
Medication
Diet Therapy for Epilepsy, Including Ketogenic Diet. High fat, very low-carbohydrate diets, when calibrated and administered by a doctor and followed precisely, can help ease recurrent seizures in some cases. Johns Hopkins offers diet therapy for epilepsy for both pediatric and adult patients, using the ketogenic diet and the modified Atkins diet. More about diet therapy for …
Procedures
The occurrence of a single seizure does not always require initiation of antiepileptic drugs. Risk of recurrent seizures should guide their use. In adults, key risk factors for recurrence are two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 24 hours apart, epileptiform abnormalities on electroencephalogr …
Therapy
Epilepsy may be treated with antiepileptic medications (AEDs), diet therapy and surgery. Medications are the initial treatment choice for almost all patients with multiple seizures. Some patients who only have a single seizure and whose tests do not indicate a high likelihood of seizure recurrence may not need medications.
Self-care
Epilepsy medications, sometimes called anti-seizure or anticonvulsant medications, change the way your brain cells work and send messages to each …
Nutrition
Treatment 101: The Basics. Good news! Treatments are available that can stop or control seizures for most people with seizures and epilepsy. The first treatment step is to find the right medicine for each person. While the majority of people can do well with the first one or two medicines tried, others find that medications just don’t work.
Is there a cure for epilepsy?
Treating Epilepsy in Adults What Are Seizure Medications? Seizure medications, also called antiseizure medications, are prescribed by one's health care team for the treatment of seizures. Some are used to control the frequency of seizures. Some are used to …
How can you treat epilepsy?
Epilepsy treatment Neurology Epilepsy treatment Epilepsy is an electrochemical disorder of the brain. It can cause loss of consciousness and muscle spasms (uncontrolled shaking). Epileptic seizures should always be investigated with neurological tests and examinations. Book now Book online or call 030 6000*
What to do during and after a seizure?
How do you cure seizures?
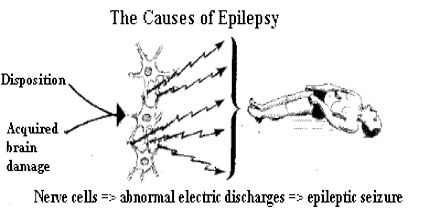
Can epilepsy be treated completely?
There's currently no cure for epilepsy, but it can be managed with medications and other strategies.
What are the main causes of epilepsy?
Causes of epilepsya stroke.a brain tumour.a severe head injury.drug abuse or alcohol misuse.a brain infection.a lack of oxygen during birth.
What is epilepsy how is it treated?
Most people with epilepsy can become seizure-free by taking one anti-seizure medication, which is also called anti-epileptic medication. Others may be able to decrease the frequency and intensity of their seizures by taking a combination of medications.Oct 7, 2021
Can epilepsy patients live normal life?
Many people with epilepsy can conduct a normal life. However, patients who have had epilepsy for a long time or whose epilepsy is difficult to control are at higher risk for unemployment. They may also need assistance in their daily life activities.Jul 22, 2019
Is epilepsy a mental illness?
Epilepsy is not a mental illness. In fact, the vast majority of people living with epilepsy have no cognitive or psychological problem. For the most part, psychological issues in epilepsy are limited to people with severe and uncontrolled epilepsy.Nov 15, 2016
What are the warning signs of epilepsy?
Epilepsy: Seizure Triggers, Warning Signs, and SymptomsTemporary confusion—often described as a “fuzzy” feeling.A staring spell.Uncontrollable jerking movements of the arms and legs.Loss of consciousness or awareness.Psychic symptoms—out-of-body feelings or not feeling “in the moment”Memory lapses.Nov 21, 2017
What are 4 drugs to treat epilepsy?
Medicines used to treat epilepsy Carbamazepine, clobazam, clonazepam, eslicarbazepine, ethosuximide, gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, perampanel, phenobarbital, phenytoin, pregabalin, primidone, rufinamide, sodium valproate, tiagabine, topiramate, vigabatrin and zonisamide.
Does epilepsy cause memory loss?
Any type of epileptic seizure could potentially affect your memory, either during or after a seizure. If you have lots of seizures, memory problems might happen more often. Some people have generalised seizures that affect all of the brain.Feb 23, 2020
Who is affected by epilepsy?
Epilepsy and seizures can develop in any person at any age. Epilepsy is more common in young children and older people. Slightly more men than women have epilepsy. About 1 in 10 people will have an unprovoked seizure in their lifetime.
Does epilepsy get worse with age?
The incidence of any type of seizure increases substantially over the age of 60, commonly due to other neurological conditions such as dementia or stroke.
What is the diagnosis of epilepsy?
There are several different types of epilepsy, characterized by seizures, with symptoms causing changes in awareness, muscle tone, emotions, behavior and sensory experience. Proper treatment starts with a careful assessment of the person’s seizures, which may include: Medical and seizure history and neurological ...
Why do people choose Johns Hopkins?
Epilepsy Treatment: Why Choose Johns Hopkins 1 The large number of patients we treat gives us unparalleled expertise in assessing and treating the full spectrum of epilepsy and seizure disorders. 2 Johns Hopkins offers a First Seizure Clinic, Genetic Testing Clinic and a well-equipped Epilepsy Monitoring Unit to help diagnose seizures and epilepsy. 3 Our team tailors each patient’s treatment plan with access to the most advanced medical, dietary and surgical therapies available. 4 If you and your doctor decide that epilepsy surgery is right for you, we offer the most modern approaches, including laser interstitial thermal therapy (LiTT).
How to stop seizures in epilepsy?
Treatment can help most people with epilepsy have fewer seizures, or stop having seizures completely. Treatments include: medicines called anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) surgery to remove a small part of the brain that's causing the seizures. a procedure to put a small electrical device inside the body that can help control seizures.
How does epilepsy surgery work?
The surgeon makes a small cut in your scalp and creates an opening in your skull so they can remove the affected part of the brain. The openings in your skull and scalp are closed at the end of the operation.
What is the test for epilepsy?
This will usually involve having several tests, such as: brain scans. an electroencephalogram (EEG) – a test of your brain's electrical activity.
What is keto diet?
A ketogenic diet is a diet high in fats, and low in carbohydrates and protein. In children, the diet is thought to make seizures less likely by changing the levels of chemicals in the brain. The ketogenic diet was one of the main treatments for epilepsy before AEDs were available.
How do AEDs work?
They help control seizures in around 7 out of 10 of people. AEDs work by changing the levels of chemicals in your brain. They do not cure epilepsy, but can stop seizures happening.
What does it mean when you get a rash on a med?
rashes – contact your GP or specialist if you get a rash, as it might mean you're having a serious reaction to your medicine. Contact your GP or specialist if you have symptoms similar to being drunk, such as unsteadiness, poor concentration and being sick. This could mean your dose is too high.
How long does it take for side effects to show on AEDs?
Side effects are common when starting treatment with AEDs. Some may appear soon after starting treatment and pass in a few days or weeks, while others may not appear for a few weeks.
What are the treatments for seizures?
For patients with seizures that are not controlled with these agents, alternative treatments include surgical resection of the seizure focus, ketogenic diets, vagus nerve stimulators, and implantable brain neurostimulators.
What are the risk factors for epilepsy in children?
In children, key risk factors are abnormal electroencephalography results, an epileptic syndrome associated with seizures, severe head trauma, and cerebral palsy. The risk of adverse effects from antiepileptic drugs is considerable and includes potential cognitive and behavioral effects. In the absence of risk factors, ...
What are the risk factors for recurrence of seizures?
In adults, key risk factors for recurrence are two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 24 hours apart, epileptiform abnormalities on electroencephalography, abnormal brain imaging, nocturnal seizures, or an epileptic syndrome associated with seizures.
Where is epilepsy surgery done?
The most common location in the brain for epilepsy surgery is the temporal lobe. About 60 percent to 80 percent of patients become seizure-free with this type of surgery. A new technique is laser surgery, which involves destroying the seizure focus with heat rather than removing it.
What is an epileptic seizure?
An epileptic seizure is an excessive, uncontrolled burst of electrical activity from nerve cells in the brain – essentially an electrical storm. There are many types of seizures that cause symptoms ranging from lightning-fast muscle jerks lasting less than a second ...
When are patients invited to participate in a trial?
Often, patients are invited to join a trial after they have failed a number of other FDA-approved medications.
What is the first do no harm movie?
For many years, a special diet has been used to control certain types of epilepsy. One in particular – the ketogenic diet – gained public attention with the 1997 movie “First Do No Harm.” In this film, which is based on a true story, Meryl Streep plays the mother of a son whose epilepsy fails to respond to conventional treatments, including epilepsy surgery. She takes him to Johns Hopkins Medical Center, which pioneered the use of the ketogenic diet and demonstrated its effectiveness. Her son responded wonderfully to the diet and became seizure-free.
What percentage of patients do not respond to medications?
Unfortunately, about 30 percent to 40 percent of patients do not respond to medications at all, and we must consider other therapies. 4. Medical marijuana. Medical marijuana is a term that now refers to one of more than 80 chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant – cannabidiol oil or CBD oil.
What is Ma Huang?
Ma huang is a natural ephedra, which is similar to a stimulant hormone in our bodies. Stimulants tend to worsen seizures, so doctors are hesitant to recommend any herbal remedies at this time. 2. Diet. For many years, a special diet has been used to control certain types of epilepsy.
How long does a seizure last?
There are many types of seizures that cause symptoms ranging from lightning-fast muscle jerks lasting less than a second to full body convulsions lasting two or three minutes. Epilepsy, if not well-controlled, can greatly worsen a person’s quality of life and can cause severe injury or death.
What is epilepsy disorder?
Check out the new videos at the bottom of the page. Epilepsy is a disorder of the brain characterized by repeated seizures. A seizure is usually defined as a sudden alteration of behavior due to a temporary change in the electrical functioning of the brain.
What is the diagnosis of epilepsy?
A doctor makes his or her epilepsy diagnosis based on symptoms, physical signs and the results of such tests as an electroencephalogram (EEG), computed tomography (CT or CAT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is essential that the type of epilepsy and the type of seizures both are diagnosed properly.
How does epilepsy affect the brain?
In epilepsy the brain's electrical rhythms have a tendency to become imbalanced, resulting in recurrent seizures.
What are the two types of seizures?
Typically, seizures belong in one of two basic categories: primary generalized seizures and partial seizures. The difference between these types is in how they begin.
How many people have epilepsy?
According to the Epilepsy Foundation, epilepsy affects three million people in the U.S. and 50 million worldwide. Epileptic seizures may be tied to a brain injury or genetics, but for 70 percent of epilepsy patients, the cause is unknown.
Do seizures need medication?
Some patients who only have a single seizure and whose tests do not indicate a high likelihood of se izure recurrence may not need medications. The medications treat the symptoms of epilepsy (the seizures), rather than curing the underlying condition.
What causes epilepsy in children?
Children may be born with a defect in the structure of their brain or they may suffer a head injury or infection that causes their epilepsy. Severe head injury is the most common known cause in young adults. For middle-age individuals, strokes, tumors and injuries are more frequent catalysts.
How to get rid of epilepsy?
Nerve Stimulation. Surgery. After you’re diagnosed with epilepsy, you have several ways to get treatment. Medication, a special diet, an implant that works on your nerves or brain, and surgery could all help you feel better.
How does a neurostimulator work?
It looks for patterns in your brain activity that can lead to a seizure. When the neurostimulator sees one of these patterns, it sends out a little pulse to interrupt it.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
More serious side effects can be: 1 Severe rash 2 Inflammation in organs like your liver 3 Depression
Do you need a blood test for epilepsy?
While you’re taking it, the doctor will want you to get blood tests to see how your body handles the treatment. How often you need them depends on your type of epilepsy medication, other drugs you take, and any health conditions you might have.
How does a vagus nerve stimulator work?
Your doctor will put a small device called a vagus nerve stimulator under the skin of your chest, and connect it to the nerve. The device sends small bursts of electricity through the nerve to your brain. You’ll probably still have to take medication.
Can you stop taking medication on your own?
If you have any concerns about side effects from your medication, do not just stop taking the medication on your own or skip a dose without talking to your doctor first. How to Get Off Your Medication. Some people are able to stop their seizure medication. This should only be done with your doctor’s advice and help.
Can you take more than one medication for epilepsy?
Drugs that work for one person might not work for another. You might have to try more than one. Most people who take medication for epilepsy find a good fit on the first or second try. You might have to start with a low dose and slowly add more. It depends which medication you take.

Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Doctors generally begin by treating epilepsy with medication. If medications don't treat the condition, doctors may propose surgery or another type of treatment.