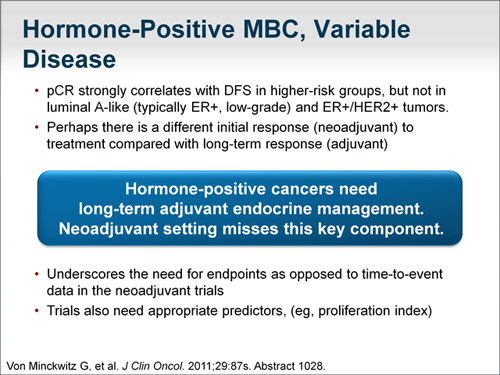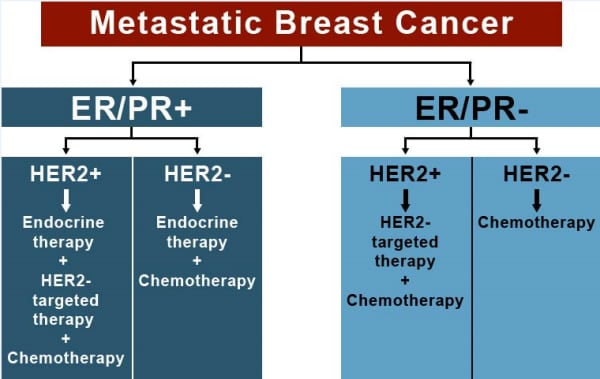
The treatment of choice in women with estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer (ER+ mBC) is classically divided into a variety of endocrine therapies, with three of the most common being: selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERM), aromatase inhibitors (AI), and selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERD).
What is the first-line treatment for breast cancer?
As mentioned above, the initial combination of medications for people with cancer that is positive for the estrogen or progesterone receptors depends on the occurrence of menopause. Chemotherapy may also be a first-line option for breast cancer that is not affected by hormonal therapy.
How is estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer (ER+ MBC) treated?
The treatment of choice in women with estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer (ER+ mBC) is classically divided into a variety of endocrine therapies, with three of the most common being: selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERM), aromatase inhibitors (AI), and selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERD).
How common is ER positive metastatic breast cancer?
Management of ER positive metastatic breast cancer There are over 2 million cases a year of breast cancer, leading to over 600,000 deaths globally [1]. Despite these large numbers, increasingly more women are being cured with early stage disease and women with advanced disease are living longer [2].
What are the treatment options for ER-positive breast cancer?
There are a few different treatment methods for ER-positive breast cancer. Your treatment plan will likely depend on what stage the cancer is in and whether you’re premenopausal or postmenopausal. All women who have ER-positive breast cancer will be recommended a type of hormone therapy.

What is first-line treatment for metastatic breast cancer?
Hormone therapy and targeted therapy. As described above, hormone therapy with or without targeted therapy is generally given as front-line treatment for metastatic breast cancer.
What chemo is used for ER positive breast cancer?
If a woman has a hormone receptor-positive (ER-positive or PR-positive) breast cancer, most doctors will recommend hormone therapy (tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor, or one followed by the other) as an adjuvant (after surgery) treatment, no matter how small the tumor is.
What is the latest treatment for metastatic breast cancer?
In March 2019 , the FDA approved atezolizumab (Tecentriq), a new type of drug known as a PD-L1 inhibitor. Atezolizumab is approved for people with locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) that can't be surgically removed, or whose tumors express a protein called PD-L1.
What is 1 treatment option for a patient who has breast cancer?
Summary of surgical options. To summarize, surgical treatment options include the following: Removal of cancer in the breast: Lumpectomy or partial mastectomy, generally followed by radiation therapy if the cancer is invasive. Mastectomy may also be recommended, with or without immediate reconstruction.
Is chemo necessary for ER-positive?
Most instances of ER-positive, HER2-negative, node-negative breast cancer <1 cm, and all cancers ≤0.5 cm, have a sufficiently good prognosis with endocrine therapy alone, that they do not typically require adjuvant chemotherapy.
How long can you take letrozole for metastatic cancer?
Most people are given letrozole for 5 years, but some will take it for up to 10 years.
Can I live 10 years with metastatic breast cancer?
What is the prognosis? While there is no cure for metastatic breast cancer, there are treatments that slow the cancer, extending the patient's life while also improving the quality of life, Henry says. Many patients now live 10 years or more after a metastatic diagnosis.
What is the life expectancy of someone with metastatic breast cancer?
While treatable, metastatic breast cancer (MBC) cannot be cured. The five-year survival rate for stage 4 breast cancer is 22 percent; median survival is three years. Annually, the disease takes 40,000 lives.
Can metastatic breast cancer go into remission?
Metastatic breast cancer may never go away completely. But treatment can control its spread. Cancer may even go into remission at some points. This means you have fewer signs and symptoms of cancer.
What is the gold standard for breast cancer treatment?
Abstract. Tamoxifen is currently the endocrine treatment of choice for all stages of breast cancer and is the gold standard for antiestrogen treatment. Over the last 25 years, the drug has revolutionized breast cancer therapy.
What is the most successful breast cancer treatment?
The most common form of treatment for breast cancer is surgery. This involves removing the tumor and nearby margins. Surgical options may include a lumpectomy, partial mastectomy, radical mastectomy, and reconstruction.
Is chemotherapy necessary for stage 1 breast cancer?
Chemotherapy is not usually offered for stage 1 breast tumours. It may be offered after surgery (called adjuvant therapy) for these tumours if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back (recur). Find out more about the risk of breast cancer recurrence and adjuvant therapy.
What happens if you have ER positive breast cancer?
If you have ER-positive breast cancer, your cancer cells grow in the presence of the hormone estrogen. Estrogen occurs naturally in the body.
What to do if your doctor suspects breast cancer?
If your doctor suspects breast cancer, you will likely have a biopsy to test for cancerous cells. If there is cancer, your doctor will also test the cells for characteristics that include what receptors, if any, are present on the surface of the cancer cells.
What receptors interact with estrogen?
Hormone receptors can interact with estrogen or progesterone. Estrogen receptors are the most common. This is why ER-positive is the most common form of breast cancer. Some people are diagnosed with progesterone receptor-positive (PR-positive) breast cancer. The key difference is whether cancerous cells are getting growth signals from estrogen ...
What are the receptors in breast cancer?
In breast cancer, hormone receptors are the proteins located in and around breast cells. These receptors signal cells — both healthy and cancerous — to grow. In the case of breast cancer, the hormone receptors tell the cancer cells to grow uncontrollably, and a tumor results. Hormone receptors can interact with estrogen or progesterone.
What is estrogen receptor positive?
Estrogen receptor-positive (ER-positive) breast cancer is the most common type of breast cancer diagnosed today. According to the American Cancer Society, about 2 out of every 3 cases of breast cancer are hormone receptor-positive. Most of these cases are ER-positive, meaning that there are estrogen receptors on the surface ...
What is the test for cancer recurrence?
The test examines 21 genes in cancerous tumors to identify the potential relapse rate. If you have a low recurrence score, you will likely not need chemotherapy. If you have a high recurrence score, you will likely need chemotherapy, surgery, and hormone therapy.
What does each number mean for breast cancer?
Each number reflects different characteristics of your breast cancer. These include the size of the tumor and whether cancer has moved into lymph nodes or distant organs, like the lungs, bones, or brain. The cancer subtype doesn’t play a role in staging, only in treatment decisions.
What is the treatment for estrogen receptor positive cancer?
Women with hormone receptor-positive (estrogen receptor-positive or progesterone receptor-positive) cancers are often treated first with hormone therapy (tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor). This may be combined with a targeted drug such as a CDK4/6 inhibitor, everolimus or a PI3K inhibitor.
What is the treatment for HER2 negative cancer?
HER2-negative cancers in women with a BRCA gene mutation. These women are typically treated with chemotherapy (and hormone therapy, if the cancer is hormone receptor-positive). An option after getting chemo is treatment with a targeted drug called a PARP inhibitor, such as olaparib or talazoparib.
What hormones are used for cancer?
For hormone receptor-positive (ER-positive or PR-positive) cancers that were being treated with hormone therapy, switching to another type of hormone therapy sometimes helps. For example, if either letrozole (Femara) or anastrozole (Arimidex) were given, using exemestane, possibly with everolimus (Afinitor), may be an option. Another option might be using fulvestrant (Faslodex) or an aromatase inhibitor (such as letrozole), along with a CDK inhibitor. If the cancer has a PIK3CA mutation and has grown while on an aromatase inhibitor, fulvestrant with alpelisib might be considered. If the cancer is no longer responding to any hormone drugs, chemotherapy is usually the next step.
What is the best treatment for bone metastases?
Treatment to relieve symptoms depends on where the cancer has spread. For example, pain from bone metastases may be treated with radiation therapy, drugs called bisphosphonates such as pamidronate (Aredia) or zoledronic acid (Zometa), or the drug denosumab (Xgeva).
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy and/or surgery may also be used in certain situations, such as: When the breast tumor is causing an open wound in the breast (or chest) To treat a small number of metastases in a certain area, such as the brain. To help prevent bone fractures. When an area of cancer spread is pressing on the spinal cord.
What is the immunotherapy for triple negative breast cancer?
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) The immunotherapy dug atezolizumab (Tecentriq) can be used along with albumin-bound paclitaxel (Abraxane) in people with advanced triple-negative breast cancer whose tumor makes the PD-L1 protein. (The PD-L1 protein is found is about 20% of triple-negative breast cancers.)
Where does stage IV breast cancer go?
When breast cancer spreads, it most commonly goes to the bones, liver, and lungs. It may also spread to the brain or other organs.
How many cases of ER positive breast cancer are there?
Management of ER positive metastatic breast cancer. There are over 2 million cases a year of breast cancer, leading to over 600,000 deaths globally [1]. Despite these large numbers, increasingly more women are being cured with early stage disease and women with advanced disease are living longer [2]. The appreciation for molecular subtypes of the ...
How many people die from breast cancer a year?
There are over 2 million cases a year of breast cancer, leading to over 600,000 deaths globally [1]. Despite these large numbers, increasingly more women are being cured with early stage disease and women with advanced disease are living longer [2]. The appreciation for molecular subtypes of the disease has led to significant therapeutic advances ...
Is chemo still used for ER+?
In addition, chemotherapy is still used frequently when endocrine manipulations have been exhausted. Like other incurable malignancies, the goal in advanced ER+ breast cancer is to prolong survival and maintain quality of life.
What is the treatment for stage 1 breast cancer?
Local therapy (surgery and radiation therapy) Surgery is the main treatment for stage I breast cancer. These cancers can be treated with either breast-conserving surgery (BCS; sometimes called lumpectomy or partial mastectomy) or mastectomy.
What are the stages of breast cancer?
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include: 1 Chemotherapy 2 Hormone therapy (tamoxifen, an aromatase inhibitor, or one followed by the other) 3 HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) 4 Some combination of these
What is the treatment for BCS?
Women who have BCS are treated with radiation therapy after surgery. Women who have a mastectomy are typically treated with radiation if the cancer is found in the lymph nodes.
How big is a stage 3 breast tumor?
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large (more than 5 cm or about 2 inches across) or growing into nearby tissues (the skin over the breast or the muscle underneath), or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
Can stage 3 breast cancer spread to lymph nodes?
If you have inflammatory breast cancer: Stage III cancers also include some inflammatory breast cancers that have not spread beyond near by lymph nodes. Treatment of these cancers can be slightly different from the treatment of other stage III breast cancers.
Can you get radiation therapy before mastectomy?
If you were initially diagnosed with stage II breast cancer and were given treatment such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery, radiation therapy might be recommended if cancer is found in the lymph nodes at the time of the mastectomy.
Can you get a mastectomy with a large breast?
For women with fairly large breasts, BCS may be an option if the cancer hasn’t grown into nearby tissues. SLNB may be an option for some patients, but most will need an ALND.