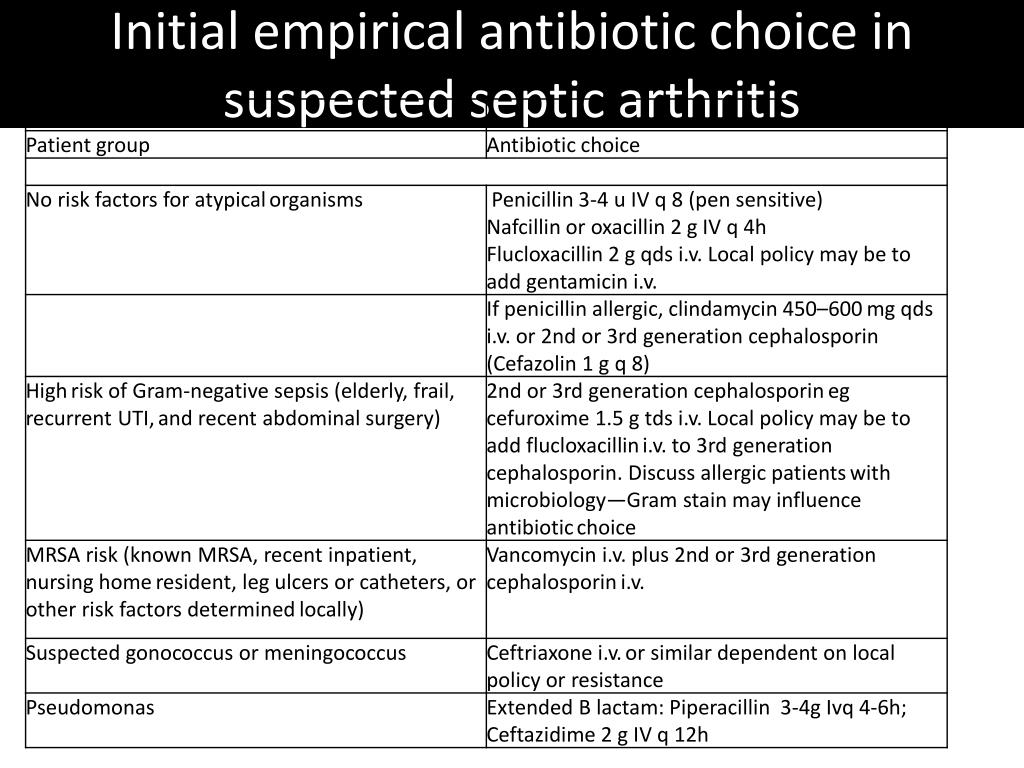
What is the optimal duration of antibiotic therapy?
Therefore, this study aimed to investigate antibiotic susceptibility profiles to identify effective empiric antibiotic treatment for early-, delayed-, and late-onset FRI. Patients treated for FRI from 2013 to 2020 were grouped into early (<2 weeks), delayed (3-10 weeks), and late (>10 weeks) onset of infection.
What illnesses require antibiotic therapy?
Recommendations for Empiric Antimicrobial Therapy in Children at UCSF Benioff's Children's Hospitals. These guidelines are consensus recommendations from the Infectious Diseases groups at UCSF Benioff Childrens' Hospitals San Francisco and …
What is the difference between an antibiotic and penicillin?
Appropriate empirical antibiotic treatment is associated with a better survival and shortened duration of hospital stay in medical patients with bacterial infections. Benefit of appropriate empirical antibiotic treatment: thirty-day mortality and duration of hospital stay. Am J Med.
What antibiotic is best for infection?
empirical treatment. Treatment given without knowledge of the cause or nature of the disorder and based on experience rather than logic. Sometimes urgency dictates empirical treatment, as when a dangerous infection by an unknown organism is treated with a broad-spectrum antibiotic while the results of bacterial culture and other tests are awaited.

What is meant by empirical antibiotic treatment?
Empiric antimicrobial therapy is directed against an anticipated and likely cause of infectious disease. It is used when antimicrobials are given to a person before the specific bacterium or fungus causing an infection is known.
Which antibiotics are empirical?
The most commonly used antibiotic for both empirical and adjusted therapy was amoxicillin/clavulanate (Table 2). Broad-spectrum antibiotics (cefepime, imipenem, meropenem, piperacillin/tazobactam) or vancomycin were initially administered to 95 patients (17.6%).Mar 26, 2007
What is an example of empiric therapy?
For example, in an otherwise healthy young adult with suspected bacterial meningitis who is seen in the emergency department, the most likely pathogens would be Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis, and thus a combination of a third-generation cephalosporin (ceftriaxone) plus vancomycin would be ...
What is the difference between prophylactic and empirical?
Antibiotic prophylaxis is the use of antibiotics (usually) before surgery, to prevent a bacterial infection. Empiric antibiotic therapy is often given to patients who have a proven or suspected infection, but where the responsible organism(s) or bacteria have not yet been identified.Aug 7, 2020
When should empirical antibiotic therapy be reviewed?
The need for antibiotics and their route of administration should be reviewed daily. A definite decision regarding treatment should be taken at 2 and 5 days. When clinically reasonable, consider changing from IV to oral therapy.
What is empiric antiviral therapy?
Empirical antiviral therapy ensures that all patients receive treatment promptly, at a cost equivalent to that of diagnostic tests alone, but results in the receipt of treatment by many patients without influenza.Jan 1, 2009
What is empiric broad spectrum antibiotics?
Empiric antibiotic therapy refers to the use of antibiotics to treat a suspected bacterial infection despite lack of a specific bacterial diagnosis. Definitive diagnosis of the species of bacteria often occurs through culture of blood, sputum, or urine, and can be delayed by 24 to 72 hours.
Is doxycycline an antibiotic?
Doxycycline: antibiotic to treat bacterial infections - NHS.
What factors are considered when making empiric antibiotic decisions?
Next, decide on the appropriate empiric antibiotic treatment regimen based on what you think the source of infection is and relevant patient factors such as severity of illness, immunocompromised status, history of drug-resistant infections, and presence of a severe penicillin allergy.
Which two antibiotics should not be prescribed with oral contraceptives?
When taking rifampin, oral contraceptives cannot be relied upon and a second method of contraception is mandatory. Amoxicillin, ampicillin, griseofulvin, metronidazole and tetracycline have been associated with contraceptive failure in three or more clinical cases.
What determines the choice of an antibiotic?
Antibiotic choice is guided by the probable causal bacteria Identification of the causal bacterium is not easy in primary care, because GPs cannot necessarily perform bacterial tests during consultations.Dec 20, 2019
What is empirical treatment?
empirical treatment. Treatment given without knowledge of the cause or nature of the disorder and based on experience rather than logic. Sometimes urgency dictates empirical treatment, as when a dangerous infection by an unknown organism is treated with a broad-spectrum antibiotic while the results of bacterial culture and other tests are awaited.
Is antihistamines an empirical treatment?
Sex, drugs, bugs, and age: rational selection of empirical therapy for outpatient urinary tract infection in an era of extensive antimicrobial resistance. For adults with this type of cough, monotherapy with antihistamines as an empirical treatment is recommended by American and European guidelines, including the American College ...
What are the strategies to optimise the use of antibiotics?
Several strategies to optimise the use of antibiotics have been developed. Most of these interventions can be classified as educational or restrictive. Restrictive measure s are considered to be more effective, but the enforcement of these measures may be difficult and lead to conflicts with prescribers. Any intervention should be aimed ...
What are the covariates of antibiotic therapy?
The covariates considered for the empirical antibiotic therapy multivariate analysis were gender, age, neurological ward, involvement of infectious disease consultants, renal failure , use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, and superficial skin infections.
What are the internal guidelines for pneumonia?
These internal guidelines include recommendations on diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia, sepsis, endocarditis, urinary tract infections, infections of the central nervous system, intravascular catheter-related infections, fever in neutropenic patients, and on empirical therapy in patients with suspected infection.
Where were the geriatrics treated?
They were treated as in-patients on the emergency department ward, or transferred to the departments of internal medicine ( including neurology and geriatrics), surgery, or to an intensive care unit, either directly after admission, or subsequently from the emergency department ward .
Is antibiotic therapy inappropriate?
The rate of inadequate antibiotic therapies was similar to the rates reported from other institutions despite the absence of a restrictive antibiotic policy. Surprisingly, adjusted antibiotic therapies were more frequently inappropriate than empirical therapies. Interventions aiming at improving antibiotic prescribing should focus on both initial empirical therapy and streamlining and adjustment of therapy once microbiological results become available.
Can antibiotics be prescribed in a hospital?
Antibiotics available within the hospital are listed in the drug formulary. All drugs included in the formulary can be prescribed without restrictions. In addition, the hospital pharmacy provides drugs which are not in the formulary upon request, although physicians are encouraged to use listed agents.
Is broad spectrum antibiotics considered adequate therapy?
In contrast, a change of antibiotic therapy according to results of microbiological investigations was associated with adequate therapy. The association between use of broad-spectrum antibiotics or vancomycin and inadequate empirical therapy confirms that the use of these medications is often unjustified.
Empirical Antibiotic Treatment for Community-acquired Pneumonia
Disclosure: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abstract
At the time of diagnosis in patients with community-acquired pneumonia, the causative pathogen is rarely known. As a result, antibiotic therapy is most often empirical, with the intent to treat a wide variety of possible causative pathogens.
What is antimicrobial therapy?
Antimicrobial agents are some of the most widely, and often injudiciously, used therapeutic drugs worldwide. Important considerations when prescribing antimicrobial therapy include obtaining an accurate diagnosis of infection; understanding the difference between empiric and definitive therapy; identifying opportunities to switch ...
When should empiric therapy be initiated?
In critically ill patients, such as those in septic shock, febrile neutropenic patients, and patients with bacterial meningitis, empiric therapy should be initiated immediately after or concurrently with collection of diagnostic specimens.
When is the antimicrobial procedure useful?
This procedure is useful when the organism burden is very high or in the management of abscesses, for which the penetration and activity of antimicrobial agents are often inadequate. Other therapies used in the treatment of infectious diseases involve modulating the host inflammatory response to infection.
When a patient does not benefit from antimicrobial therapy chosen on the basis of clinical presentation, are additional investigations needed
Similarly, when a patient does not benefit from antimicrobial therapy chosen on the basis of clinical presentation, additional investigations are needed to determine the etiologic agent or exclude noninfectious diagnoses.
What is the difference between antibacterial and bactericidal?
A commonly used distinction among antibacterial agents is that of bactericidal vs bacteriostatic agents. Bactericidal drugs, which cause death and disruption of the bacterial cell, include drugs that primarily act on the cell wall (eg, β-lactams), cell membrane (eg, daptomycin), or bacterial DNA (eg, fluoroquinolones).
Why is combination therapy used for HIV?
This is why combination drug therapy is used as the standard for treatment of infections such as tuberculosis and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) when treatment duration is likely to be prolonged, resistance can emerge relatively easily, and therapeutic agents are limited.
Do antimicrobials have a wide therapeutic index?
Fortunately, most antimicrobial agents have a wide therapeutic index,20allowing standard doses to be used, with predictable modifications on the basis of age, weight, and renal and hepatic function. However, certain antimicrobial agents require monitoring of serum levels because the therapeutic window is narrow.
