Blood pressure reduction is appropriate for the primary prevention of CAD in patients with hypertension. The consensus goal for blood pressure is less than 140/90 mm Hg in general.
Is 150 over 90 a good blood pressure?
Your blood pressure reading of 150/90 indicates Hypertension Stage 1. It is the lowest form of high blood pressure. A blood pressure on hypertension stage 1 for a longer period of time is not healthy, because it already means that your heart has a hard time supplying your body, your vessels and organs with blood.
How to treat high blood pressure naturally?
Your treatment plan may include one or more of the following medications:
- Beta-blockers. Beta-blockers work by blocking the action of chemicals in your body that stimulate your heart. ...
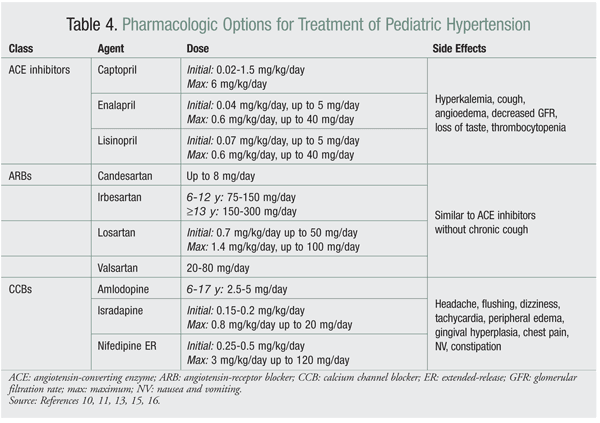
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ...
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). ...
- Calcium channel blockers. ...
- Diuretics. ...
- Vasodilators. ...
- Central agonists. ...
- Alpha-blockers and alpha-beta-blockers. ...
- Direct renin inhibitors (DRIs). ...
How to manage Stage 1 hypertension or mild hypertension?
Try to:
- Change your expectations. For example, plan your day and focus on your priorities. ...
- Focus on issues you can control and make plans to solve them. If you are having an issue at work, try talking to your manager. ...
- Avoid stress triggers. Try to avoid triggers when you can. ...
- Make time to relax and to do activities you enjoy. ...
- Practice gratitude. ...
What is the normal range for hypertension?
What can I do to prevent or manage high blood pressure?
- Getting at least 150 minutes of physical activity each week (about 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week)
- Not smoking
- Eating a healthy diet, including limiting sodium (salt) and alcohol
- Keeping a healthy weight
- Managing stress

What is the goal blood pressure for hypertension?
Evidence for the Universal Blood Pressure Goal of <130/80 mm Hg Is Strong | Hypertension.
What is the goal of blood pressure treatment?
The goal of hypertension treatment is to lower high blood pressure and protect important organs, like the brain, heart, and kidneys from damage.
What is the most important goal of treating hypertension?
The primary goal in the treatment of hypertension is to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients. Studies performed to assess the impact of treating hypertension have revealed very disappointing reductions in the incidence of coronary heart disease.
What is the goal of prevention of hypertension?
High blood pressure can often be prevented or reduced by eating healthily, maintaining a healthy weight, taking regular exercise, drinking alcohol in moderation and not smoking.
What range of blood pressure requires medication?
140/90 or higher (stage 2 hypertension): You probably need medication. At this level, your doctor is likely to prescribe medicine now to get your blood pressure under control. At the same time, you'll also need to make lifestyle changes. If you ever have blood pressure that's 180/120 or above, it's an emergency.
What is the best treatment for hypertension?
Here's what you can do:Eat healthy foods. Eat a heart-healthy diet. ... Decrease the salt in your diet. Aim to limit sodium to less than 2,300 milligrams (mg) a day or less. ... Maintain a healthy weight. ... Increase physical activity. ... Limit alcohol. ... Don't smoke. ... Manage stress. ... Monitor your blood pressure at home.More items...•
What is the target BP for patients with diabetes and hypertension?
Current ADA guidelines recommend a treatment goal of SBP <140 mmHg and DBP <90 mmHg for most patients with diabetes (Table 1). Those at higher cardiovascular risk may require more intensive blood pressure control to <130/80 mmHg.
Introduction
The guidelines on the management of hypertension released by European and US Task Forces in 2013 and 2014 1, 2 recommend target blood pressure (BP) levels below 140/90 mm Hg in most hypertensive patients, with higher values (<150/90 mm Hg) in the elderly.
The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial
The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) was performed in 9361 patients with a high cardiovascular risk and an entry systolic BP (SBP) of 130 to 180 mm Hg 3 who were randomized to an intensive (SBP <120 mm Hg) or a standard BP goal (SBP <140 mm Hg).
New Meta-Analyses
The results of SPRINT are in line with those of recent meta-analyses that have been able to include both early and late randomized trials, for a huge number of patients and outcomes, and thus with an extremely large statistical power.
Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus
Patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus carry a much greater cardiovascular risk, as well as a greater susceptibility to hypertension-related complications.
HOPE-3 Trial: Antihypertensive Treatment at High Normal BP and in Grade 1 Hypertension at Intermediate Cardiovascular Risk
The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE-3) trial 20 has recently investigated the effects of BP lowering in 12 705 people with an intermediate cardiovascular risk level and a baseline mean BP of 138/82 mm Hg who were randomized to take active drug treatment (a combination of an angiotensin receptor antagonist and a diuretic) or placebo during a median follow-up of 5.6 years.
Conclusions
In summary, the results of randomized clinical trials as well as of large-scale systematic reviews on the effects of BP reduction on cardiovascular risk provide new important ground for discussing the target BP to aim at by antihypertensive treatment, as well the BP level at which antihypertensive drug administration should be started.
Acknowledgments
The fruitful and precious comments of Prof Giuseppe Mancia are gratefully acknowledged.
What does blood pressure measure?
A blood pressure reading, as shown in the blood pressure monitor in the image, measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats (systolic pressure) in the first number, and the pressure in your arteries between heartbeats (diastolic pressure) in the second number.
Why do doctors take blood pressure readings?
Because blood pressure normally varies during the day and may increase during a doctor visit (white coat hypertension), your doctor will likely take several blood pressure readings at three or more separate appointments before diagnosing you with high blood pressure.
What is elevated blood pressure?
Elevated blood pressure is a systolic pressure ranging from 120 to 129 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure below (not above) 80 mm Hg. Elevated blood pressure tends to get worse over time unless steps are taken to control blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure may also be called prehypertension. Stage 1 hypertension.
What to do if you have chest pain?
If you also have chest pain, vision problems, numbness or weakness, breathing difficulty, or any other signs and symptoms of a stroke or heart attack, call 911 or your local emergency medical number. Both numbers in a blood pressure reading are important. But after age 50, the systolic reading is even more important.
How to stop high blood pressure?
Try the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, poultry, fish and low-fat dairy foods. Get plenty of potassium, which can help prevent and control high blood pressure. Eat less saturated fat and trans fat. Decrease the salt in your diet.
What happens if your blood pressure is high?
If your blood pressure remains stubbornly high despite taking at least three different types of high blood pressure drugs, one of which usually should be a diuretic, you may have resistant hypertension.
What tests are done to confirm if you have high blood pressure?
Ambulatory monitoring. This 24-hour blood pressure monitoring test is used to confirm if you have high blood pressure.

Introduction
- The guidelines on the management of hypertension released by European and US Task Forces in 2013 and 20141,2recommend target blood pressure (BP) levels below 140/90 mm Hg in most hypertensive patients, with higher values (<150/90 mm Hg) in the elderly. However, recent randomized trials as well as new meta-analyses of the available data have obtaine...
The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial
- The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) was performed in 9361 patients with a high cardiovascular risk and an entry systolic BP (SBP) of 130 to 180 mm Hg3 who were randomized to an intensive (SBP <120 mm Hg) or a standard BP goal (SBP <140 mm Hg). After a treatment duration longer than 3 years, the intensively treated group showed a 25% and 27% low…
New Meta-Analyses
- The results of SPRINT are in line with those of recent meta-analyses that have been able to include both early and late randomized trials, for a huge number of patients and outcomes, and thus with an extremely large statistical power. Xie et al11 have pooled data from 19 trials (44 989 participants), which evaluated the effect of more- versus less-intensive BP-lowering treatment o…
Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus
- Patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus carry a much greater cardiovascular risk, as well as a greater susceptibility to hypertension-related complications. Whether in these patients lower BP targets should be recommended is still matter of debate, however, because with few exceptions, reducing BP more aggressively has not been found to increase the protecti…
Conclusions
- In summary, the results of randomized clinical trials as well as of large-scale systematic reviews on the effects of BP reduction on cardiovascular risk provide new important ground for discussing the target BP to aim at by antihypertensive treatment, as well the BP level at which antihypertensive drug administration should be started. All these studies have largely focused o…