What are the best metals for conducting heat?
Which Metal is the Best Conductor of Electricity
- Electric Conductivity. Metallic bonding causes metals to conduct electricity. ...
- Conductive Order of Metals. This list of electric conductivity includes alloys as well as pure elements. ...
- Best to Worst – Which Metal is the Best Conductor of Electricity. ...
- Factors That Affect Electrical Conductivity. ...
- Visit Tampa Steel & Supply for Quality Steel and Aluminum. ...
What happens when metals undergo heat treatment?
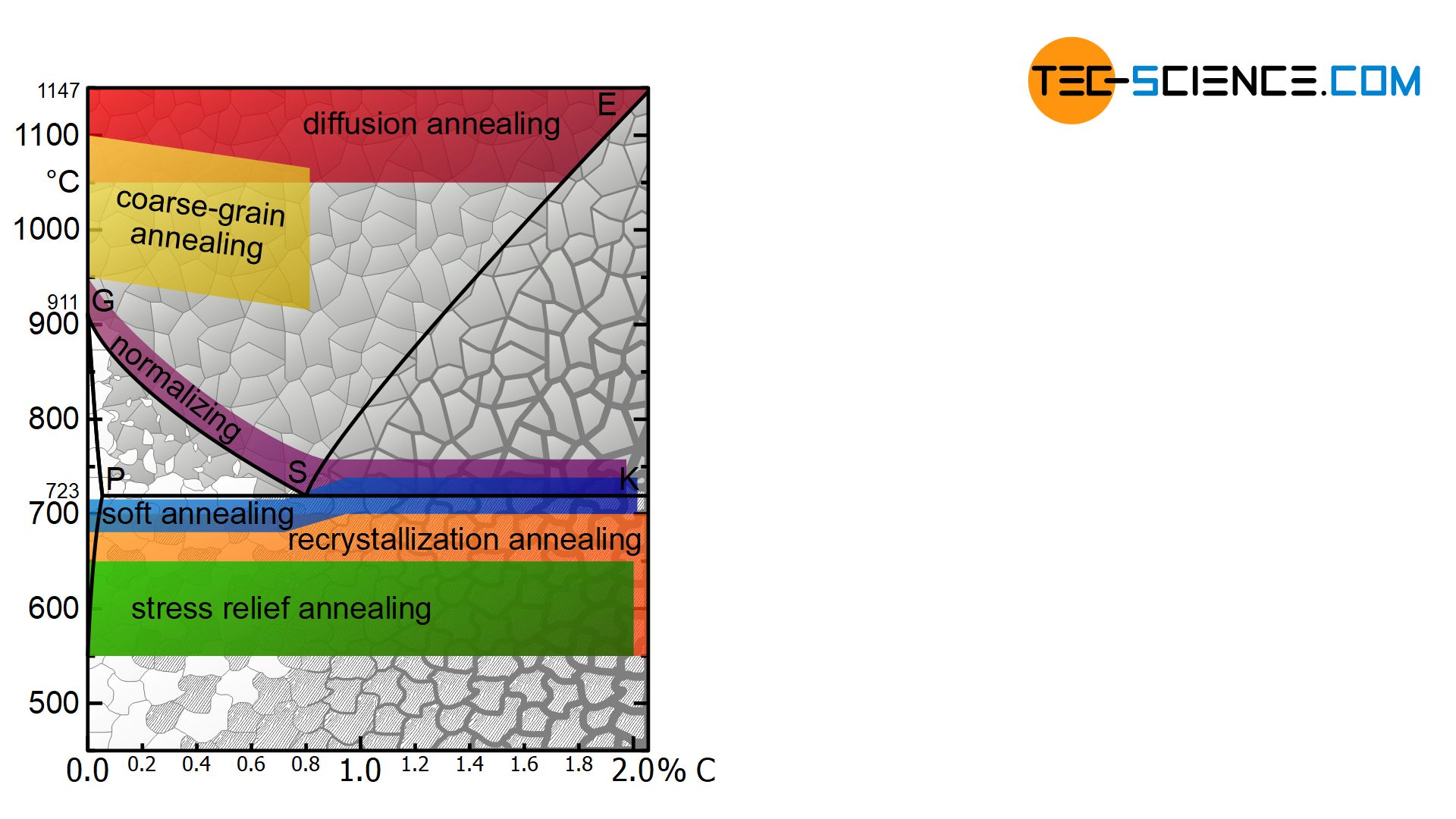
The temperature metals are heated to and the rate of cooling after heat treatment can significantly change metal’s properties. The most common reasons metals undergo heat treatment are to improve their strength, hardness, toughness, ductility and corrosion resistance. Get a better idea of the process with the examples of common heat treatments that follow. Understanding Annealing
Are metals good insulators of heat?
Metals such as copper typify conductors, while most non-metallic solids are said to be good insulators, having extremely high resistance to the flow of charge through them. Metals are also generally good heat conductors while nonmetals are not.
What are the applications of heat treatment of metals?
Heat treatment helps to improves a metal’s manufacturability. This is done by the removal of internal stress from previous fabrication processes such as hot work, cold work, machining, welding, and stamping. For example, if a metal is highly hard to bend or machine, it can be subjected to annealing or stress relieving.

What is metal heat treatment?
Heat treatment is the process of heating metal without letting it reach its molten, or melting, stage, and then cooling the metal in a controlled way to select desired mechanical properties. Heat treatment is used to either make metal stronger or more malleable, more resistant to abrasion or more ductile.
What is heat treatment method?
Heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to extreme temperatures, to achieve the desired result such as hardening or softening of a material. Heat treatment techniques include annealing, case hardening, precipitation strengthening, tempering, carburizing, normalizing and quenching.
What is heat treatment and why is it done?
Heat Treatment is the controlled heating and cooling of metals to alter their physical and mechanical properties without changing the product shape. Heat treatment is sometimes done inadvertently due to manufacturing processes that either heat or cool the metal such as welding or forming.
What is heat treatment of metal or alloys?
The heat treatment of metals involves raising the temperature of an alloy, often through a prescribed thermal profile, to a defined temperature. The material is then held at this temperature for a period of time before being cooled either at a prescribed rate or under rapid quenching conditions to a fixed temperature.
Why are metals heat treated?
Heat treating can improve wear resistance by hardening the material. Metals (including steel, titanium, inconel, and some copper alloys) can be hardened either on the surface (case hardening) or all the way through (through hardening), to make the material stronger, tougher, more durable and more resistant to wear.
Why is heat treatment important?
Heat treatment is an important process in the refining and petrochemical industry. It gives us the ability to alter the metallurgical characteristics of piping and equipment to better suit their intended applications. Oftentimes, this means altering a material's hardness, strength, toughness, ductility, and elasticity.
What are the 3 stages of heat treatment process?
The stages of the heat treatment process include heating, soaking, and cooling.Heating: Heating is the first stage in a heat-treating process. ... Soaking: Soaking is the stage at which the complete part of the heated metal completely changes in its structure. ... Cooling: The third stage of heat treatment is cooling.
What are the five basic heat treatment process?
There are five basic heat treating processes: hardening, case hardening, annealing, normalizing, and tempering. Although each of these processes bring about different results in metal, all of them involve three basic steps: heating, soaking, and cooling. Heating is the first step in a heat-treating process.
What are the properties of heat treatment?
The heat treatment develops hardness, softness, and improves the mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, ductility, corrosion resistance and creep rupture. These processes also help to improve machining effect, and make them versatile.
What is the process of heat treatment answer?
Heat Treatment Process Steps. In simple terms, heat treatment is the process of heating the metal, holding it at that temperature, and then cooling it back. During the process, the metal part will undergo changes in its mechanical properties. This is because the high temperature alters the microstructure of the metal.
What metals are heat treated?
Another heat-treatable metal is stainless steel. For stainless steel , they are generally treated based on the grade or alloy type. Heat treatment methods including hardening, stress-relieving, and annealing help to strengthen the corrosion resistance and ductility properties of stainless-steel during fabrication. It also helps to generate a hard structure that can resist abrasion and high mechanical stresses.
What is heat treatment?
Heat treatment is a general process of the usage of heating and cooling operations at various staged levels to alter the physical properties of metals (microstructure) such as steel, aluminum, and many more. The major purpose of such treatment is to improve the physical and structural properties for some specific use or future work of the metal. ...
What is quenching in metal?
Quenching or quench hardening involves the heating of parts above their upper critical temperature rapidly return such part’s temperature to room temperature. The returning to room temperature is done by placing the hot metal in the oil, brine, a polymer dissolved in water, or another suitable liquid to harden the structure fully. This process is carried out in a rapid state. Quenching is done for both ferrous alloys and non-ferrous alloys. While non-ferrous metal produces softer than normal parts, ferrous alloys produce a harder part.
What is the most heat treated ferrous metal?
As mentioned earlier, the most heat-treated ferrous metal is steel. The adjustment of the carbon content of steel is the simplest heat treatment of steel. This helps to change the mechanical properties of steel. Additional changes are done by heat treating – for example by accelerating the rate of the cooling through the austenite-to-ferrite transformation point. Also, increasing the rate of cooling of pearlitic steel (0.77% carbon) to about 200 o C per minute generates a DPH of about 300, and cooling at 400 o C per minute rases the DPH to about 400. The increasing hardness is attributed to the formation of a finer pearlite and ferrite microstructure that can be obtained during slow cooling under ambient air.
How does heat treatment work?
Heat treatment helps to improves a metal’s manufacturability. This is done by the removal of internal stress from previous fabrication processes such as hot work, cold work, machining, welding, and stamping. For example, if a metal is highly hard to bend or machine, it can be subjected to annealing or stress relieving. This will help to reduce the hardness of such material. If a material deforms when machined, to keep it from deformation, the material can be annealed or stress relieved. Heat treatment using induction or flame can also be used the soften a specific area of the metal, leaving the remaining part of the metal untouched.
What is annealing in metals?
Annealing is a heat treatment method that consists of heating a metal to a particular temperature and then cooling the same metal at a slow rate that will produce a refined microstructure. This process can be done either fully or partially by separating the constituents. This method is usually used to soften a metal for cold working to enhance its features or properties such as machinability, electrical conductivity, ductility, and toughness.
What happens if a metal is too brittle?
Besides, if the received material is too brittle, it can be heat treated either re-tempered or annealed to make it more usable (ductile). Improvement in Magnetic Properties. Many metals including 316 or 1008 tend to gain magnetism which is measure as magnetic permeability.
Why do metals need to be heat treated?
Heat Treatment of Metals. Metals can be heat treated to alter the properties of strength, ductility, toughness, hardness or resistance to corrosion. There is a number of phenomena that occur in metals and alloys at elevated temperatures.
What is metal processing?
Stone Age, Bronze Age, Iron Age). Processing of metals involves the production of alloys, the shaping, the heat treatment and the surface treatment of the product. Determining the hardness of the metal using the Rockwell, Vickers, and Brinell hardness scales is a commonly used practice that helps better understand the metal’s elasticity and plasticity for different applications and production processes. The task of material engineers is to achieve balance between material properties such as cost, weight, strength, toughness, hardness, corrosion, fatigue resistance, and performance in temperature extremes. To achieve this goal, the operating environment must be carefully considered. In a saltwater environment, ferrous metals and some aluminium alloys corrode quickly. Metals exposed to cold or cryogenic conditions may endure a ductile to brittle transition and lose their toughness, becoming more brittle and prone to cracking. Metals under continual cyclic loading can suffer from metal fatigue. Metals under constant stress at elevated temperatures can creep.
What is the purpose of tempering?
Tempering. The term tempering refers to a heat treatment which is used to increase the toughness of iron-based alloys. Tempering is usually performed after hardening, to reduce some of the excess hardness, and is done by heating the metal to some temperature below the critical point for a certain period of time, then allowing it to cool in still air. Tempering makes the metal less hard while making it better able to sustain impacts without breaking. Tempering will cause the dissolved alloying elements to precipitate, or in the case of quenched steels, improve impact strength and ductile properties.
What is annealing metal?
Annealing. The term annealing refers to a heat treatment in which a material is exposed to an elevated temperature for an extended time period and then slowly cooled. In this process, metal gets rid of stresses and makes the grain structure large and soft-edged so that when the metal is hit or stressed it dents or perhaps bends, rather than breaking; it is also easier to sand, grind, or cut annealed metal.
What is the process of quenching?
The term quenching refers to a heat treatment in which a material is rapidly cooled in water, oil or air to obtain certain material properties, especially hardness. In metallurgy, quenching is most commonly used to harden steel by introducing martensite. There is a balance between hardness and toughness in any steel; the harder the steel, the less tough or impact-resistant it is, and the more impact-resistant it is, the less hard it is.
What is Metal Heat Treatment?
Metal heat treatment is a process in which metal workpieces are heated to a suitable temperature in a certain medium, maintained at this temperature for a certain time, cooled at different speeds, and their properties are controlled by changing the surface or internal structure of metal materials.
Stages and Types of Heat Treatment Process
The heat treatment process includes three different stages: heating, soaking, and cooling. Sometimes there is only heating and cooling.
What metals are heat treated?
Iron and steel are the most common heat treated metals. However, non-ferrous metals such as aluminum alloys, copper, and other materials also benefit from the application of heat treating.
What industries benefit from heat treating metals?
The industries that benefit from heat treating metals are countless and include automotive, construction, aerospace, and agriculture, to mention just a few.
What is Heat Treating?
Many standard CNC production facilities use heat treating. Manufacturers can modify the strength, plasticity, and corrosion resistance of a finished component by opting to include a heat treatment process.
What is annealing furnace?
Annealing is one of the most common heat treatments and is achieved through retort, air, or vacuum processing. Retort furnaces are optimal for the continuous heat treating of small parts.
Why is quenching versus annealing important?
The goal of quenching versus annealing is to keep the metal’s original microstructure as intact as possible. This consistency is needed if the slower cooling process results in undesirable changes, such as making the material brittle.
How to cryogenically treat a part?
Cryogenic treating. Components can also be cryogenically treated by slowly lowering the temperature of a part in liquid nitrogen, leaving it in that state for a defined period, and then putting the part through a more standard heat treatment process. This cryogenic treating results in a more corrosion resistant piece.
Why is heat treated metal used in wire forming?
Specific heat treating processes will change the grain structure of steel, and make metals harder or more ductile – an optimal characteristic needed for wire forming. Additional reasons for incorporating heat treatment into the production process include increasing a metal’s resistance to electrical current or making it less magnetic.
