Medications with A1c of 7.0
- Rapid-Acting Injections The insulin takes effect within 5 to 15 minutes and lasts for 2 to 4 hours. ...
- Short-Acting Injections The insulin takes effect between 30 minutes and 1 hour and lasts for 3 to 6 hours. ...
- Intermediate-Acting Injections The insulin takes effect between 1 to 4 hours and lasts for 12 to 18 hours. ...
Full Answer
Is an A1C of 7 good for diabetes?
An A1c of 7.1 falls into the diabetic range between 6.5 and 10.0. Reducing an A1c of 7.1 will take a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications. Seek medical advice to gain control of your blood sugar and avoid further damage to critical organs.
How can I lower my A1c from 7?
An A1c of 7.0 falls into the diabetic range between 6.5 and 10.0. Reducing an A1c of 7.0 will take a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications. Seek medical advice to gain control of your blood sugar and avoid further damage to critical organs. Keep an eye on your blood sugar by testing at home.
What should I do if my A1c test shows prediabetes?
If your result shows you have prediabetes, talk to your doctor about taking steps now to improve your health and lower your risk for type 2 diabetes. Repeat the A1C test as often as your doctor recommends, usually every 1 to 2 years.
What is the A1c test?
The A1C test—also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c test—is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months. It’s one of the commonly used tests to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, and is also the main test to help you and your health care team manage your diabetes.

At what A1C level do you start medication?
What A1c levels require medication/treatment? There is no specific A1c level that makes it necessary for you to be on medication. While an A1c of 6.5% or higher is indicative of diabetes, some people may need to start taking medication for an A1c under 6.5%.
What happens if your A1C is over 7?
Your A1C Result A normal A1C level is below 5.7%, a level of 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, and a level of 6.5% or more indicates diabetes. Within the 5.7% to 6.4% prediabetes range, the higher your A1C, the greater your risk is for developing type 2 diabetes.
Is 7 high for diabetic?
Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is normal. 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) is diagnosed as prediabetes. 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests is diagnosed as diabetes.
What does an A1C of 7.1 mean?
An A1c level of 7.1 percent is considered high and means that 7.1% of the hemoglobin in your blood is saturated with sugar. A1c levels of 6.5 or greater are considered diabetes. If your A1c is high, a combination of diet and lifestyle changes and medications can help you lower your levels.
What is the danger zone for A1c?
What are dangerous levels?A1C valueeAG valuePotential diagnosis5.6% or less117 mg/dl or lessNormal5.7–6.4%117–137 mg/dlPrediabetes6.5% or more137 mg/dlDiabetesOct 29, 2021
How can I get my A1c down quickly?
Since exercise prompts your muscles to take up sugar from your bloodstream, it helps your blood sugar levels drop more quickly after you eat a meal. As you make exercise a regular habit, you'll see a downward trend in your A1c numbers. Never miss your meds. You can reliably lower your A1c through diet and exercise.
Is 7.2 blood sugar normal?
A fasting blood sugar level less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is normal. A fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) is considered prediabetes. If it's 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests, you have diabetes.
What is the best medicine to lower A1C?
While results showed liraglutide and insulin were the most (and similarly) effective in keeping A1C levels less than 7%, glimepiride had a smaller effect and sitagliptin showed the lowest effect, resulting in the highest frequency of developing A1C levels persistently greater than 7%.
What blood sugar level requires insulin?
Insulin therapy will often need to be started if the initial fasting plasma glucose is greater than 250 or the HbA1c is greater than 10%.
Is 7.0 A good A1c?
An A1C reading of 7.0 or less indicates that your blood sugar control is probably quite good. Patients who maintain their hemoglobin AIC levels below 7.0 are less at risk for developing the complications of diabetes and are more likely to retain their vision. Hemoglobin AIC readings above 8.0 are not as good.
Is 7.0 blood sugar normal?
In general: Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L ) is normal. 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L ) is diagnosed as prediabetes. 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L ) or higher on two separate tests is diagnosed as diabetes.
How much can I lower my A1c in a month?
If you, from one day to the next, decreased your daily average blood sugar from 300 mg/dl (16.7 mmol/l) to 120 mg/dl (6.7 mmol/l), your A1c would decrease from 12% to 6% in around two months. However, it may not be a good idea to lower your A1c so quickly, as I will explain below.
How to reduce A1C to 7.0?
Reducing an A1c of 7.0 will take a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications. Seek medical advice to gain control of your blood sugar and avoid further damage to critical organs. Keep an eye on your blood sugar by testing at home.
What does 7.0 mean on A1C?
An A1C of 7.0 means that you have diabetes. The A1c test measures blood sugar over the last three months by looking at the percentage of hemoglobin saturated with sugar. An A1c of 7.0 means that 7.0% of the hemoglobin in your blood are saturated with sugar. You may already be experiencing symptoms of diabetes, which include increased thirst, ...
How long does insulin take to take effect?
Intermediate-Acting Injections. The insulin takes effect between 1 to 4 hours and lasts for 12 to 18 hours. Often referred to as NPH insulin, popular brands include Humulin N and Novolin N. Long-Acting Injections. The insulin takes effect after 1 or 2 hours and lasts up to 24 hours.
How long does insulin take to work in diabetes?
There are four main forms of insulin. Rapid-Acting Injections. The insulin takes effect within 5 to 15 minutes and lasts for 2 to 4 hours.
What drugs are used to treat sugar in urine?
Popular brands of SGLT2 Inhibitors include Invokana, Farxiga, Jardiance and Steglatro .
What is a GLP-1 agonist?
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. These injectable medications are also referred to as incretin mimetics. This class of drug mimics the hormone incretin, which stimulates the release of insulin after meals. GLP-1 receptor agonists are also associated with modest weight loss and may reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
What is the best medicine for diabetes?
Metformin. This oral biguanide is often the first medication prescribed for type 2 diabetes. Metformin reduces glucose production in the liver, decreases the absorption of glucose in the stomach and improves your body’s insulin sensitivity. Popular brands include Glucophage and Glumetza. Sulfonylureas.
What does A1C mean?
It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. The higher your blood sugar levels, the more hemoglobin you'll have with sugar attached. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates that you have diabetes.
How to treat type 1 diabetes?
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. Treatment of type 2 diabetes primarily involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with diabetes medications, insulin or both.
What are the best ways to treat diabetes?
Treatment. Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral medications may play a role in your treatment. Eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight and participating in regular activity also are important factors in managing diabetes.
How to prevent prediabetes?
Make physical activity part of your daily routine. Regular exercise can help prevent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, and it can help those who already have diabetes to maintain better blood sugar control. A minimum of 30 minutes of moderate exercise — such as brisk walking — most days of the week is recommended.
When was the artificial pancreas approved?
A second artificial pancreas was approved in December 2019.
What is the best diet for diabetics?
Contrary to popular perception, there's no specific diabetes diet. You'll need to center your diet on more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains — foods that are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fat and calories — and cut down on saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and sweets.
What blood test is used to determine blood sugar levels?
Tests for type 1 and type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test. This blood test, which doesn't require fasting, indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells.
What does A1C mean in a child?
This test indicates your child's average blood sugar level for the past three months. An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes. Fasting blood sugar test. A blood sample is taken after your child fasts overnight.
What is the recommended A1C level for a child?
The American Diabetes Association generally recommends an A1C of 7.5 or lower for all children and teens.
How to treat diabetes in children?
Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes: Taking insulin. Carbohydrate counting. Frequent blood sugar monitoring.
What to do if your child's blood sugar is high?
If your child's blood sugar is higher than the target range, follow your child's diabetes treatment plan or check with your child's doctor. High blood sugar levels don't come down quickly, so ask your doctor how long to wait until you check your child's blood sugar again.
What tests are needed to determine if you have type 1 diabetes?
If blood sugar testing indicates diabetes, your doctor will likely recommend additional tests to distinguish between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes because treatment strategies differ by type. These additional tests include: Blood tests to check for antibodies that are common in type 1 diabetes. Urine or blood tests to check ...
What is the best way to deliver insulin?
There are several options for insulin delivery, including: Fine needle and syringe. This looks like a shot you might get in a doctor's office, but with a much thinner needle. Insulin pen with fine needle. This device looks like an ink pen, except the cartridge is filled with insulin. An insulin pump.
What type of diabetes is a hospitalization?
Preparing for your appointment. Your child's primary care doctor will probably make the initial diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Hospitalization is often needed to stabilize your child's blood sugar levels.
What is the best A1C level for diabetics?
The findings of a major diabetes study, the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT), showed that people who keep their hemoglobin A1c levels close to 7% have a much better chance of delaying or preventing complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, and nerves than people with hemoglobin A1c of approximately 9%.
What is the A1C test?
The hemoglobin A1c test, sometimes called a glycated hemoglobin test, measures the proportion of hemoglobin molecules in your red blood cells that have glucose attached to them (and thus are “glycated”).
How often should I get a hemoglobin A1C test?
If your treatment changes or if your blood sugar level stays too high, you should get a hemoglobin A1c test at least every three months until your blood sugar level improves.
What is the purpose of blood sugar testing?
Regular testing will help you and your doctor to track your blood sugar levels over time and plan long-term treatment options to reach your target level of control . Hemoglobin is an oxygen-carrying pigment-it’s what makes red blood cells red.
What is the A1C level for diabetes?
However, for some people, especially older adults and those with certain medical conditions or limited life expectancy, a higher A1C level of up to 8% may be appropriate.
How does A1C work?
This blood test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. It works by measuring the percentage of blood sugar attached to the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells (hemoglobin).
How does insulin help with hyperglycemia?
Insulin reverses the processes that cause ketones to build up in your blood. Along with fluids and electrolytes, you'll receive insulin therapy — usually through a vein. As your body chemistry returns to normal, your doctor will consider what may have triggered the severe hyperglycemia.
How to treat hyperglycemia?
If you have frequent episodes of hyperglycemia, your doctor may adjust the dosage or timing of your medication. Follow your diabetes eating plan. It helps to eat smaller portions and avoid sugary beverages and frequent snacking. If you're having trouble sticking to your meal plan, ask your doctor or dietitian for help. Check your blood sugar.
What is the purpose of insulin supplement?
Adjustments to your insulin program or a supplement of short-acting insulin can help control hyperglycemia. A supplement is an extra dose of insulin used to help temporarily correct a high blood sugar level. Ask your doctor how often you need an insulin supplement if you have high blood sugar.
What is the recommended blood sugar level for diabetics?
For many people who have diabetes, the American Diabetes Association generally recommends the following target blood sugar levels: Between 80 and 130 mg/dL (4.4 and 7.2 mmol/L) before meals. Your target blood sugar range may differ, especially if you're pregnant or you have developed diabetes complications.
How to control blood sugar?
Your doctor may suggest the following treatments: Get physical. Regular exercise is often an effective way to control your blood sugar.
How to reduce A1C to 7.1?
Reducing an A1c of 7.1 will take a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications. Seek medical advice to gain control of your blood sugar and avoid further damage to critical organs. Keep an eye on your blood sugar by testing at home.
What does 7.1 mean on A1C?
An A1c of 7.1 means that 7.1% of the hemoglobin in your blood are saturated with sugar. You may already be experiencing symptoms of diabetes, which include increased thirst, frequent urination, ...
How long does insulin take to take effect?
Intermediate-Acting Injections. The insulin takes effect between 1 to 4 hours and lasts for 12 to 18 hours. Often referred to as NPH insulin, popular brands include Humulin N and Novolin N. Long-Acting Injections. The insulin takes effect after 1 or 2 hours and lasts up to 24 hours.
How long does insulin take to work in diabetes?
There are four main forms of insulin. Rapid-Acting Injections. The insulin takes effect within 5 to 15 minutes and lasts for 2 to 4 hours.
What drugs are used to treat sugar in urine?
Popular brands of SGLT2 Inhibitors include Invokana, Farxiga, Jardiance and Steglatro .
What is a GLP-1 agonist?
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. These injectable medications are also referred to as incretin mimetics. This class of drug mimics the hormone incretin, which stimulates the release of insulin after meals. GLP-1 receptor agonists are also associated with modest weight loss and may reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
What is the best medicine for diabetes?
Metformin. This oral biguanide is often the first medication prescribed for type 2 diabetes. Metformin reduces glucose production in the liver, decreases the absorption of glucose in the stomach and improves your body’s insulin sensitivity. Popular brands include Glucophage and Glumetza. Sulfonylureas.
Case for guidelines
Evidence-based recommendations should be at the core of the guidelines. Not all practice guidelines on antihyperglycemic drugs, however, are consistent with available evidence ( 12 ).
Specific advantages and disadvantages of individual main drug classes
Metformin as first-line therapy is in the general consensus, since its efficacy is similar to other antihyperglycemic drugs—besides insulin. It has a large safety margin and can be used by most patients other than a small number who experience gastrointestinal side effects.
Other antihyperglycemic drug options
Other antihyperglycemic drugs including α-glucosidase inhibitors, pramlintide, colesevelam, and quick-release bromocriptin are in general less effective, associated with adverse events that limit their use as second or third line in patients who fail to reach target with metformin, or there is very limited experience of their use; they will not be discussed further..
Identifiable clinical groups of patients
Both A1C target and antihyperglycemic drugs used to achieve the target might need specific considerations for identifiable clinical groups of patients, i.e., patients with comorbidities or patients with short life expectancy. In this counterpoint article, however, we focus on patients with long-term good prognosis.
Economic considerations
There is a paucity of studies today to demonstrate the cost-effectiveness of relatively new antihyperglycemic drugs in diabetes.
Stepwise treatment according to guidelines: is it justified?
The answer is yes, since under current guideline therapy, with the availability of newer drug classes with minor side effects, using a stepwise increase in antihyperglycemic drug therapy as soon as A1C is above target can be implemented and might prevent disease progression similarly to combination or triple therapy.
When did A1C test become available?
Some people may have high blood sugars at 3 a.m. and be totally unaware of it. Once A1C tests became available in the 1980s, they became an important tool in controlling diabetes. A1C tests measure average blood glucose over the past two to three months.
What is A1C blood test?
Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test This test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. Specifically, the test measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells (hemoglobin).
What does a high A1C mean?
An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests indicates you have diabetes . A result between 5.7 and 6.4 percent is considered prediabetes, which indicates a high risk of developing diabetes.
What is the blood test for HBA1C?
Hemoglobin A1c Test (hba1c) Hemoglobin A1c, often abbreviated HbA1c, is a form of hemoglobin (a blood pigment that carries oxygen) that is bound to glucose. The blood test for HbA1c level is routinely performed in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
What is the name of the test that measures hemoglobin?
Other alternate names include the glycosylated hemo globin test, glycohemoglobin test, and glycated hemoglobin test. A1C measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it. Hemoglobin is a protein found inside red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body.
What blood test is used to diagnose type 2 diabetes?
Print Diagnosis To diagnose type 2 diabetes, you'll be given a: Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test. This blood test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells.
What does it mean if your A1C is 6.5%?
If the glucose level is 200 mg/dL or higher at 2 hours, then you might have diabetes. The A1c test is a simple blood test that shows your average blood sugar levels for the past 2-3 months. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher may mean you have diabetes. Your doctor may also suggest a zinc transporter 8 autoantibody (ZnT8Ab) test.

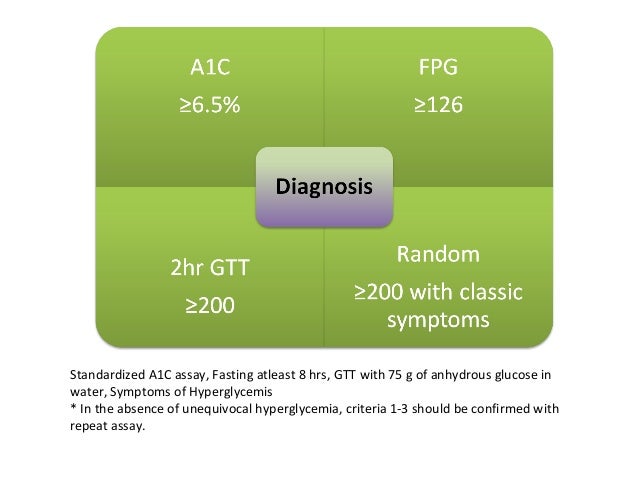
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral medications may play a role in your treatment. Eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight and participating in regular activity also are important factors in managing diabetes.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Diabetes is a serious disease. Following your diabetes treatment plan takes round-the-clock commitment. Careful management of diabetes can reduce your risk of serious — even life-threatening — complications. 1. Make a commitment to managing your diabetes.Learn all you can about diabetes. Establish a relationship with a diabetes educator, and ask your diabetes treatme…
Alternative Medicine
- Numerous substances have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity in some studies, while other studies fail to find any benefit for blood sugar control or in lowering A1C levels. Because of the conflicting findings, there aren't any alternative therapies that are currently recommended to help everyone with blood sugar management. If you decide to try any type of alternative therapy, don'…
Coping and Support
- Living with diabetes can be difficult and frustrating. Sometimes, even when you've done everything right, your blood sugar levels may rise. But stick with your diabetes management plan, and you'll likely see a positive difference in your A1C when you visit your doctor. Because good diabetes management can be time-consuming, and sometimes overwhelming, some people fin…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to start by seeing your primary care doctor if you're having diabetes symptoms. If your child is having diabetes symptoms, you might see your child's pediatrician. If blood sugar levels are extremely high, you'll likely be sent to the emergency room. If blood sugar levels aren't high enough to put you or your child immediately at risk, you may be referred to a doctor who speciali…
Diagnosis
- There are several blood tests for type 1 diabetes in children. These tests are used to diagnose diabetes and to monitor diabetes management: 1. Random blood sugar test.This is the primary screening test for type 1 diabetes. A blood sample is taken at a random time. A blood sugar level of 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 11.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L), or higher, along wit…
Treatment
- Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes: 1. Taking insulin 2. Monitoring blood sugar 3. Eating healthy foods 4. Exercising regularly You'll work closely with your child's diabetes treatment team — health care provider, certified diabetes care and education specialist, and registered dietitian. The goal of treatment is to keep your child's blood suga...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Following a diabetes treatment plan requires 24-hour care and significant lifestyle changes. Careful management of type 1 diabetes helps reduce your child's risk of serious complications. As your child gets older: 1. Encourage him or her to take an increasingly active role in diabetes management 2. Stress the importance of lifelong diabetes care 3. Teach your child how to test h…
Coping and Support
- If managing your child's diabetes seems overwhelming, take it one day at a time. Some days you'll manage your child's blood sugar ideally and on other days, it may seem as if nothing works well. No one can do it perfectly. But your efforts are worthwhile. Don't forget that you're not alone and that your diabetes treatment team can help.
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Your child's primary care provider will probably make the initial diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Hospitalization may be needed to stabilize your child's blood sugar levels. Your child's long-term diabetes care will likely be handled by a pediatric endocrinologist. Your child's health care team also generally includes a certified diabetes care and education specialist, a registered dietitian, a…