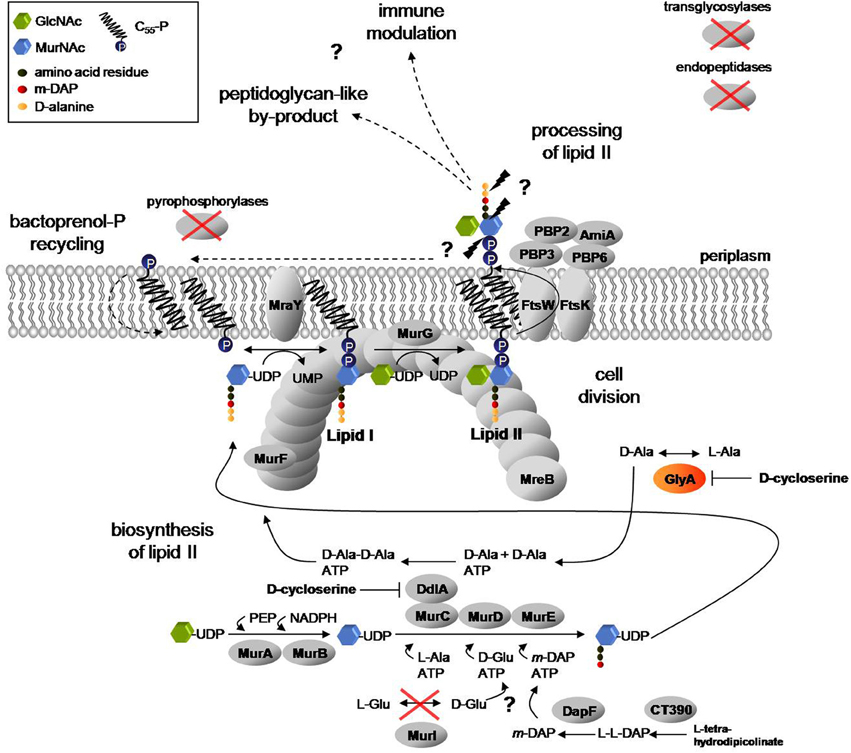
2.0 Treatment of streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus vaccine. ...
- Antibiotic treatment of streptococcal pneumonia. ...
- Penicillin. ...
- Vancomycin and linezolid. ...
- Haemophilus influenza. ...
- Legionella species. ...
- Viral pneumonia treatment. ...
- Vaccine. ...
- Oseltamivir mode of action. ...
- Influenza pneumonia. ...
What is the first-line treatment for bacterial pneumonia?
In previously healthy patients who are appropriate for outpatient treatment, recommended first-line treatment is with a macrolide antibiotic such as azithromycin targeting the most common causal pathogen S. pneumoniae. Doxycycline is an alternative option.
How long should antibiotics be used to treat streptococcus pneumoniae?
Antibiotics are active against the Streptococcus Pneumoniae. once a day not more than 10 days. The introduction of the drug is recommended to continue for another 2-3 days after normalization of body temperature and symptoms disappear.
What are the treatment options for pneumococcal infections?
Treatment. Antibiotic treatment for invasive pneumococcal infections typically includes ‘broad-spectrum’ antibiotics until results of antibiotic sensitivity testing are available. Broad-spectrum antibiotics work against a wide range of bacteria. Once the sensitivity of the bacteria is known, a more targeted (or ‘narrow spectrum’)...
What antibiotics are used to treat pneumonia?
Even in case of gram positive bacteria, the antibiotics group for treating a Streptococcus pneumoniae infection and a Staphylococcus aureus infection of the lungs will differ! Coming back to treating pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, the preferred antibiotics are erythromycin and amoxicillin.
See more
Which antibiotic is best for Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Penicillin and its derivatives are inexpensive effective antibiotics for treating pneumococcal infections when they are used against susceptible isolates. Penicillins can be administered orally or parenterally and work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
What are treatments for streptococcus pneumoniae?
Treatment. Invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae infections are treated with antibiotics. There is an increasing problem of Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria developing drug resistance due to the overuse and misuse of antibiotics.
What is the best IV antibiotic for pneumonia?
Cefuroxime and levofloxacin were the most commonly used IV agents, while orally-treated subjects primarily received a macrolide or levofloxacin. The proportion of subjects receiving IV antibiotics differed significantly among the seven sites: 1.4%–10.6% (p > 0.0001).
What antibiotic regimen should be started to treat both pneumonia and meningitis?
People with pneumococcal meningitis will be admitted to the hospital for immediate intravenous antibiotic treatment. Typically, doctors use an antibiotic called ceftriaxone to treat pneumococcal meningitis....Other antibiotics used include:penicillin.benzylpenicillin.cefotaxime.chloramphenicol.vancomycin.
What antibiotic kills Streptococcus?
Doctors most often prescribe penicillin or amoxicillin (Amoxil) to treat strep throat. They are the top choices because they're safer, inexpensive, and they work well on strep bacteria.
Does azithromycin treat Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Conclusion: Most patients responed well to azithromycin, indicating that azithromycin might be clinically effective for the treatment of CAP with macrolide-resistant S. pneumoniae. However, a larger study is necessary to prove the efficacy against macrolide-resistant S. pneumoniae.
What is the initial antibiotic treatment for pneumonia based on?
The Pneumonia Severity Index should be used to assist in decisions regarding hospitalization of patients with CAP. The initial treatment of CAP is empiric, and macrolides or doxycycline (Vibramycin) should be used in most patients.
What is the drug of choice for pneumonia?
In otherwise uncomplicated pneumonia, azithromycin is the initial drug of choice, as it covers most of the potential etiologic agents, including Mycoplasma species.
What is the most common treatment for pneumonia?
Mild pneumonia can usually be treated at home with rest, antibiotics (if it's likely be caused by a bacterial infection) and by drinking plenty of fluids. More severe cases may need hospital treatment.
Does doxycycline treat Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Doxycycline is now used primarily for the treatment of presumed or proven atypical pneumonias since some physicians are hesitant to use it as monotherapy in community-acquired pneumonia because of presumed inactivity against Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Does amoxicillin treat Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Amoxicillin Is Effective against Penicillin-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Strains in a Mouse Pneumonia Model Simulating Human Pharmacokinetics.
Does levofloxacin cover Strep Pneumo?
Conclusions: These data support the use of levofloxacin for patients with community-acquired pneumonia caused by S. pneumoniae, including MDR strains.
How many serotypes are there in Streptococcus pneumoniae?
There are 100 known serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae, the bacteria that cause pneumococcal disease. Streptococcus pneumoniae are lancet-shaped, gram-positive, facultative anaerobic bacteria with 100 known serotypes. Most S. pneumoniae serotypes can cause disease, but only a minority of serotypes produce the majority of pneumococcal infections.
How many people are carriers of pneumococci?
The bacteria may be isolated from the nasopharynx of 5–90% of healthy persons, depending on the population and setting: 5–10% of adults without children are carriers. 20–60% of school-aged children may be carriers.
What is the best medicine for pneumonia?
To treat outpatients for pneumonia, the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends, in no particular order, a macrolide, doxycycline, amoxicillin (with or without clavulanic acid), or a quinolone.
How often should I use port scoring for pneumonia?
The importance of the decision to hospitalize or even to directly admit to intensive care cannot be overemphasized, and Pneumonia Patient Outcomes Research Team (PORT) scoring should be used to help decide whether hospitalization is needed. Pneumococcal pneumonia caused by organisms that are susceptible or intermediately resistant to penicillin responds to treatment with penicillin, one million units intravenously every 4 hours, ampicillin, 1g every 6 hours, or ceftriaxone, 1g every 24 hours. Ease of administration favors the use of ceftriaxone. The principal problem is that at the time treatment is begun, the etiology is likely not to be known. If a Gram stain of sputum at admission shows pneumococci, ceftriaxone is the preferred drug, unless the patient is extremely ill, in which case vancomycin should be added until the susceptibility of the infecting organism is known.
How many pneumococci are susceptible to penicillin?
93% of all pneumococci are susceptible to penicillin if given parenterally or amoxicillin if given orally; 5% are intermediate, and 2% are resistant. In cases of meningitis, 65% of organisms are susceptible to penicillin and 35% are resistant (no intermediate resistance is defined).
How long can you take amoxicillin for tympanic membrane?
In the absence of a perforated tympanic membrane or some other complication, therapy need not be continued beyond 5 days.
What is the MIC of penicillin?
For infections other than those involving the CNS that are treated with parenteral penicillin, susceptibility, intermediate resistance and resistance to penicillin are now defined as mean inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than 2μg/mL, 4μg/mL, and greater than or equal to 8μg/mL, respectively.
What causes pneumonia in the lungs?
S. pneumoniae causes infection of the middle ear, sinuses, trachea, bronchi, and lungs by direct spread of organisms from the nasopharyngeal site of colonization and causes infection of the CNS, heart valves, bones, and joints by hematogenous spread; the peritoneal cavity may be infected by local extension along the female genital tract or hematogenously. Infection of the pleura or peritoneal cavity and also of the CNS may occur by direct extension or by hematogenous spread; in any individual case, the route of infection can usually not be determined.
What is the MIC of a CNS infection?
In CNS infection, organisms with MIC less than or equal to 0.06μg/mL are susceptible; those with MIC greater than or equal to 0.12μg/mL are regarded as resistant. Similar approaches have been developed to define susceptibility to amoxicillin, ceftriaxone, and other beta-lactam antibiotics.
How many cases of pneumococcal infection are resistant to antibiotics?
Available data. show that pneumococcal bacteria are resistant to one or more antibiotics in 3 out of every 10 cases. Antibiotic treatment for serious pneumococcal infections typically includes ‘broad-spectrum’ antibiotics until results of antibiotic sensitivity testing are available.
What fluid is collected during lumbar puncture?
If doctors suspect serious pneumococcal disease, like meningitis or bloodstream infections, they will collect samples of cerebrospinal fluid or blood. Cerebrospinal fluid is fluid near the spinal cord. View the lumbar puncture illustration to see how a doctor collects this fluid. Doctors then send the samples to a laboratory for testing.
Can a doctor test for pneumonia?
Doctors can use a urine test to help make a diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia in adults. Doctors usually diagnose ear and sinus infections based on a history and physical exam findings that support pneumococcal infection.
Do antibiotics work against bacteria?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics work against a wide range of bacteria. Once the sensitivity of the bacteria is known, clinicians may choose a more targeted (or ‘narrow-spectrum’) antibiotic. The number of antibiotic-resistant pneumococcal infections has decreased due to the success of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine.
What antibiotics are used for C. pneumoniae?
C. pneumoniae shows in vitro resistance to the following antibiotics, which are not recommended for treatment: 1 Penicillin 2 Ampicillin 3 Sulfa drugs
Can C pneumoniae reappear after antibiotics?
Symptoms of C. pneumoniae infection can reappear after a short or conventional course of antibiotics. Persistent infection after treatment has been demonstrated by recovery of viable bacteria; therefore, a secondary course of treatment may be recommended.
