Cancer Genomics Overview. Cancer is a group of diseases caused by changes in DNA that alter cell behavior, causing uncontrollable growth and malignancy. These abnormalities can take many forms, including DNA mutations, rearrangements, deletions, amplifications, and the addition or removal of chemical marks.
Why is genomics important in cancer research?
Why Genomics Research Is Critical to Progress against Cancer. For example, the discovery of cancer-causing genetic and epigenetic changes in tumors has enabled the development of therapies that target these changes as well as diagnostic tests that identify patients who may benefit from these therapies.
What is advanced genomic cancer treatment?
Advanced genomic testing Immunotherapy Targeted therapy Advanced genomic testing is designed to help identify the DNA alterations that may be driving the growth of a specific tumor. Information about genomic mutations that are unique to your individual cancer may help doctors identify treatments designed to target those mutations.
What does the Human Genome Project mean for Cancer Research?
The Human Genome Project has allowed us to establish what "normal" usually looks like for a human genome, so that we can now tell when changes in our genome have taken place that lead to cancer.
What is genomic profiling for cancer?
FDA Approves Two Genomic Profiling Tests for Cancer Tests can identify different cancer-associated genetic alterations. Some tests, called whole-exome sequencing, look at all the genes in your cancer. Others, called whole-genome sequencing, look at all the DNA (both genes and outside of genes) in your cancer.

What is genomic cancer?
Cancer genomics is the study of the totality of DNA sequence and gene expression differences between tumour cells and normal host cells.
How is genomics used in cancer?
Genomic data is increasingly used alongside information about the morphology (visual appearance) of a tumour to inform diagnosis, treatment selection and management of the patient and their family; there is a need for all oncologists to be up to date with genomics, as testing is increasingly part of the diagnostic ...
What is genomic treatment?
Genomic medicine is an emerging medical discipline that involves using genomic information about an individual as part of their clinical care (e.g. for diagnostic or therapeutic decision-making) and the health outcomes and policy implications of that clinical use.
Can genome sequencing cure cancer?
Researchers have used whole genome sequencing to analyse breast cancers and reveal which are more responsive to treatments, which could improve the development of oncologic therapies. A study has found that whole genome sequencing (WGS) of tumour cells could be used to improve cancer treatments.
How long does genomic testing take?
Genomic Testing Cooperative (GTC) is using disruptive technology and will report results within 5-10 days of receiving the sample. GTC tests all exons of 434 genes for solid tumors and 179 genes for hematology and provides a comprehensive report within 7 days from receiving a sample at our lab.
How does genomics work?
Genomics is the study of whole genomes of organisms, and incorporates elements from genetics. Genomics uses a combination of recombinant DNA, DNA sequencing methods, and bioinformatics to sequence, assemble, and analyse the structure and function of genomes.
What is an example of genomic medicine?
The ways in which genomic medicine is making a difference As an example, take the treatment of colorectal cancers. Some people with a particular gene mutation have better survival rates when treated with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, such as aspirin, than those without this mutation.
What is the difference between genetic and genomic medicine?
The main difference between genomics and genetics is that genetics scrutinizes the functioning and composition of the single gene where as genomics addresses all genes and their inter relationships in order to identify their combined influence on the growth and development of the organism.
How expensive is genomic testing?
Genomic testing of tumor tissue includes tests to look for changes in a specific gene or chromosome, as well as tumor-panel tests to look for changes in multiple genes at the same time. These tests can cost from $300 to over $10,000, and the prices of targeted treatments are often higher than $100,000 a year.
How has gene sequencing improved treatment of cancer?
Now, technology is once again transforming our understanding of cancer's origins and complexity. Instead of broad categorizations based on the location of tumours, genome sequencing is providing detailed characterizations of the combination of genetic mutations that trigger or aid cancer development in an individual.
What is genome sequencing and how is it done?
Listen to pronunciation. (jeh-NOH-mik SEE-kwen-sing) A laboratory method that is used to determine the entire genetic makeup of a specific organism or cell type. This method can be used to find changes in areas of the genome.
How do cancer cells come back?
Cancer may sometimes come back after cancer drug treatment or radiotherapy. This can happen because the treatment didn't destroy all the cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells by attacking cells that are in the process of doubling to form 2 new cells.
What is the role of BRAF in cancer?
The mutation in the BRAF gene, which encodes the protein BRAF, plays an important role in cell growth. Because the BRAF protein is constantly active, it continuously generates signals for the growth of the cell. This causes both cancer development and a faster course for an existing cancer. The effect of BRAF mutation has been clearly demonstrated in many cancers such as colorectal, lung, and malignant melanoma. Therefore, drugs that prevent BRAF protein from working, have been developed.
What are the mutations in the MET gene?
Mutations in the MET (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ) gene and its MET receptor, also known as hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR), can induce cancer growth, either by an increase in the number of gene copies, or specific alterations such as MET Exon 14. This condition is most common in lung, head and neck, liver, gastric and other cancers. Today, there are several drugs that prevent tumor growth and bind to the MET receptor to prevent it from working. However, before treatment and these drugs are used, MET mutation analysis must be performed, usually with advanced genomic testing.
Why is genomics important?
Why Genomics Research Is Critical to Progress against Cancer. The study of cancer genomes has revealed abnormalities in genes that drive the development and growth of many types of cancer. This knowledge has improved our understanding of the biology of cancer and led to new methods of diagnosing and treating the disease.
What are the challenges of genomics?
Another challenge is acquiring high-quality biological samples needed for genomic studies, particularly for tumor types that are uncommon or rare, or those not treated primarily by surgery. Developing cell lines and animal models that capture the diversity of human cancer is also an unmet need.
Why is CGCI important?
This large number is important for discovering DNA, RNA, and protein abnormalities that are responsible for cancers in small numbers of patients. The Cancer Genome Characterization Initiative (CGCI) also studies cancer genomes, including cancers associated with HIV infection.
What is HCMI in cancer?
The Human Cancer Models Initiative (HCMI) is generating new cancer models using cutting-edge technologies. These models will provide researchers with more accurate representations of a wide variety of cancers, and genomic characterization of the models may reveal links between genomic traits and how cells behave.
What cancers are caused by mutations in the HER2 gene?
For instance, mutations in the HER2 gene (distinct from amplifications of this gene, for which therapies have been developed for breast, esophageal, and gastric cancers) have been found in a number of cancers, including breast, bladder, pancreatic, and ovarian.
What type of cancer has molecular subtypes?
Researchers have also shown that a given type of cancer, such as breast, lung, and stomach, may have several molecular subtypes. For some types of cancer, the existence of certain subtypes had not been known until researchers began to profile the genomes of tumor cells.
What is the FDA approved drug for melanoma?
One such targeted drug is vemurafenib (Zelboraf), which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2011 for the treatment of some patients with melanoma who have a specific mutation in the BRAF gene as detected by an FDA-approved test. Over the past decade, large-scale research projects have begun to survey and catalog ...
What Is Genomic Testing?
Genomic testing is helpful in treating cancer because it looks at how genetic mutations can influence the behavior of cancer, including how aggressive it is, whether it will spread (metastasize) throughout the body, and what treatments might work best.
Is Genomic Testing the Same As Genetic Testing?
Genomic testing is not exactly the same as genetic testing. Both genomic testing and genetic testing involve studying genetic material, but genetic testing looks at the genes people inherit from their parents and can help detect a person’s risk for cancers and other diseases. A genetic test is useful to:
How Is Genomic Testing Used for Cancer Treatment?
Tumor genomic profiling (also called tumor profiling) can help determine which treatments might be most effective against cancer.
What is advanced genomic testing?
Advanced genomic testing is designed to help identify the DNA alterations that may be driving the growth of a specific tumor. Information about genomic mutations that are unique to your individual cancer may help doctors identify treatments designed to target those mutations.
What diseases are linked to genomics?
Researchers have used the discoveries to link dozens of diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and inherited colon cancer, to specific genes. In recent years, researchers have taken the advancements one step further, with genomic tests of the cancer itself.
What are some examples of cancers that are similar to cancer?
Some cancers even bear similarities to cancers that were once thought to be completely different. A breast tumor, for example, may look and act like a lung tumor. By looking at the tumor’s profile with genomic testing, physicians may be able to recommend a drug or protocol not previously considered.
How many genes are in a human cell?
Researchers mapped the entire human genetic code, discovering that every human cell is packed with an estimated 20,000 to 30,000 genes. This marked a dramatic shift in the understanding of cancer and other diseases.
Is genomic testing harmful?
Instead of one-size-fits-all medicine, which can lead to unnecessary and even harmful treatments for some patients, advanced genomic testing devotes its attention to studying a single individual—the patient whose tumor is being tested.
Is cancer in the breast a lung cancer?
The traditional approach to cancer care defined the disease and its treatment by its location—cancer in the breast is breast cancer; cancer in the lung is lung cancer. Cancer treatment has typically followed a similarly generalized line of attack. In recent years, researchers and physicians have found that a cancer in one patient may not behave ...
Is genomic testing appropriate for cancer patients?
Precision cancer care is an evolving science, and advanced genomic testing is not appropriate for every patient. Even when the test is recommended, it may not produce results that lead directly to a treatment plan. The analyses may help doctors consider more precise therapies in many cases, but not all mutations can be matched with known treatment ...
How does genomics help cancer?
As well as advancing physicians’ understanding of what causes each person’s cancer, genomics is providing insights into how an individual’s cancer might progress, and its likely response to treatment. For some, this information will save their lives — knowledge of the genetic drivers of cancer is already changing how some people’s cancer is treated.
How many cancer samples are there in the cancer genome?
The Cancer Genome Atlas programme, set up by the US National Cancer Institute (NCI), has sequenced more than 20,000 primary cancer samples of 33 cancer types. This is just one of a suite of NCI initiatives to collect and analyse cancer-genomic data, and support the translation of those data into new treatments.
What is genome sequencing?
Genome sequencing is providing physicians with more data about the causes of cancer and changing the way some forms of the disease are treated. Bianca Nogrady is a freelance science writer in Sydney, Australia. DNA sequencing allows oncologists to characterize tumours on the basis of genetic mutations.
Who says identifying cancer-causing mutations is particularly important for haematological cancers?
Piers Blombery (left) says identifying cancer-causing mutations is particularly important for haematological cancers. Credit: Vision Super Pty Ltd. The possibility of treating cancer on the basis of an individual tumour’s genetic profile has led to a surge in cancer-genome profiling of patients.
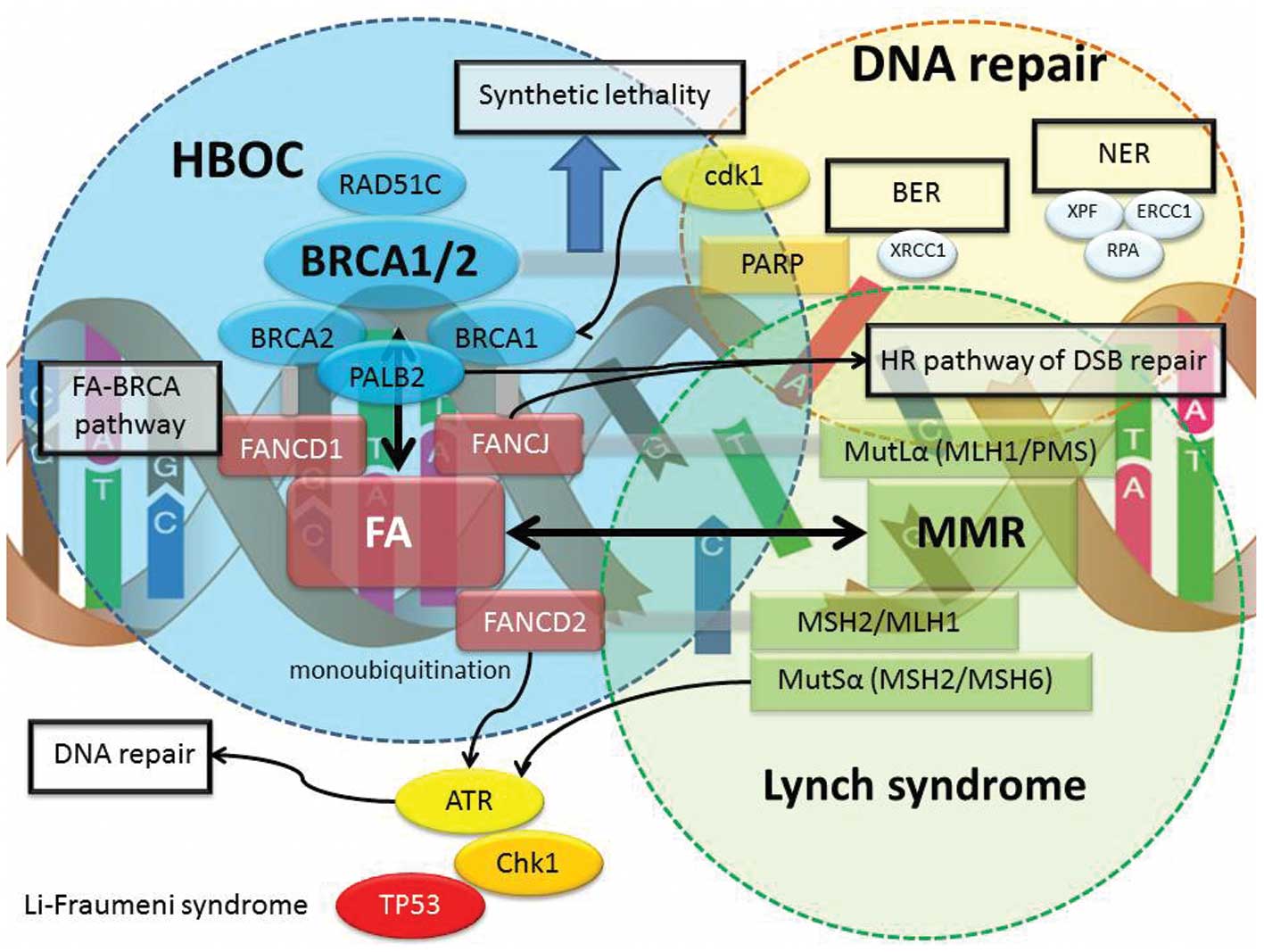
Which genes are linked to breast cancer?
Mutations in the tumour-suppressor genes BRCA1 and BRCA2, for example, have been linked to a much higher risk of breast, ovarian and prostate cancer. Part of Nature Outlook: Cancer diagnosis.
Who first identified cancer?
Download PDF. When cancer was first described by the ancient Greek physician Hippocrates, he identified just two forms: the non-ulcer-forming carcinos and the ulcer-forming carcinoma. In the late nineteenth century, physicians found, with the help of the microscope, that cancer had multiple cellular forms.
Is genetic mutation a target for drug development?
For others, it currently only adds new data, not years to their lives or new treatment options. But each cancer- causing or cancer-influencing genetic mutation that is discovered is a potential target for drug development, including for cancers for which there are currently few treatment choices.
What is the FDA testing for cancer?
FDA Approves Two Genomic Profiling Tests for Cancer. Tests can identify different cancer-associated genetic alterations. Some tests, called whole-exome sequencing, look at all the genes in your cancer. Others, called whole-genome sequencing, look at all the DNA (both genes and outside of genes) in your cancer.
What type of cancer is a biomarker?
Biomarker testing is also done routinely to select treatment for people who are diagnosed with certain types of cancer—including non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer.
What are biomarkers used for?
Most biomarker tests used to select cancer treatment look for genetic markers. But some look for proteins or other kinds of markers. Some tests check for one certain biomarker. Others check for many biomarkers at the same time and may be called multigene test s or panel tests.
Why are biomarkers not helpful?
One other reason biomarker tests might not help is because the biomarkers in your cancer can change over time.
What is biomarker testing?
Biomarker testing is a way to look for genes, proteins, and other substances (called biomarkers or tumor markers) that can provide information about cancer. Each person’s cancer has a unique pattern of biomarkers. Some biomarkers affect how certain cancer treatments work. Biomarker testing may help you and your doctor choose a cancer treatment ...
Why isn't my cancer test working?
There could be several different reasons why they may not help you. One reason is that the test might not find a biomarker in your cancer that matches with an available therapy. Even if your cancer has a biomarker that matches an available treatment , the therapy may not work for you.
What is precision medicine?
For cancer treatment, precision medicine means using biomarker and other tests to select treatments that are most likely to help you, while at the same time sparing you from getting treatments that are not likely to help.
