What is the difference between HRT and HRT in wastewater treatment?
HRT depends on the biodegradable nature of wastewater, whereas Zhang et al. reported higher HRT in the anode chamber favoring higher treatment efficiency.
What is the meaning of the term HRT in a reactor?
HRT, defined as the ratio between the reactor volume and the feed flow rate, represents the average time the cells and substrates stay inside the reactor. HRT is a very important parameter for the hydrogen and methane production in continuous mode.
What is hydraulic retention time (HRT)?
In a wastewater treatment facility, the hydraulic retention time (HRT) is used as a measurement of the average time spent keeping wastewater in a tank. Hydraulic Retention Time is also commonly known as Hydraulic residence time.
How long does it take to remove cod from HRT?
Tubular MFC was operated in continuous mode in the range of 2.5–10 days using benzene and phenanthrene as the substrate and inferred that reduction of HRT from 10 to 2.5 days reduced the COD removal efficiency from 74% to 57% [71].
What is HRT in activated sludge?
The hydraulic retention time or HRT is the amount of time in hours for wastewater to pass through a tank, such as an aeration tank. Changes in the HRT of an activated sludge process can affect bio- logical activity.
How do you calculate HRT?
The HRT of an aeration tank is determined by dividing the volume of the aera- tion tank (gallons) by the flow rate through the aeration tank (Equation I. 4). The flow rate through the aeration tank must be expressed as gallons per hour (gph).
What is hydraulic retention time and solid retention time?
Hydraulic retention time (HRT) and solids retention time (SRT) are the terms commonly used to denote the average time that substrate and bacteria (solids) spend in the AD, respectively. In conventional low-rate digesters or reactors without recycle or supernatant withdrawal, the SRT equals to the HRT.
What is hydraulic retention time in water treatment?
The Hydraulic retention time (HRT) or t (tau) is a measure of the average length of time that a soluable compound remains in a constructed bioreactor. The volume of the aeration tank divided by the influent flowrate is τ (tau), the hyraulic retention time.
How is HRT calculated in wastewater treatment?
So, for accurate HRT calculation, use the hydraulic retention time formula “HRT = V/Q.” Here, you are dividing the volume of the aeration tank, which is a value of meters cubed, by the influent flow rate.
What is the difference between HRT and SRT?
The SRT is the average time that bacteria (solids) are in the anaerobic digester. The HRT is the time that the wastewater or sludge is in the anaerobic digester.
What is HRT hydraulic retention time?
Hydraulic retention time (HRT) is defined as the average time interval over which the substrate is kept inside the digester. The organic load rate (OLR) is determined as organic matter feed-in per unit time and volume of the reactor.
How is SRT calculated in wastewater treatment?
The solids retention time (SRT) is the time the solid fraction of the wastewater spends in a treatment unit. It is the quantity of solids maintained in the reactor divided by the quantity of solids coming out of the reactor each day: SRT = V *Cd / Qout* Cout.
What is MLSS in wastewater treatment?
2.2 Mixed liquor suspended solids. MLSS are the concentration of suspended solids in mixed liquor, usually expressed in grams per litre (Wateronline, 2011). Mixed liquor is a mixture of raw or settled wastewater and activated sludge contained in an aeration basin in the activated sludge process.
What is FM ratio wastewater?
What is an F-M ratio? Simply put, the F-M ratio is a measure of the amount of food, or BOD, that is given to the microorganisms in the aeration tank. The microorganisms are the mixed liquor volatile suspended solids, or MLVSS.
How does HRT affect the treatment of wastewater?
Hydraulic retention time (HRT) affects the contact between substrates and microorganisms which also favors toward higher treatment efficiency. HRT depends on the biodegradable nature of wastewater, whereas Zhang et al. [70] reported higher HRT in the anode chamber favoring higher treatment efficiency. Double-chamber BET was operated with chemical wastewater with a COD of 18.6 g/L for a duration of 40 days, which reported higher substrate removal (0.38 g of COD/day) for 30 days and lower degradation rate for the next 10 days (0.12 g of COD/day). Mixed cultures as anodic biocatalyst permits a wider substrate utilization capability due to integration of multiple and simultaneous metabolic activities manifested by diverse species present in the system for the initial days of operation [11]. Tubular MFC was operated in continuous mode in the range of 2.5–10 days using benzene and phenanthrene as the substrate and inferred that reduction of HRT from 10 to 2.5 days reduced the COD removal efficiency from 74% to 57% [71]. Pharmaceutical wastewater with a COD concentration of 12 g/L reported a COD removal efficiency of 85% for a retention time of 18 days [24].
How is HRT controlled?
If the growth rate of organisms is high, then HRT should be less and vice versa to get the maximum output. HRT in continuous stirred tank reactor can be controlled by controlling the dilution rate. HRT and dilution rate are inversely proportional in nature. Dilution rate can be controlled by controlling the feed flow rate. Eq. (3.8) can express dilution rate
What is the HRT of algae?
The hydraulic retention time (HRT) is an operating parameter to select algae cells with sufficiently high growth rates to withstand volumetric dilution caused by continuous liquid flow. Typical specific growth rate of methane-producing algae is 0.0167–0.02/h in dark fermentation, which is smaller than hydrogen-producing algae of around 0.172/h [40 ]. Therefore, methane-producing algae can be washed out while hydrogen-producing algae can be preserved through controlling HRT. Methane content ranged between 0.0011 and 0.0058 mol/L at high HRTs with dilution rates 0.002–0.0167/h was recorded. The methane was hardly detected at higher dilution (D > 0.075/h), demonstrating negligible methanogenic activity at lower HRTs [ 40 ]. This finding indicated that HRT can suppress or promote methanogenesis in dark fermentation.
What is the HRT of a reactor?
HRT, defined as the ratio between the reactor volume and the feed flow rate, represents the average time the cells and substrates stay inside the reactor [3]. HRT is a very important parameter for the hydrogen and methane production in continuous mode. Very low HRT comports the washout of the reactor, which means all the active microorganisms escape out from the reactor. On the contrary, an adequate HRT results in abundant hydrogen and methane yields. This parameter is linked to the specific and different growth rates of hydrogen- and methane-producing bacteria. Low HRT favored the washout of methanogens, guarantying the survival of hydrogen producers. Thus low HRT and slight acid pH (6.0–6.5) represent the best condition for hydrogen production; on the contrary, the hydrogen fermentation pattern may shift to methanogenic one when HRT is increased.
Why is short HRT preferred?
Furthermore, a short HRT can result in reduced efficiency of substrate degradation. In general, short HRT is preferred for hydrogen-producing bacteria, as the growth rate of hydrogen-producing bacteria is much higher than that of hydrogen-consuming bacteria such as methanogens.
Why should HRTs be chosen?
HRTs should be chosen so that cells will be in their exponential growth phase, which is the most favorable condition in terms of biomass productivity and WWT efficiency (Kim et al., 2014).
Environmental Biotechnology and Safety
The design of a constructed wetland and its future performance depend upon the system hydrology. Precipitation, infiltration (or exfiltration), evapotranspiration, hydraulic loading rate, hydraulic residence time, and water depth can all affect the pollutant removal.
Industrial Biotechnology and Commodity Products
Chuanshu He, ... Zhengbo Yue, in Comprehensive Biotechnology (Third Edition), 2019
Artificial Neural Networks Based on Nonlinear Bioprocess Models for Predicting Wastewater Organic Compounds and Biofuel Production
Kelly J. Gurubel DSc, ... Roxana Recio MSc, in Artificial Neural Networks for Engineering Applications, 2019
Immobilized Cells
To obtain the maximum sulphate conversion rate, reactor selection should aim at maximum activity or, otherwise stated, a maximum biomass concentration. Since the generation time of the sulphate-reducing microorganisms generally will exceed the hydraulic retention time, biomass retention i.e., immobilization, is necessary.
Environmental Biotechnology and Safety
F. Cecchi, ... J. Mata-Alvarez, in Comprehensive Biotechnology (Second Edition), 2011
Solid Retention Time-
Hydraulic Retention Time-
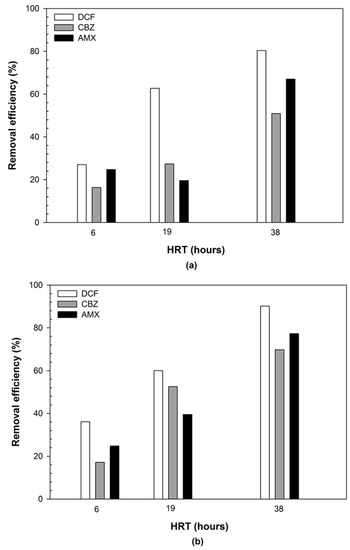
- The HRT regulates the conversion of volatile solids to gaseous products in an anaerobic digester. The HRT's design is determined by the digested sludge's end destination. If the digested sludge is to be land applied or burned, the HRT may be relatively high or low.
Effect of HRT
- The HRT regulates the time for absorption and biodegradation in water by measuring the duration of time a solublechemical stays in the bioreactor (measured as the volume of the aeration tank divided by the influent flow rate). The rate and extent of methane generation are affected by HRT values. Thus, HRT is arguably the most critical operational condition determining the conversio…
Importance of HRT
- In the production of hydrogen and methane, HRT plays an important role: 1. In cases where HRT is very low, it results in the washout of the reactor, which means that all of the active microorganisms depart from the reactor. 2. On the other hand, a good HRT, produces a lot of hydrogen and methane. The distinct and different growth rates of hydrogen- and methane-produ…