Inherited factor X deficiency
Factor X
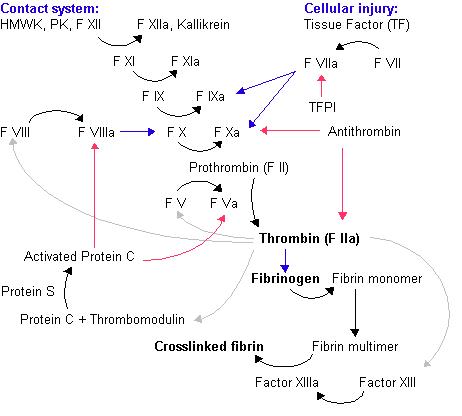
Factor X, also known by the eponym Stuart–Prower factor, is an enzyme of the coagulation cascade. It is a serine endopeptidase. Factor X is synthesized in the liver and requires vitamin K for its synthesis.
Is there a cure for Factor X syndrome (FXS)?
There is no cure for FXS. However, treatment services can help people learn important skills. Services can include therapy to learn to talk, walk, and interact with others. In addition, medicine can be used to help control some issues, such as behavior problems.
What are the treatment options for Factor X deficiency?
Genetic counseling may be of benefit for affected individuals and their families. The treatment of factor X deficiency has greatly improved in the last several years, progressing from broad treatments like fresh frozen plasma to prothrombin complexes (PCCs) and then to a dedicated factor X concentrate approved by the FDA.
How is Factor X deficiency (FX) diagnosed?
A diagnosis of factor X deficiency is based upon identification of characteristic symptoms, a detailed patient and family history, a thorough clinical evaluation and a variety of specialized tests.
What is Factor X and why is it important?
This causes people to bleed for a longer of amount of time. Factor X is a clotting protein (also called a clotting factor). Clotting factors are specialized proteins that are essential for proper clotting, the process by which blood clumps together to plug the site of a wound to stop bleeding.
What treatments are available for fragile X syndrome and its symptoms?
A genetic blood test can diagnose Fragile X. There is no cure. You can treat some symptoms with educational, behavioral, or physical therapy, and with medicines. Getting treatment early can help.
Can you recover from Fragile X Syndrome?
Some individuals with fragile X syndrome are able to live independently. Surveys show that around 4 in 10 women and 1 in 10 men with fragile X syndrome grow up to have a high level of independence.
What is the average lifespan of a person with fragile X syndrome?
It is the most common cause of inherited intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and it is estimated to affect 1 in 4,000 males and 1 in 8,000 females. People with fragile X have a generally normal life expectancy.
What does a person with Fragile X look like?
These features include a long and narrow face , large ears, a prominent jaw and forehead, unusually flexible fingers, flat feet , and in males, enlarged testicles (macroorchidism) after puberty.
How Common Is Factor X Deficiency?
Factor X deficiency is a rare disorder. It only occurs in 1 out of every 500,000 to 1 million people. People of any gender have an equal chance of getting it.
How much factor X is normal?
Your body produces 10% to 40% of the usual amount of factor X if you have a moderate case of the deficiency. It is considered severe if you have less than 10% of the normal amount of factor X.
Can factor X stop bleeding?
It is a version of factor X that people with factor X deficiency can take to either prevent a bleeding episode or stop bleeding after it has already started. Your doctor may also recommend this drug if you are going to have surgery and you have factor X deficiency. PPC.
How to treat acquired factor X deficiency?
To treat acquired factor X deficiency, your doctor will adjust or change your medication or address your underlying condition. The outlook is generally good, but sometimes severe bleeding can occur.
What is factor X deficiency?
Factor X deficiency, also called Stuart-Prower factor deficiency, is a condition caused by not having enough of the protein known as factor X in your blood. Factor X plays a role in blood clotting, also called coagulation, which helps you to stop bleeding. Known as coagulation factors, several crucial proteins, including factor X, ...
What medications can cause factor X deficiency?
These medications are called anticoagulants. Other illnesses that may result in acquired factor X deficiency include severe liver disease and amyloidosis.
What is the risk of a woman with a factor X deficiency bleeding during her period?
Women with the deficiency may experience heavy bleeding during menstruation (periods). Factor X-deficient women who become pregnant are at high risk for miscarriage during the first trimester and severe bleeding during and after delivery.
How is factor X passed down?
An inherited disorder is passed down from parents to children through genes. This type of factor X deficiency occurs when one of the genes is defective. The risk of parents giving it to their child is the same for both male and female children. The inherited type is estimated to occur in about one of every 500,000 people.
How to diagnose factor X deficiency?
Factor X deficiency is diagnosed through a blood test called a factor X assay. The test measures the activity of factor X in your blood. Tell your doctor if you are taking any medications or have any other diseases or conditions before taking this test.
What is factor X concentrate?
Food and Drug Administration approved a factor X concentrate called Coagadex. This drug is specifically meant to treat people who have inherited factor X deficiency.
What causes factor X deficiency?
The non-inherited form of Factor X deficiency is caused by other health conditions, including liver disease, amyloidosis, vitamin K deficiency, and others. [1]
What causes factor X protein to be lower?
Mutations in F10 lead to lower amounts of factor X protein or a factor X protein that doesn’t work correctly. [1] [3] The non-inherited form of Factor X deficiency is caused by other health conditions, including liver disease, amyloidosis, vitamin K deficiency, and others. [1] Last updated: 1/22/2019.
What test is used to determine the F10 gene?
Tests may include a partial prothrombin time ( PTT), prothrombin time (PT), and a Russell viper venom test. [1] [2] Additional testing includes tests to measure the amount and activity of the factor X protein. Genetic testing for changes in the F10 gene may also be helpful for diagnosis. Last updated: 1/22/2019.
How many copies of each gene are there in a factor X deficiency?
The inherited form of factor X deficiency is passed down in families in an autosomal recessive pattern. [1] [2] Everyone inherits two copies of each gene. To inherit factor X deficiency, a person must have a genetic change ( mutation) in both copies of the F10 gene in each cell. There is nothing either parent can do, before or during a pregnancy, to cause a child to have this.
How to find a doctor for a syphilis?
You may find these specialists through advocacy organizations, clinical trials, or articles published in medical journals. You may also want to contact a university or tertiary medical center in your area, because these centers tend to see more complex cases and have the latest technology and treatments.
Can factor X cause miscarriages?
Women with factor X deficiency may also experience heavy menstrual bleeding and may have an increased risk for first trimester miscarriages. [1] [2] Acquired (non- inherited) factor X deficiency, which is the most common form of the disorder, generally occurs in people with no family history of the disorder. Acquired factor X deficiency has ...
Is factor X deficiency a good outlook?
With treatment, people with both the mild and more severe forms of factor X deficiency have a good outlook. [1]
What is fragile X syndrome?
Fragile X syndrome can be a difficult diagnosis for the child’s family and friends. It’s the start of a lot of change and adjustment. Therapy, medications and accommodations at school are now part of your child’s life. While helping your child with their issues, be sure not to neglect your own needs. Remember that if your child has fragile X syndrome, that means you’re more vulnerable to dementia, depression, migraines, chronic pain, premature menopause, high blood pressure, anxiety, hypothyroidism and sleep apnea. Don’t neglect your own care!
When to take a child for fragile X syndrome?
Take your child in to see their pediatrician as soon as you notice the symptoms of fragile X syndrome. Don’t wait, as early intervention is important.
How does fragile X syndrome get passed from parent to child?
Fragile X syndrome gets passed from parent to child. A DNA part called the “CGG triplet repeat” expands within a gene called “FMR1,” producing a mutation that causes fragile X syndrome. A normal part repeats five to 40 times, but in people with fragile X syndrome it repeats more than 200 times. That “silences” the FMR1 gene, stopping it from producing an important protein called “FMRP” (fragile X mental retardation protein). This messes up the nervous system and causes the symptoms of fragile X syndrome.
Why is FXS called FXS?
FXS is named fragile X syndrome because, when looked at through a microscope, part of the X chromosome looks “broken” or “fragile.”. FXS is one of three syndromes in the fragile X family. The other two syndromes are: Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS). Symptoms include balance problems, shaky hands, unstable mood, memory loss, ...
How many times does fragile X syndrome repeat?
A normal part repeats five to 40 times, but in people with fragile X syndrome it repeats more than 200 times .
How many people have fragile X syndrome?
Although the exact number isn’t clear, researchers estimate that, worldwide, about 1 in 8,000 to 11,000 females and 1 in 4,000 to 7,000 males have fragile X syndrome. Experts don’t know for sure how many people carry the fragile X premutation, which can be passed down to their child and cause fragile X. Some studies estimate that, in the United ...
What test is done to determine if a child has fragile X syndrome?
If you’re pregnant and concerned that your child has fragile X syndrome, you can see a genetic counselor where you may undergo the following prenatal tests: Amniocentesis: The healthcare provider takes a sample of the amniotic fluid for testing.
How many people are affected by factor X?
The disorder is estimated to affect about 1 in every 500,000-1,000,000 people in the general population.
How is factor X deficiency inherited?
Factor X deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Genetic diseases are determined by the combination of genes for a particular trait that are on the chromosomes received from the father and the mother. Disorders inherited in a recessive pattern occur when an individual inherits the same variant gene for the same trait from each parent. If an individual receives one normal gene and one gene for the disease, the person will be a carrier for the disease, but usually will not show symptoms. The risk for two carrier parents to both pass the defective gene and, therefore, have an affected child is 25% with each pregnancy. The risk to have a child who is a carrier like the parents is 50% with each pregnancy. The chance for a child to receive normal genes from both parents and be genetically normal for that particular trait is 25%. The risk is the same for males and females.
What causes a clotting factor X deficiency?
Factor X deficiency is a rare genetic blood disorder that causes the normal clotting process (coagulation) to take longer than normal. This causes people to bleed for a longer of amount of time. Factor X is a clotting protein (also called a clotting factor). Clotting factors are specialized proteins that are essential for proper clotting, the process by which blood clumps together to plug the site of a wound to stop bleeding. Clotting requires a series of reactions to ultimately form a clot to plug a wound. This is referred to as the clotting (coagulation) cascade. The clotting cascade involves different substances in addition to clotting factors. Factor X, which is produced (synthesized) in the liver, eventually interacts with other clotting factors and certain cells or substances, e.g. platelets or fibrinogen, to help to form a clot. Factor X deficiency is caused by a variation (mutation) in the F10 gene. In 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a drug called Coagadex for adults and children over 12. This medication restores functional factor X levels.
What is 10% of factor X?
Individuals with 10%-40% activity have moderate disease and general symptoms associated with bleeding disorders. Individuals with 10% or less factor X activity have severe disease, particularly those with less than 1% of factor X. In some instances, the amount of secreted factor X is normal or near-normal, but cannot function normally;
Can factor X deficiency be broken down?
Sometimes, factor X deficiency is broken down based on the residual amount of factor X activity. Individuals with about 40% or more protein activity have mild disorder and often do not have symptoms (asymptomatic).
Does factor X deficiency cause bleeding complications?
little to no residual protein activity results in severe disease). This is not true for all bleeding disorders , but is true for factor X deficiency – generally the less protein activity the more severe the bleeding complications.
Is Coagadex a factor X?
In 2015, the FDA approved Coagadex (human coagulation factor X) for the treatment of adults and children over the age of 12 with factor X deficiency. Coagadex is a dedicated factor X concentrate that is approved for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding episodes, and for individuals, including those with mild disease, who are about to undergo surgical procedure (perioperative management). This therapy restores functional levels of factor X to affected individuals. This medication has also been authorized by the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
How does fragile X syndrome affect children?
Fragile X syndrome affects a child's learning, behavior, appearance, and health. Symptoms can be mild or more severe. Boys often have a more serious form of it than girls. Children who are born with this genetic condition can get special education and therapy to help them learn and develop like other kids.
What test can be done to diagnose fragile X syndrome?
After the child is born, a blood test can diagnose fragile X syndrome. This test looks for the FMR1 gene change. Babies born with fragile X syndrome don't always show signs of it. The doctor might notice that the baby's head is larger than usual. As the child gets older, learning and behavior problems can start.
What happens if you have a X chromosome?
If the X chromosome has the gene change, they will have symptoms of fragile X syndrome. Some people inherit the fragile X gene without having symptoms. They are called carriers. Carriers can pass the gene change to their children.
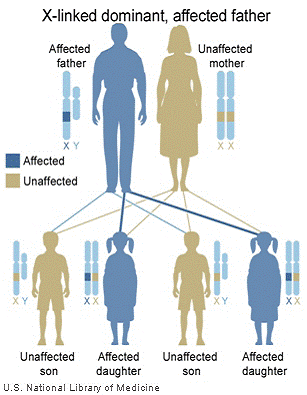
Why are boys more likely to have a X chromosome than girls?
Boys are more likely to have fragile X than girls, and they have more severe symptoms. This is because girls have two copies of the X chromosome. Even if one X chromosome has the gene change, the other copy can be fine. Boys have one X and one Y chromosome. If the X chromosome has the gene change, they will have symptoms of fragile X syndrome.
What tests can be done to check for fragile X?
These tests can be done during pregnancy to see if an unborn baby has fragile X: Amniocentesis -- doctors check a sample of amniotic fluid for the FMR1 gene change. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) -- doctors test a sample of cells from the placenta to check for the FMR1 gene.
How to learn more about fragile X?
To learn more about fragile X, join a support group. Or, reach out to an organization like the National Fragile X Foundation for advice and resources.
What are the changes in fragile X?
Extreme sensitivity to light or sound. Hyperactivity and trouble paying attention. Aggressive and self-destructive behavior in boys. Some children with fragile X also have changes to their face and body that can include: A large head. A long, narrow face. Large ears. A large forehead and chin. Loose joints.
What is fragile X syndrome?
Inheritance and Screening. Fragile X syndrome is a medical condition that causes intellectual disability and other medical problems. It is the most common kind of genetically inherited intellectual disability, and the second-most common type of intellectual disability overall (after Down syndrome ). Fragile X syndrome is estimated ...
What are the major issues in fragile X syndrome?
Developmental delay and intellectual disability are major issues in fragile X syndrome. For example, a child might first learn to talk or walk at a much later age than normal. Some people with fragile X syndrome have normal intellectual functioning. At the other extreme, some people have severe intellectual disability.
Why can't FMR1 make FMRP?
Because of a genetic error, the FMR1 gene can’t make FMRP the way it normally would. Most commonly, the genetic error causes an abnormal repeated series of nucleotides (components of DNA) to be inserted in the normal DNA sequence. This specific mutation is called a CGG repeat. In people with fragile X syndrome, this sequence is repeated over 200 times (compared to a normal repeat number of 5 to 44). 6
What is the National Fragile X Foundation?
The National Fragile X Foundation provides much helpful support, advocacy, and information for families dealing with a fragile X syndrome diagnosis.
What percentage of people with fragile X syndrome have autism?
Some of the possible issues include: Researchers estimate that about 50% of males and 20% of females with fragile X syndrome have an autism spectrum disorder as well. 4 In fact, though autism has many different multi-factorial causes, fragile X syndrome is the most common known cause of the condition.
What is the IEP for fragile X?
This is written up in something called an individualized education plan (IEP). This provides a plan so that children with fragile x syndrome can receive the best support while also being included in general education to the extent that is possible.
How many people have fragile X syndrome?
Fragile X syndrome is estimated to occur in about one male in 5,000 to 7,000 and in about one female in 4,000 to 6,000. 1 It is named for the unusual appearance of the X chromosome of people with fragile X syndrome (seen in certain laboratory tests). PhotoAlto/Frederic Cirou / Getty Images.
How to confirm triple X syndrome?
If triple X syndrome is suspected based on signs and symptoms, it can be confirmed by genetic testing — chromosome analysis using a blood sample. In addition to genetic testing, genetic counseling can help you gain comprehensive information about triple X syndrome.
How to help a child with X and Y chromosome disorders?
Connect with others. Support groups provide help and support for people with X and Y chromosome disorders and their families. They offer information and advice on coping, as well as ways to meet and talk with others in similar situations. Ask your child's doctor or therapist if there is a local support group for people with similar types of disorders. You can also contact AXYS — Association for X and Y Chromosome Variations.
Can triple X syndrome be discovered?
Because many girls and women with triple X syndrome are healthy and show no outward signs of the condition, they may remain undiagnosed all their lives, or the diagnosis may be discovered while checking other issues. Triple X syndrome may also be discovered during prenatal testing to identify other genetic disorders.
Can triple X be repaired?
The chromosome error that causes triple X syndrome can't be repaired, so the syndrome itself has no cure. Treatment is based on symptoms and needs. Options that may be helpful include: Periodic screenings. The doctor may recommend periodic screenings throughout childhood and into adulthood.

Testing/Diagnosis
Finding Support
- Having support and community resources can help increase confidence in managing FXS, enhance quality of life, and assist in meeting the needs of all family members. It might be helpful for parents of children with FXS to talk with one another. One parent might have learned how to address some of the same concerns another parent has. Often, parents of children with special …
CDC’s Work on Fragile X Syndrome
- CDC is working to learn more about the natural history of fragile X so that better approaches to intervention can be developed. As part of this effort, CDC: 1. Supported the National Fragile X Foundation to develop the Fragile X Online Registry With Accessible Research Database (FORWARD)external icon. The purpose of FORWARD is to learn more about 1.1. Other condition…
Other Resources
- Fragile X Online Registry With Accessible Research Database (FORWARD)external icon Funded by CDC, FORWARD is the largest source of data on people with fragile X syndrome and their families. FRAXA Research Foundationexternal icon FRAXA’s mission is to accelerate progress toward effective treatments and ultimately a cure for fragile X by directly funding the most promising re…
References
- Hunter J, Rivero-Arias O, Angelov A, Kim E, Fotheringham I, Leal J. Epidemiology of fragile X syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Jul 164A(7): 1648-58.