Medication
Surgery. Surgery for retinoblastoma includes: Surgery to remove the affected eye (enucleation). During surgery to remove the eye, surgeons disconnect the muscles and tissue around the eye and remove the eyeball. A portion of the optic nerve, which extends from the back of the eye into the brain, also is removed.
Procedures
Plaque radiotherapy can also be used to manage diffuse anterior segment retinoblastoma with or without IVC in the absence of choroidal or retinal tumors. Typically, a 2 mm safety margin is added to the largest basal diameter for optimal tumor coverage.
Nutrition
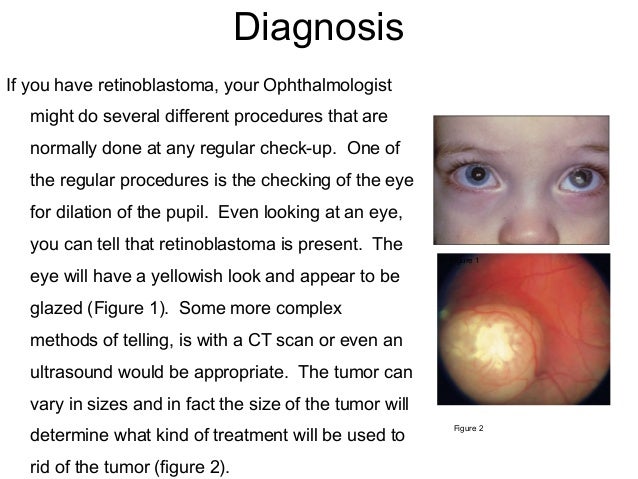
Intraocular retinoblastoma. In intraocular retinoblastoma, cancer is found in one or both eyes and may be in the retina only or may also be in other parts of the eye such as the choroid, ciliary body, or part of the optic nerve. Cancer has not spread to tissues around the outside of the eye or to other parts of the body.
See more
What is the treatment for retinoblastoma?
How is diffuse anterior segment retinoblastoma treated with plaque radiotherapy?
What is intraocular retinoblastoma?
What is the most common treatment for retinoblastoma?
The main types of treatment for retinoblastoma are: Surgery (Enucleation) for Retinoblastoma. Radiation Therapy for Retinoblastoma. Laser Therapy (Photocoagulation or Thermotherapy) for Retinoblastoma.
What is laser therapy for retinoblastoma?
Laser therapy is a noninvasive, outpatient treatment for retinoblastoma. Lasers very effectively destroy smaller retinoblastoma tumors. This type of treatment is usually done by focusing light through the pupil onto and around the tumor. The light slowly heats up the tumor, destroying it.
What chemotherapy is used for retinoblastoma?
The drugs used most often for retinoblastoma are vincristine (Oncovin, Vincasar PFS), carboplatin (Paraplatin), and etoposide (Toposar, VePesid). Depending on the extent of the tumor, a combination of 2 or more drugs may be recommended. All chemotherapy has side effects that occur during treatment.
How long is retinoblastoma treatment?
If the retinoblastoma is in both eyes, doctors will try to save at least one eye if at all possible so that the child maintains some vision. Many children will get several types of treatment. Treatment might be needed for months or even years.
What is Cryotherapy for retinoblastoma?
In cryotherapy, the doctor uses a small metal probe that is cooled to very low temperatures, killing the retinoblastoma cells by freezing them. It is only effective for small tumors toward the front of the eye. It is not used routinely for children with several tumors.
What is photocoagulation of retina?
Photocoagulation of the retina or retinal laser photocoagulation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat various diseases of the retina. Several conditions may cause the retina to swell due to abnormal leaky blood vessels growing over it.
Can retinoblastoma come back?
While it is unlikely, retinoblastoma can come back after treatment. Your child is at highest risk for recurrence until age 6, but retinoblastoma can even return later in life. We will carefully monitor your child to catch any recurrences at the earliest stages.
What is the survival rate of retinoblastoma?
Doctors often use the observed survival rate when they talk about a prognosis. The 5-year observed survival for retinoblastoma in children 0 to 14 years of age is 96%. This means that, on average, 96% of children diagnosed with retinoblastoma are expected to live at least 5 years after their diagnosis.
What cyclophosphamide is used for?
Cyclophosphamide is used to treat cancer of the ovaries, breast, blood and lymph system, and nerves (mainly in children). Cyclophosphamide is also used for retinoblastoma (a type of eye cancer mainly in children), multiple myeloma (cancer in the bone marrow), and mycosis fungoides (tumors on the skin).
Is there any cure for retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma is almost always curable, especially if it hasn't spread beyond the eye. Children treated for retinoblastoma need very close follow-up care. Your child will have frequent checkups to watch for signs that the cancer has come back.
What happens if retinoblastoma is not treated?
Untreated, retinoblastoma can spread widely: Throughout the retina. Throughout the fluid inside the eye (also called the vitreous). Large tumors may detach from the retina and break into smaller tumors, called vitreous seeds.
Is retinoblastoma benign or malignant?
A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread. Retinoblastoma is a rare cancer that begins in the part of the eye called the retina. The retina is a thin layer of nerve tissue that coats the back of the eye and enables the eye to see.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is when doctors use drugs to treat cancer. Doctors use these treatments to shrink the tumor. Chemotherapy is the most common treatment for retinoblastoma. It’s often the first treatment doctors try, and it may help your child avoid surgery.
Cryotherapy (freeze therapy)
During cryotherapy, doctors place a very cold tool called a freezing pen (probe) on the surface of the eye. Using this pen, doctors freeze and thaw the tumor cells several times to kill them. This helps keep the tumor cells from spreading outside of the eye.
Laser therapy
Doctors can use different lasers to heat and kill cancer cells directly — or to destroy the blood vessels in the eye that are “feeding” the tumor.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses x-rays to kill cancer cells. There are 2 types of radiation therapy:
Surgery
In some cases, doctors may recommend surgery to get rid of the tumor by removing the eye completely. Doctors may recommend surgery if the tumor:
What kind of doctor treats retinoblastoma?
Children with retinoblastoma are treated by a team of doctors that often includes: 1 A pediatric ophthalmologist: a doctor who treats eye diseases in children 2 An ocular oncologist: a doctor (usually an ophthalmologist) who treats cancers of the eye 3 A pediatric oncologist: a doctor who treats children with cancer 4 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy
Why is it important to treat hereditary retinoblastoma?
To preserve as much vision as possible. To limit the risk of side effects later in life that can be caused by treatment, particularly second cancers in children with hereditary retinoblastoma. The most important factors that help determine treatment are: The size and location of the tumor (s)
What to do when your child has cancer?
Making treatment decisions. Once the cancer is found and the needed tests have been done, the cancer care team will discuss treatment options with you. It’s important to discuss all of the options as well as their possible side effects with your child’s doctors to help you make an informed decision.
How many children with retinoblastoma are cured?
Overall, more than 9 in 10 children with retinoblastoma are cured. The chances of long-term survival are much better if the tumor has not spread outside the eye. Treatment of Retinoblastoma, Based on Extent of the Disease.
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. The team might also include other doctors, physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, therapists, child psychologists, social workers, genetic counselors, and other professionals.
What are the services that help with cancer?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. For children and teens with cancer and their families, other specialists can be an important part of care as well.
What can I do to help my child with a tumor?
These methods can include vitamins, herbs, and special diets, or other methods such as acupuncture or massage, to name a few.
What is the treatment for retinoblastoma?
The treatment usually starts with chemotherapy, followed by focal treatments. Surgery might still be needed if these treatments aren’t effective. If the cancer has spread outside of the eye, treatment is usually a combination of chemotherapy, radiation, and in some cases surgery. In all cases, children who have had retinoblastoma need ...
What is the treatment for a tumor in the eye?
Treatment options might include brachytherapy (plaque radiotherapy), cryotherapy, or laser therapy (photocoagulation or thermotherapy).
What is the best treatment for cancer in the eye?
If the cancer is in only one eye and the potential for saving sight is good, chemotherapy (either by vein or directly into the artery of the eye) and focal treatments such as cryotherapy, laser therapy (photocoagulation or thermotherapy), or plaque radiation are used (although very small tumors, which are very rare, can be treated with focal treatments alone). If there is little or no chance to save the eye (or useful vision), the eye will likely need to be removed.
What happens if a child has retinoblastoma?
If your child has retinoblastoma, a number of factors can affect the treatment options your child’s doctor recommends. Some of these include: Many of these factors are taken into account as part of the stage of the cancer. If the retinoblastoma is only in one eye, treatment depends on whether vision in the eye can be saved.
How long does it take for a tumor to shrink?
If systemic chemotherapy (chemotherapy given by vein) is used, it is typically given for about 6 months to shrink the tumor as much as possible. More recently, many centers have begun to give chemotherapy directly into the artery that feeds the eye ...
How to treat eye cancer?
If the tumor is small, the child’s sight can often be saved and the cancer destroyed with local treatments such as cryotherapy, laser therapy, radiation therapy (if not already used), or other treatments.
What is the treatment for cancer in the orbit?
If the cancer has spread only to the orbit (the area around the eye), treatment with chemotherapy, surgical removal (enu cleation) of the eye, and radiation therapy to the orbit is often successful. If the cancer has spread outside the orbit to distant parts of the body such as the liver or the bones and bone marrow, ...
What is the treatment for retinoblastoma?
Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Types of radiation therapy used in treating retinoblastoma include: Local radiation. During local radiation, also called plaque radiotherapy or brachytherapy, the treatment device is temporarily placed near the tumor.
What is the procedure to remove retinoblastoma?
Eye removal surgery for retinoblastoma includes: Surgery to remove the affected eye (enucleation). During surgery to remove the eye, surgeons disconnect the muscles and tissue around the eye and remove the eyeball. A portion of the optic nerve, which extends from the back of the eye into the brain, also is removed.
How to diagnose retinoblastoma in children?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose retinoblastoma include: Eye exam. Your eye doctor will conduct an eye exam to determine what's causing your child's signs and symptoms. For a more thorough exam, the doctor may recommend using anesthetics to keep your child still. Imaging tests.
Why do you put radiation near a tumor?
Placing radiation near the tumor reduces the chance that treatment will affect healthy tissues outside the eye. This type of radiotherapy is typically used for tumors that don't respond to chemotherapy. External beam radiation.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Cold treatment (cryotherapy) Cryotherapy uses extreme cold to kill cancer cells. During cryotherapy , a very cold substance, such as liquid nitrogen, is placed in or near the cancer cells. Once the cells freeze, the cold substance is removed and the cells thaw.
What tests can be done to determine if a child has retinoblastoma?
Imaging tests. Scans and other imaging tests can help your child's doctor determine whether retinoblastoma has grown to affect other structures around the eye. Imaging tests may include ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), among others.
Can you remove your eye to treat retinoblastoma?
When the cancer is too large to be treated by other methods, surgery to remove the eye may be used to treat retinoblastoma. In these situations, eye removal may help prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body. Eye removal surgery for retinoblastoma includes:
What is the treatment for retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma: Focal Therapy – Laser Treatment, Cryotherapy , and Brachytherapy. Tumors not more than 3 mm in diameter with no evidence of seeding, and located anterior to the equator. “Cutting cryo” for posterior tumors.
What is focal treatment in oncology?
The term “consolidation,” as used in oncology, is a therapy that is used in tandem with primary therapy to “mop up” or eliminate the tumor cells that were resistant to, or were not inactivated by, the primary therapy. In most other childhood tumors, consolidation involves switching treatment modalities entirely or at least changing to different agents and/or doses of the primary modality. In the case of intraocular retinoblastoma, focal consolidation consists of direct laser photocoagulation, thermotherapy, cryotherapy, or brachytherapy.
How effective is an 810 nm laser?
The 810 nm diode laser is most effective when there is intact RPE beneath the tumor. Through a 28D lens, the indirect ophthalmoscope delivery system offers a spot size of 0.35 mm (small spot) and 1.4 mm (large spot). We typically use the large spot indirect system, which provides improved safety and convenience for treating larger tumors versus the argon laser. Safety comes from the reduced likelihood of concentrated power intensity in a small spot creating tumor dissemination. The larger spot size as compared with argon saves treatment time, thus conferring convenience. It is also our impression that the depth of treatment with the diode laser is greater than the argon laser. However, it is more difficult to control the size of the burn with the diode laser, and care is warranted near the optic nerve and fovea.
What is retinoblastoma eye exam?
Key Points. Retinoblastoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the retina. Children with a family history of retinoblastoma should have eye exams to check for retinoblastoma. Retinoblastoma occurs in heritable and nonheritable forms.
Where is intraocular retinoblastoma found?
In intraocular retinoblastoma, cancer is found in one or both eyes and may be in the retina only or may also be in other parts of the eye such as the choroid, ciliary body, or part of the optic nerve. Cancer has not spread to tissues around the outside of the eye or to other parts of the body.
What is the heritable form of retinoblastoma?
A child is thought to have the heritable (inherited) form of retinoblastoma when there is a certain mutation (change) in the RB1 gene. The mutation in the RB1 gene may be passed from the parent to the child, or it may occur in the egg or sperm before conception or soon after conception.
Why is retinoblastoma not a routine screening?
CT (computerized tomography) scans are usually not used for routine screening in order to avoid exposing the child to ionizing radiation. Heritable retinoblastoma also increases the child's risk of other types of cancer such as lung cancer, bladder cancer, or melanoma in later years.
How old is a child diagnosed with retinoblastoma?
The brain tumor is usually diagnosed between 20 and 36 months of age. Regular screening using MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may be done for a child thought to have heritable retinoblastoma or for a child with retinoblastoma in one eye and a family history of the disease.
How often do you check for retinoblastoma?
After heritable retinoblastoma has been diagnosed and treated, new tumors may continue to form for a few years. Regular eye exams to check for new tumors are usually done every 2 to 4 months for at least 28 months.
What is the name of the disease where the brain receives light?
Retinoblastoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the retina. The retina is made of nerve tissue that lines the inside wall of the back of the eye. It receives light and converts the light into signals that travel down the optic nerve to the brain.
What is EBRT therapy?
Prior to the introduction to IVC, external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) was used as globe salvage therapy. Today, EBRT is mostly of historical significance in most developed nations, due to the many associated side effects and improved outcomes following introduction of effective chemotherapy for retinoblastoma.
How much safety margin is needed for optic nerve tumor?
Typically, a 2 mm safety margin is added to the largest basal diameter for optimal tumor coverage. Tumors within 2 mm of the optic nerve require a notched plaque, with deep notch used for 3 or more clock hours of tumor around the nerve.
Can antibiotics be used to treat papillary conjunctivitis?
Infection can be managed topically or systemically with antibiotics but implant removal can be necessary in severe cases. Giant papillary conjunctivitis secondary to continuous contact of the prosthesis can be managed with antibiotic-steroid ointments and copious amounts of lubricants.
Is IvitC used as primary therapy?
3]. It is noteworthy to highlight that IvitC is almost never used as primary therapy, but mostly as globe salvage therapy, given the limited efficacy on the primary tumor.
Is retinoblastoma a cancer?
Retinoblastoma, the most common ocular malignancy in childhood, is lethal if left untreated. In high-income countries (HICs), retinoblastoma is considered a curable cancer with a near 100% disease-free survival rate.[1] .