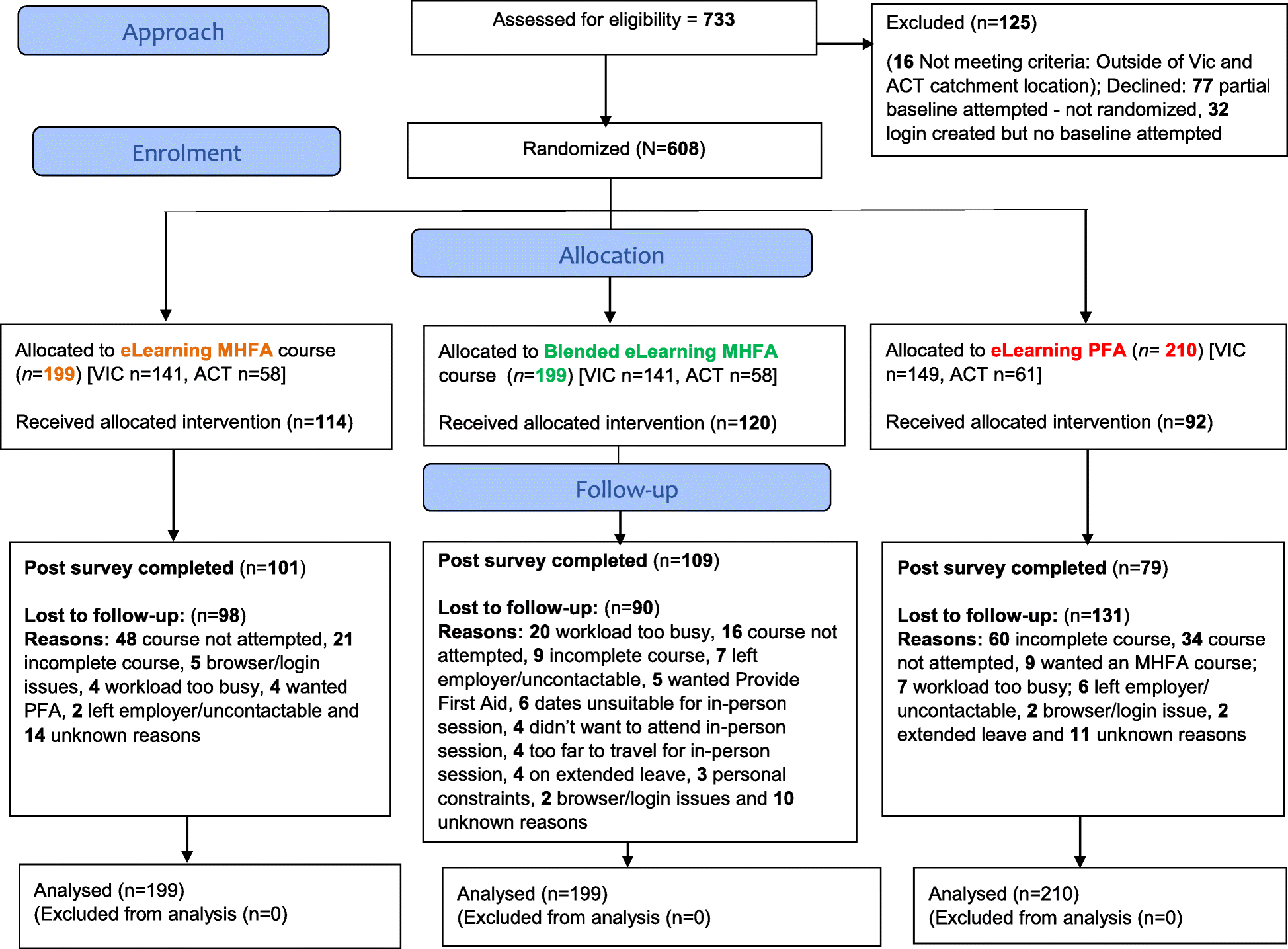
In the United States of America, returning combat veterans (RCVs) are faced with the challenges of coming home from war zones where they experienced and/or witnessed violence and destruction. For many RCVs these experiences can be traumatic and create a significant degree of stress and in many cases depression. Typically, the most common diagnoses for RCVs who have been injured or have witnessed a fellow in arms getting injured or killed is Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and Major Depression (MD). According to the Rand Corporation, approximately 22% of RCVs exhibit symptoms of PTSD and depression [1]. Further, this study suggests that, despite the severe anxiety, fear and depression often associated with PTSD, 46% of RCVs prefer to seek psychological counseling outside of the Veterans Administration (VA) and 50% of those who did seek help within the VA report receiving “minimally adequate treatment.” If left untreated, these symptoms may lead to serious and dangerous outcomes such as increased risk for substance abuse or suicide. In addition, according to a 2016 Veterans Administration report, 27% of RCVs who suffer from PTSD also experience signs of substance use disorder (SUD). It is important to point out that the authors of this report feel that 27% is a low representation of the actual numbers since not all veterans seek help through the VA. In addition, several recent studies have strongly suggested that the current limited quality of care and a significant absence of concern by the Mental Health community and the U.S government has also contributed to an increase in substance abuse, homelessness and suicide (according to the same VA report, 22 veterans commit suicide each day among the RCV population).
What are the symptoms of PTSD?
The first is intrusion symptoms, which are recurring involuntary distressing memories of the traumatic event. The second is avoiding potential stimuli associated with the traumatic event. The third is negative alterations in cognition and mood. This can include symptoms such as persistent negative emotional states and dissociative amnesia. The fourth is marked alterations in arousal to stimuli associated with the traumatic event. This is sometimes referred to as hyper-arousal. PTSD is highly comorbid with other mental disorders, such as depression, anxiety and substance use disorder. The APA also reports an association between PTSD and suicidal ideation and suicidal attempts.
What is the goal of counseling for RCVs?
Traditionally, the goal of treatment when counseling RCVs is to minimize the anxiety and “inappropriate behavioral reactions” to stimuli that elicit memories of the combat experience . Based on recent data (suicide rates, rise in substances abuse rates and veteran rates of homelessness) these approaches (CBT and medication) are not in the best interests of RCVs. Although CBT has the potential to assist RCVs in changing learned behaviors to decrease effects of trauma, RCVs are typically offered a limited amount of counseling sessions, reducing the possibility of long-term recovery. Instead, medication is prescribed but not paired with regular counseling, which contradicts the recommendation that Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI) drugs be accompanied by therapy. While medication can help RCVs with symptoms of trauma it is not a cure for PTSD or any other disorder resulting from combat. In fact, the overuse of medication can be counter-therapeutic because it implies that RCV’s have a disease. This decreases the effectiveness of CBT and a number of other therapeutic modalities. Without consistent access to therapy, RCVs are not given the opportunity to build a foundation of trust with professionals which could lead to a feeling of understanding and support that they otherwise do not have. The authors of this article strongly believe that in order to help the RCV create a healthy quality of life, the MHP must first develop and gain an understanding and insight into the RCV’s experience. In order to create change they must focus on helping the RCV to resolve their feelings of isolation, guilt, shame, helplessness and abandonment.
What is the role of MHP in RCV?
From an Existential/Humanistic perspective, the role of the MHP in terms of helping the RCV to find meaning and purpose is not to be “the expert” who will cure the patient. Rather the MHP needs to be viewed as a therapeutic partner who is there to guide the RCV through the therapeutic process. The Existential/Humanistic MHP recognizes the RCV as an individual with a sense of honor, an individual who is loyal to others and most of all an individual with a desire to live their lives as kind, compassionate and honest individuals who want nothing more than to enjoy a genuine/authentic relationship with others. MHP need to help the RCV to understand that their purpose is not to fix the RCV. The Existential/Humanistic therapeutic process is about helping the RCV re-discover their core values and then guiding them and helping them design a lifestyle based on these values that they decide is meaningful and genuine. Specifically, the responsibility of the MHP is to help the RCV identify the values and characteristics that mark the Existential/Humanistic model, such as compassion, authenticity, and sensitivity. Secondly, to nurture and help the RCV incorporate these values which are the cornerstones for connecting with others and forming healthy relationships, based on mutual trust, mutual respect, and a commitment to personal growth.
What is humanistic therapy?
Humanistic therapy. This approach emphasizes people's capacity to make rational choices and develop to their maximum potential. Concern and respect for others are also important themes. Humanistic philosophers like Jean-Paul Sartre, Martin Buber and Søren Kierkegaard influenced this type of therapy.
What is psychotherapy approach?
Approaches to psychotherapy fall into five broad categories: Psychoanalysis and psychodynamic therapies. This approach focuses on changing problematic behaviors, feelings, and thoughts by discovering their unconscious meanings and motivations. Psychoanalytically oriented therapies are characterized by a close working partnership between therapist ...
What is behavior therapy?
Behavior therapy. This approach focuses on learning's role in developing both normal and abnormal behaviors.#N#Ivan Pavlov made important contributions to behavior therapy by discovering classical conditioning, or associative learning. Pavlov's famous dogs, for example, began drooling when they heard their dinner bell, because they associated the sound with food.#N#" Desensitizing " is classical conditioning in action: A therapist might help a client with a phobia through repeated exposure to whatever it is that causes anxiety.#N#Another important thinker was E.L. Thorndike, who discovered operant conditioning. This type of learning relies on rewards and punishments to shape people's behavior.#N#Several variations have developed since behavior therapy's emergence in the 1950s. One variation is cognitive-behavioral therapy, which focuses on both thoughts and behaviors. 1 Ivan Pavlov made important contributions to behavior therapy by discovering classical conditioning, or associative learning. Pavlov's famous dogs, for example, began drooling when they heard their dinner bell, because they associated the sound with food. 2 " Desensitizing " is classical conditioning in action: A therapist might help a client with a phobia through repeated exposure to whatever it is that causes anxiety. 3 Another important thinker was E.L. Thorndike, who discovered operant conditioning. This type of learning relies on rewards and punishments to shape people's behavior. 4 Several variations have developed since behavior therapy's emergence in the 1950s. One variation is cognitive-behavioral therapy, which focuses on both thoughts and behaviors.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy?
One variation is cognitive-behavioral therapy, which focuses on both thoughts and behaviors. Cognitive therapy. Cognitive therapy emphasizes what people think rather than what they do. Cognitive therapists believe that it's dysfunctional thinking that leads to dysfunctional emotions or behaviors.
What are the different approaches to therapy?
Some focus on the collaboration between therapist and client. Some focus on the type of analysis is done. Still others focus on the tools used during therapy.
What is the best therapy for mental health?
Eclectic Therapy is a great option if you’re having trouble deciding which form of therapy may best assist you, as Eclectic Therapists are seasoned in various modalities. Ecotherapy helps you address your mental health, challenges, feelings, and behaviors by connecting with nature.
What is acceptance and commitment therapy?
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) encourages mindfulness to overcome the negative attitudes, thoughts, and feelings that result from difficulties that come with life. ACT builds on a model of accepting our reactions, staying present, and making choices that then enable us to take action.
What is Adlerian therapy?
Adlerian Therapy is a great approach for someone that is looking to achieve a specific goal. Through engagement, insight, and reorientation, your therapist can help you understand what your roadblocks are in achieving your goals, and to recognize the steps you need to take to get closer to your ultimate goal.
What is behavioral therapy?
Behavior therapy is built on the belief that behaviors are learned and can be unlearned. For someone wanting to let go of unhealthy behaviors that are proving to be harmful, Behavioral Therapy is worth considering. Bibliotherapy leverages literature when your therapist finds it complementary to your healing process.
What is bibliotherapy therapy?
Bibliotherapy is a great approach for those who are interested in literature that encourages their self-awareness and development, or in reading narratives that may feel relatable.
What is dance and movement therapy?
Dance and Movement Therapy uses dance to identify the intersection of the emotional, social, cognitive, and physical components that contribute to your well-being.
What is humanistic therapy?
Humanistic therapy#N#This approach focuses on the individual as a whole. It encourages people to think about their feelings and take responsibility for their thoughts and actions. The emphasis is on self-development and achieving your highest potential rather than on problematic behaviour. Gestalt therapy, person-centred therapy, transactional analysis and transpersonal therapy are all humanistic approaches.
What is eclectic counselling?
E. Eclectic counselling. An eclectic counsellor will use a range of different theories, methods and practices according to an individual client's needs. This is based on their belief that no particular theoretical approach works better than all others for a specific problem.
What is Adlerian therapy?
Adlerian therapy#N#Adlerian therapy is an approach developed by Alfred Adler, who worked with Sigmund Freud. It is also known as individual psychology. Adlerian counsellors believe our experiences in early life, particularly within our families, affect the way we see the world and react to events. Even if we are not aware of them, the logic and goals we develop as children still govern our behaviour when we are adults. Your counsellor will help you to understand why you behave in the way you do so you can find ways to act more effectively.
What is the best treatment for anxiety?
It works well for anxiety and anti-social behaviours. Art therapy . Art therapy is a form of psychotherapy which uses the creative process of making art to explore and communicate issues, feelings and emotions which may be too difficult or distressing to express in words.
How long does a coaching session last?
Sessions may be quite structured and directional or interactive, and can last up to three hours. Coaching may follow a specific model, but many coaches integrate more than one model, along with elements of therapeutic approaches such as person-centred, solution focused or CBT.
What is behavior therapy?
Behavioural therapy. Behavioural therapies are based on the belief that your unwanted or unhealthy behaviours are a learned response to your past experiences. They focus on current problems and aim to help you learn new, more positive behaviours without having to analyse the past.
How long does CAT therapy last?
CAT is a time-limited therapy, typically lasting around 16 weeks . Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) CBT aims to help you change the way you think (cognitive) and what you do (behaviour). Rather than looking at past causes, it focuses on current problems and practical solutions to help you feel better now.