Here are a few characteristics of experimental research:
- Dependent variables are manipulated or treated while independent variables are exerted on dependent variables as an experimental treatment. ...
- Researchers deliberately operate independent variables on the subject of the experiment. ...
- Once a variable is manipulated, researchers observe the effect an independent variable has on a dependent variable. ...
What does experimental treatment mean?
Sep 28, 2021 · Experimental research is considered a standard method that uses observations, simulations and surveys to collect data. One of its unique features is the ability to control extraneous variables and their effects. It’s a suitable method for those looking to examine the relationship between cause and effect in a field setting or in a laboratory.
What is a treatment in an experiment?
In true experimental research, the researcher not only manipulates the independent variable, he or she also randomly assigned individuals to the various treatment categories (i.e., control and treatment). In quasi experimental research, the researcher does not randomly assign subjects to treatment and control groups. In other words, the treatment is not distributed among …
What is the treatment of an experiment?
experimental treatment Internal medicine An unproven therapy which may or may not be superior to a current 'gold standard' therapy Experimental treatment–criteria Not generally accepted by …
What is the purpose of experimental research?
Apr 07, 2013 · 1. Research. The conditions applied to some groups that may cause change in outcomes. 2. A treatment showing promise but is still being evaluated to gtreat a disease or condition. See treatment combination - treatment level. EXPERIMENTAL TREATMENT: "Joe was undergoing experimental treatment for his cancer that seemed to be having an effect."

What is experimental treatment example?
For example, a human experimental group could receive a new medication, a different form of counseling, or some vitamin supplements. A plant treatment group could receive a new plant fertilizer, more sunlight, or distilled water. The group that does not receive the treatment is called the control group.Oct 1, 2015
How do you write an experimental treatment?
Design experimental treatments to manipulate your independent variable. Assign subjects to groups, either between-subjects or within-subjects....Step 1: Define your variables. ... Step 2: Write your hypothesis. ... Step 3: Design your experimental treatments. ... Step 4: Assign your subjects to treatment groups.More items...•Dec 3, 2019
What is an example of experimental research?
Human Behavior: Social scientists are the ones who mostly use experimental research to test human behaviour. For example, consider 2 people randomly chosen to be the subject of the social interaction research where one person is placed in a room without human interaction for 1 year.Jan 23, 2020
Why are experimental treatments important?
The continued advancement of medical therapeutics and procedures through experimentation is vital to creating safer, more effective, and more accessible treatments for disease.May 18, 2021
What is treatment structure?
◆ Treatment Structure. ⇨ Consists of the set of treatments, treatment. combinations or populations the experimenter has. selected to study and/or compare.
What are examples of experiments?
To experiment is defined as to try out something new or to test a theory. An example of experiment is when you try out a new hair style. An example of experiment is when you use test tubes and chemicals in a lab to complete a project and to try to better understand chemical reactions.
What are the 2 types of experimental research?
Experimental research can be grouped into two broad categories: true experimental designs and quasi-experimental designs. Both designs require treatment manipulation, but while true experiments also require random assignment, quasi-experiments do not.
Why do we apply experimental research?
Through accurate and precise empirical measurement and control an experimental design increases a researcher's ability to determine causal relationships and state causal conclusions. Experimental design as a subset of scientific investigation is a popular and widely used research approach.
What are the 3 characteristics of experimental research?
In general, designs that are true experiments contain three key features: independent and dependent variables, pretesting and posttesting, and experimental and control groups.
What distinguishes experimental research from other types of research?
The major feature that distinguishes experimental research from other types of research is that the researcher manipulates the independent variable. There are a number of experimental group designs in experimental research. Some of these qualify as experimental research, others do not.
What is quasi experimental research?
In this case, quasi-experimental research involves using intact groups in an experiment, rather than assigning individuals at random to research conditions. (some researchers define this latter situation differently.
Why does causal comparative research not meet the standards of an experiment?
It does not meet the standards of an experiment because the independent variable in not manipulated. The statistics by themselves have no meaning. They only take on meaning within the design of your study.
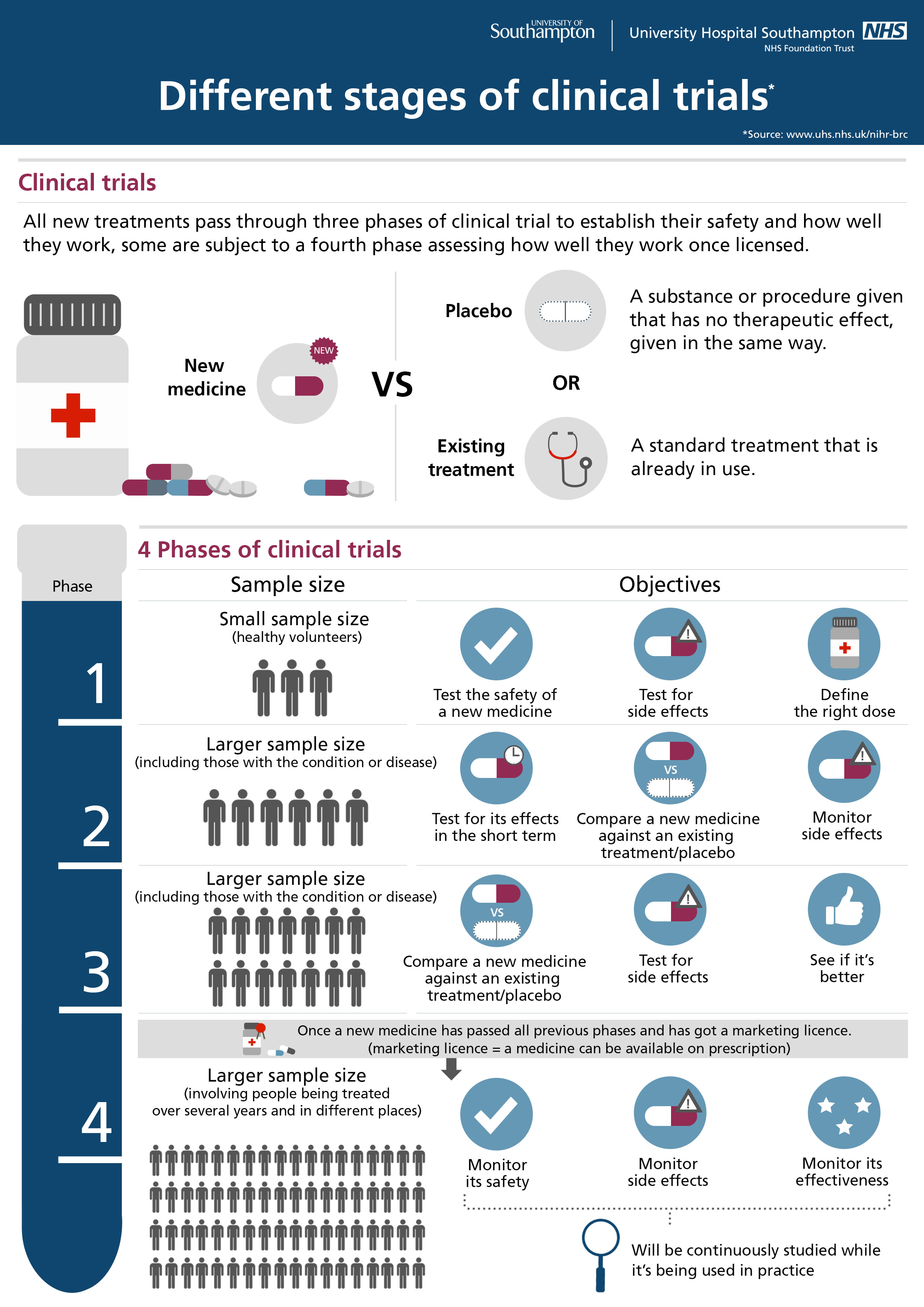
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials. In other cases, an experimental, or investigational, treatment may be just what you want. For example, you may have tried standard treatments without success. You may want to take part in a clinical trial—a study in humans—of a promising new treatment. To start looking for such a trial, ask your doctor.
What to do if you can't enroll in a clinical trial?
What to do if you can’t enroll in a clinical trial but still want an investigational treatment. Appealing Decisions That a Treatment Is Experimental. If your insurer denies your claim because it says the treatment is experimental, follow your insurer’s appeals process. Also, follow the advice in Appealing a Reimbursement Decision.
Do health insurance plans cover experimental treatments?
Most health plans don’t cover treatments they regard as “experimental.” Sometimes, they may deny a claim for such a treatment. But, you and your doctor may think the treatment is well supported by evidence. Then, you have grounds for an appeal.
Does a health insurance plan cover research?
Health plans don’t have to cover the research costs of a clinical trial. That includes extra blood tests done only for research. Often, the trial sponsor will cover such costs. If you’re not sure about what your health plan will pay, check with your plan representative to find out.
Do you pay for routine care in a trial?
But, often, the trial sponsor will supply that treatment for free. Usually, you’ll keep on getting routine care from your own doctor, and your insurer should continue to pay for that. In the trial setting, most plans are required to pay for routine care costs under certain conditions. Expanded Access.
What is quasi experimental design?
Quasi-experimental designs are almost identical to true experimental designs, but lacking one key ingredient: random assignment. For instance, one entire class section or one organization is used as the treatment group, while another section of the same class or a different organization in the same industry is used as the control group. This lack of random assignment potentially results in groups that are non-equivalent, such as one group possessing greater mastery of a certain content than the other group, say by virtue of having a better teacher in a previous semester, which introduces the possibility of selection bias . Quasi-experimental designs are therefore inferior to true experimental designs in interval validity due to the presence of a variety of selection related threats such as selection-maturation threat (the treatment and control groups maturing at different rates), selection-history threat (the treatment and control groups being differentially impact by extraneous or historical events), selection-regression threat (the treatment and control groups regressing toward the mean between pretest and posttest at different rates), selection-instrumentation threat (the treatment and control groups responding differently to the measurement), selection-testing (the treatment and control groups responding differently to the pretest), and selection-mortality (the treatment and control groups demonstrating differential dropout rates). Given these selection threats, it is generally preferable to avoid quasi-experimental designs to the greatest extent possible.
What is instrumentation threat?
Instrumentation threat , which also occurs in pre-post designs, refers to the possibility that the difference between pretest and posttest scores is not due to the remedial math program, but due to changes in the administered test, such as the posttest having a higher or lower degree of difficulty than the pretest.
What are two group designs?
The two basic two-group designs are the pretest-posttest control group design and the posttest-only control group design, while variations may include covariance designs. These designs are often depicted using a standardized design notation, where R represents random assignment of subjects to groups, X represents the treatment administered to the treatment group, and O represents pretest or posttest observations of the dependent variable (with different subscripts to distinguish between pretest and posttest observations of treatment and control groups).
What is a threat in pre-post design?
Testing threat is a threat in pre-post designs where subjects’ posttest responses are conditioned by their pretest responses. For instance, if students remember their answers from the pretest evaluation, they may tend to repeat them in the posttest exam. Not conducting a pretest can help avoid this threat.
What is the main effect of a factorial design?
In a factorial design, a main effect is said to exist if the dependent variable shows a significant difference between multiple levels of one factor, at all levels of other factors. No change in the dependent variable across factor levels is the null case (baseline), from which main effects are evaluated.
What is factorial design?
Factorial Designs. Two-group designs are inadequate if your research requires manipulation of two or more independent variables (treatments). In such cases, you would need four or higher-group designs. Such designs, quite popular in experimental research, are commonly called factorial designs.
Why are experimental studies so rare?
But such experiments are relatively rare, because of the difficulties associated with manipulating treatments and controlling for extraneous effects in a field setting. Experimental research can be grouped into two broad categories: true experimental designs and quasi-experimental designs.
What is experimental research?
Experimental research is a quantitative research method with a scientific approach, where a set of variables are kept constant while the other set of variables are being measured as the subject of an experiment. Learn about various types of experimental research design along with its advantages. Products .
Why is experimental research important?
Experimental research allows you to test your idea in a controlled environment before taking it to market . It also provides the best method to test your theory, thanks to the following advantages: Researchers have a stronger hold over variables to obtain desired results.
What is the difference between quasi experimental and experimental?
A quasi-experimental design is similar to experimental, but it is not the same. The difference between the two is the assignment of a control group. In this research, an independent variable is manipulated, but the participants of a group are not randomly assigned.
What is a pre-experimental design?
1. Pre-experimental research design: A group, or various groups, are kept under observation after implementing factors of cause and effect. You’ll conduct this research to understand whether further investigation is necessary for these particular groups.
What are the different types of experimental design?
There are three primary types of experimental design: Pre-experimental research design. True experimental research design. Quasi-experimental research design. The way you classify research subjects, based on conditions or groups, determines the type of design. 1.
What is the difference between experimental and quantitative research?
The first set acts as a constant, which you use to measure the differences of the second set. Quantitative research methods, for example, are experimental. If you don’t have enough data to support your decisions, you must first determine the facts. Experimental research gathers the data necessary to help you make better decisions.
Why is time important in research?
Time is a vital factor in establishing a relationship between cause and effect. Invariable behavior between cause and effect. You wish to understand the importance of the cause and effect. Learn about: Quantitative Market Research. Types of experimental research design.