
What's new in this edition of soil erosion research methods?
Among in vitro models, simple (single- or multiple-exposure) models can be used for screening products regarding their erosive potential, while more elaborate pH cycling models can be used to simulate erosion in vivo. However, in vitro models provide limited information on intra-oral erosion. In situ models allow the effect of an erosive challenge to be evaluated under intra-oral …
What is treatment in research?
chitosan and multivalent metal ions are available. Beyond all available materials and methods, the most critical point in treatment is the detection and elimination of the erosion causing factor. This is only possible with the early diagnosis of the erosive lesion, and the detection and elimination of the etiological factor with a good anamnesis.
What is water erosion and how can you prevent it?
Restorative treatment is dependent on individual circumstances and the perceived needs and concerns of the patient. Long-term success is only possible when the cause is eliminated. In all situations, the restorative preparations have to follow the principles of …
What is the first stage of erosion?
The soil erosion is the most serious environmental problem in watershed areas in Turkey. The main factors affecting the amount of soil erosion include vegetation cover, topography, soil, …
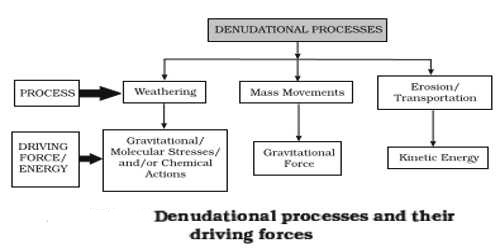
What is erosion research?
What is a method of erosion?
What are the three methods of erosion?
What are some erosion control methods?
- cellular confinement systems.
- crop rotation.
- conservation tillage.
- contour bunding.
- contour plowing.
- cover crops.
- fiber rolls (also called straw wattles)
- gabions.
What is an example of erosion?
What are the 6 types of erosion?
- Type # 1. Splash Erosion:
- Type # 2. Sheet Erosion:
- Type # 3. Channel Erosion:
- Type # 4. Water Fall Erosion:
- Type # 5. Marine Erosion:
- Type # 6. Landslide or Slip Erosion:
What is the types of erosion?
- Sheet Erosion. ...
- Gully Erosion. ...
- Wind Erosion. ...
- Floodplain Erosion. ...
- Protecting Your Topsoil From Many Types of Soil Erosion.
What are the 5 types of erosion?
- Splash Erosion. This is the first stage in the erosion process that is caused by rain. ...
- Sheet Erosion. ...
- Rill Erosion. ...
- Gully Erosion. ...
- Tunnel Erosion. ...
- Impact On Flora. ...
- Impact On Fauna. ...
- Flooding.
What causes erosion?
What are 5 ways to prevent erosion?
- Plant Grass and Shrubs. Grass and shrubs are very effective at stopping soil erosion. ...
- Use Erosion Control Blankets to Add Vegetation to Slopes. ...
- Build Terraces. ...
- Create Diversions to Help Drainage.
Why is erosion control important?
Is tooth erosion a multifactorial background?
Dental erosion is considered to have a multifactorial background in which individual and lifestyle differences are important. Despite the methodological differences in research, data from many countries confirm that tooth erosion which progresses rapidly is common in children and young people (4). While the concentration of hydrogen in plaque fluid is the main determinant for erosion
Does fluoride prevent tooth erosion?
Sodium fluoride-containing toothpastes can prevent the loss of material caused by erosion, but their effects are limited, especially against severe tooth wear. Fluoride causes remineralization of the enamel with the formation of calcium-fluorine-like components on the tooth surface. At the same time, however, some research suggests that abrasive ingredients present in toothpastes prevent precipitation (3, 17). Although all fluorides help to strengthen teeth against caryogenic acids, the current fluoride sources do not provide the same degree of erosion protection. The daily use of a stabilized stannous fluoride tooth cleaner has been shown to be the most effective way of protecting teeth against the risk of tooth wear (18, 19).
What are protease inhibitors used for?
Recent studies have focused on the role of protease inhibitors on erosion. The use of protease inhibitors in dentine tissue to protect the organic matrix after an erosive attack may have a protective role against future mineral losses. However, in spite of promising results in in situ studies, these preventive measures are not evidence-based. Clinical trials are required to confirm these findings and establish the protocols to be used (16).
What is the purpose of oil in pellicle?
Oils in the pellicle protect the tooth tissues against decreasing pH. In one study, it was observed that it protects the tooth surface against abrasion. Use of oils with fluoride-containing agents may be recommended (3).
Is chitosan an antibacterial?
Chitosan is an antibacterial agent that contributes to tissue regeneration. It may be present in toothpastes. It has anti-erosive properties as it has high positive charge at acidic pH. It may prevent the formation of dental erosion by forming a protective layer on the teeth by connecting to the pellicle (13).
Which metals have the strongest effect on erosion?
Metal ions such as stannous and titanium, have strong effects on erosion. Stannous fluoride, stannous chloride or titanium tetrafluoride are some of these materials (13).
What is CPP APC?
Casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-APC) is a compound with remineralization effect, and can be added to mouthwashes and gums to prevent erosion. However, some studies indicate that it is insufficient to prevent erosion (22, 23).
How does soil erosion affect the environment?
This process has an effect on the environment including loss of soil fertility, reduction of water bodies' depth (lakes, ponds, reservoirs, etc.), increase in water turbidity, flood hazard problems, etc. Identifying the erosion hotspot areas using different techniques is an essential tool for sustainable natural resources management. This study focusses on the mapping of soil erosion-prone areas of Ribb watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. This study aimed to identify the erosion of hotspot areas for the setting of effective soil and conservation strategies. Different soil erosion contributing factors, viz. Slope, land use, soil, rainfall, and stream power index, were integrated on ArcGIS 10.3 environment for determining the erosion-prone areas. Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) technique was used to develop erosion hotspot areas using thematic layers pair-wise comparison tool. The weights for each thematic layer and feature were decided based on the expert's judgment and review of the literature. Hence, the results of soil erosion map showed very high, high, moderate, low, and very low vulnerability to erosion with areal coverage of 7.04%, 20.40%, 17.60%, 32.01%, and 22.95%, respectively. The findings of this study will help decision-makers to plan and carry out effective soil and water conservation practices in highly vulnerable areas to soil erosion. MCDA was found as a basic tool for determining erosion-prone areas coupled with GIS. The spatial distribution map indicated that most of the erosion-prone areas were found in northern, eastern, and northeastern parts of the watershed due to the steep slope and agricultural practice which needs integrated soil and water conservation practice.
How does mulching the soil reduce water infiltration?
Mulching the soil surface with a layer of plant residue is considered an effective method of conserving water and soil because it increases water infiltration into the soil, reduces surface runoff and the soil erosion, and reduces flow velocity and the sediment carrying capacity of overland flow. However, application of plant residues increases operational costs and so optimal levels of mulch in order to prevent soil and/or water losses should be used according to the soil type and rainfall and slope conditions. In this study, the effect of wheat straw mulch rate on the total runoff and total soil losses from 60-mm simulated rainstorms was assessed for two intensive rainfalls (90 and 180 mm h−1) on three slope gradients typical conditions on the Loess Plateau of China and elsewhere. For short slopes (1 m), the optimal mulch rate to save water for a silt loam and a loam soil was 0.4 kg m−2. However, for a clay loam soil the mulch rate of 0.4 kg m−2 would be optimal only under the 90 mm h−1 rainfall; 0.8 kg m−2 was required for the 180 mm h−1. In order to save soil, a mulch rate of 0.2 kg m−2 on the silt loam slopes prevented 60%–80% of the soil losses. For the loam soil, mulch at the rate of 0.4 kg m−2 was essential in most cases in order to reduce soil losses substantially. For the clay loam, 0.4 kg m−2 may be optimal under the 90 mm h−1 rain, but 0.8 kg m−2 may be required for the 180 mm h−1 rainstorm. These optimal values would also need to be considered alongside other factors since the mulch may have value if used elsewhere. Hence doubling the optimal mulch rate for the silt loam soil from 0.2 kg m−2 or the clay loam soil under 90 mm h−1 rainfall from 0.4 kg m−2 in order to achieve a further 10% reduction in soil loss needs to be assessed in that context. Therefore, Optimal mulch rate can be an effective approach to virtually reduce costs or to maximize the area that can be treated. Meantime, soil conservationist should be aware that levels of mulch for short slopes might not be suitable for long slopes. Keywords: Straw mulch, Soil losses, Runoff, Rain simulator
What are the causes of degradation in peatlands?
Once they are drained to provide optimal crop growth conditions, however, a series of degradation processes is generated. Wind and water erosion, subsidence and soil organic matter oxidation are the main causes of degradation observed in cultivated histosols. This study evaluated the decomposition dynamics and chemical changes of three biomass crops during an in‐situ incubation in a cultivated histosol. The decomposition dynamics characterized in the field study were then used in a simulation to determine if sustainability could be reached by using biomass crops as a soil amendment. The results showed that an exponential decay fitting curve best represented the weight loss of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) in the in‐situ bags over time, while a logistic fitting curve best represented that of miscanthus (Miscanthus X giganteus) and willow (Salix miyabeana). The quality of the crop determined the initial and overall decomposition dynamics observed. The loss of carbon from the crushed biomass crop was much more important in sorghum than in miscanthus and willow. The long‐term simulation of histosol amendment revealed that using miscanthus and willow at input rates of 7.5 and 10 T of carbon per year, respectively, would be sufficient to ensure sustainability. Improving knowledge on carbon loss in cultivated histosols as related to soil and crop management would help in developing a soil amendment program at the farm scale. In addition, more knowledge is needed to determine the impact of long‐term and successive amendment with biomass crops on the physical and biochemical properties of histosols.
What is water erosion?
Water erosion is the removal of the top layer of land by water from irrigation, rainfall, snowmelt, runoff, and poor irrigation management. Ultimately, rainwater is most frequently to blame when it comes to this issue. The flowing water moves the soil organic and inorganic particles alongside the land surface, depositing them in the lower landscape.
Why is water erosion important?
Water erosion control is vital in battling the issue of land degradation caused by water. And the. water erosion solutions differ depending on the soil type, topography, climate, crop rotation, and land use. However, there are water erosion prevention measures for its every type. The table below shows both the common and ...
Is water erosion bad for agriculture?
Water erosion is among the many factors that are harmful to farmland productivity, eventually making the land completely unsuitable for agriculture. Depending on its causes and stages, there are different types of erosion caused by water. To prevent any type of water erosion and its adverse effects, the farmer has to know what each ...
How does water affect soil?
The flowing water moves the soil organic and inorganic particles alongside the land surface, depositing them in the lower landscape. The result of this would be flooding in the long run. The eroded soil material can either form a new soil or move to water reservoirs nearby (lakes, streams, etc.).
What causes land depletion?
Natural water erosion is beyond human control and does not have a significant effect on soil fertility. It is caused by rainfall, melted snow, or runoff, i.e the natural forces.
Does water erosion affect soil fertility?
Natural water erosion is beyond human control and does not have a significant effect on soil fertility. It is caused by rainfall, melted snow, or runoff, i.e the natural forces. Each soil type has its natural erosion rate, depending on farmland properties and the climate in which it is located.
What causes accelerated erosion?
It is caused by rainfall, melted snow, or runoff, i.e the natural forces. Each soil type has its natural erosion rate, depending on farmland properties and the climate in which it is located. On the contrary, accelerated erosion is the consequence of irrational farming.
