What does EEG measure in psychology?
An EEG is a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain. During the procedure, electrodes consisting of small metal discs with thin wires are pasted onto your scalp. The electrodes detect tiny electrical charges that result from the activity of your brain cells.
Are You sedated for an EEG?
Neurofeedback, also known as EEG (electroencephalogram) biofeedback, is a therapeutic intervention that provides immediate feedback from a computer-based program that assesses a client’s brainwave...
Does an EEG use radiation?
Neurofeedback, formerly called electroencephalographic (EEG) biofeedback, and occasionally referred to as neurotherapy, is an intervention for ADHD based on findings that many individuals with ADHD show low levels of arousal in frontal brain areas, with excess of theta waves and deficit of beta waves. Supporters of this treatment suggest that the brain can be trained to …
How does an EEG diagnose epilepsy?
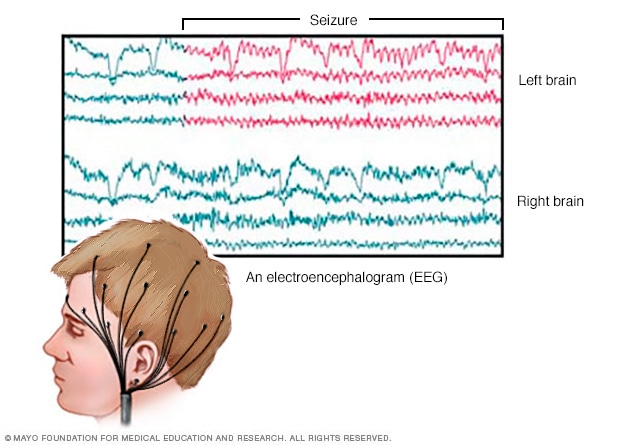
Oct 07, 2021 · Electroencephalogram (EEG). This is the most common test used to diagnose epilepsy. In this test, electrodes are attached to your scalp with a paste-like substance or cap. The electrodes record the electrical activity of your brain.

What is an EEG?
An EEG is a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain. During the procedure, electrodes consisting of small metal discs with thin wires are pasted onto your scalp. The electrodes detect tiny electrical charges that result from the activity of your brain cells.
Why do we need an EEG?
The EEG may also be used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain (for example, to evaluate trauma, drug intoxication, or extent of brain damage in comatose patients). The EEG may also be used to monitor blood flow in the brain during surgical procedures. There may be other reasons for your healthcare provider to recommend an EEG.
How long should a child sleep before a sex test?
Children may not be allowed to sleep for more than 5 to 7 hours the night before. Avoid fasting the night before or the day of the procedure. Low blood sugar may influence the results. Based on your medical condition, your healthcare provider may request other specific preparations.
What causes low blood sugar?
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) caused by fasting. Body or eye movement during the tests (but this will rarely, if ever, significantly interfere with the interpretation of the test) Lights, especially bright or flashing ones. Certain medicines, such as sedatives.
How many electrodes are used in an EEG?
Generally, an EEG procedure follows this process: You will be asked to relax in a reclining chair or lie on a bed. Between 16 and 25 electro des will be attached to your scalp with a special paste, or a cap containing the electrodes will be used. You will be asked to close your eyes, relax, and be still.
Can EEG cause seizures?
In rare instances, an EEG can cause seizures in a person with a seizure disorder. This is due to the flashing lights or the deep breathing that may be involved during the test. If you do get a seizure, your healthcare provider will treat it immediately.
What to do before a blood test?
Ask your healthcare provider to tell you what you should do before your test. Below is a list of common steps that you may be asked to do. Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure to you and you can ask questions. You will be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the procedure.
What is an EEG used for?
EEGs are usually done to detect seizures and to diagnose epilepsy, but they can be used to evaluate or diagnose other conditions, such as sleep disorders or brain injuries. EEGs are also often used to monitor brain activity in someone who is in an induced coma or undergoing certain types of surgery. An EEG may be ordered by a general practitioner ...
What is an EEG?
After the Test. Results. An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive test that records electrical activity in the brain. It works by picking up abnormal brain waves via electrodes that are attached to the scalp. EEGs are usually done to detect seizures and to diagnose epilepsy, but they can be used to evaluate or diagnose other conditions, ...
How many types of EEG are there?
Your experience will be based on your specific situation. Very generally speaking, however, there are two basic types of EEG: 6
Where is an EEG performed?
In most cases, an EEG test is an outpatient procedure performed in a doctor's office, hospital, lab, or clinic. In some cases of extended monitoring, you may need to be admitted to the hospital for a few days.
How long does it take to do an EEG?
In general, a routine EEG can take as little as 20 to 30 minutes as an outpatient procedure, or as many as 24 hours to several days in a hospital, so that brain waves can be measured during sleep. This is sometimes referred to as a prolonged or 24-hour EEG 6 .
Can you eat before an EEG?
On the day of an EEG, or for at least eight to 12 hours beforehand, you should not eat or drink anything that contains caffeine, such as coffee, tea, or cola, as it can affect the test. However, it's important that you not fast the night before or day of your test. Low blood sugar can interfere with your results. 7 .
What is an EEG for seizures?
Sleep disorders caused by seizures. For this purpose, an EEG may be done in conjunction with a standard sleep study called a polysomnogram, which monitors sleep stages and cycles to identify disruptions in sleep patterns, and why they may be occurring.
What is neurofeedback therapy?
Neurofeedback, also known as EEG (electroencephalogram) biofeedback, is a therapeutic intervention that provides immediate feedback from a computer-based program that assesses a client’s brainwave activity. The program then uses sound or visual signals to reorganize or retrain these brain signals.
How long does neurofeedback therapy last?
Neurofeedback therapy typically consists of once-a-week sessions for an average of 20 weeks. Some people need fewer sessions, while others require more. While you are sitting in a chair, the therapist will attach sensors to your scalp.
What is the name of the device that measures the brain's electrical activity?
The human brain emits electrical activity in waves that can be measured by a device called an electroencephalograph (EEG). When the results of an EEG measurement are analyzed, scientists are able to identify certain brain wave patterns recorded by the machine. There are several frequencies of brain waves when we are awake;
What is neurofeedback therapy?
Neurofeedback, formerly called electroencephalographic (EEG) biofeedback, and occasionally referred to as neurotherapy, is an intervention for ADHD based on findings that many individuals with ADHD show low levels of arousal in frontal brain areas, with excess of theta waves and deficit of beta waves. Supporters of this treatment suggest that the ...
How does neurofeedback work?
Neurofeedback treatment involves placing electrodes on a person’s head to monitor brain activity. Feedback is given to the patient with cues that can be as simple as an audio beep or as complex as a video game. When the brainwaves are of the desired frequency, the beep may inform the patient, or the character in the game will move in ...
What does OP mean in medical?
Option (OP) applies to recommendations that are acceptable based on emerging empirical evidence or clinical opinion, but lack strong empirical evidence and/or clinical consensus. Not Endorsed (NE) applies to practices that are known to be ineffective.
What are confounding variables?
Confounding variables: Treatments other than the one being studied may not be accounted for and could distort the results (an example would be a person with ADHD who is taking medication to treat the condition and the investigators not accounting for the effects of the medication treatment); Small sample sizes ;
Does neurofeedback help with ADHD?
The concept of neurofeedback as an intervention for ADHD is based on data showing that many individuals with ADHD have more slow-wave (especially theta) power in their EEG than those without ADHD, and conversely, less beta power.
What is EEG brain activity?
EEG brain activity. An EEG records the electrical activity of your brain via electrodes affixed to your scalp. EEG results show changes in brain activity that may be useful in diagnosing brain conditions, especially epilepsy and other seizure disorders. CT scanner.
What is high density EEG?
High-density EEG. In a variation of an EEG test, your doctor may recommend high-density EEG, which spaces electrodes more closely than conventional EEG — about a half a centimeter apart. High-density EEG may help your doctor more precisely determine which areas of your brain are affected by seizures.
How to diagnose epilepsy?
To diagnose your condition, your doctor will review your symptoms and medical history. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose epilepsy and determine the cause of seizures. Your evaluation may include: A neurological exam. Your doctor may test your behavior, motor abilities, mental function and other areas to diagnose your condition ...
What test is used to diagnose epilepsy?
Your doctor may also suggest tests to detect brain abnormalities, such as: Electroencephalogram (EEG). This is the most common test used to diagnose epilepsy. In this test, electrodes are attached to your scalp with a paste-like substance or cap. The electrodes record the electrical activity of your brain.
How to get rid of seizures in epilepsy?
Medication. Most people with epilepsy can become seizure-free by taking one anti-seizure medication, which is also called anti-epileptic medication. Others may be able to decrease the frequency and intensity of their seizures by taking a combination of medications.
What to do if you have a migraine?
Tell your doctor if you have migraines. Doctors may prescribe one of the anti-epileptic medications that can prevent your migraines and treat epilepsy.
What is the procedure for seizures?
When medications fail to provide adequate control over seizures, surgery may be an option. With epilepsy surgery, a surgeon removes the area of your brain that's causing seizures. Doctors usually perform surgery when tests show that: Your seizures originate in a small, well-defined area of your brain.
Why is EEG important?
Because EEG records brain activity in real time, the technique can be useful in diagnosing certain neurological conditions, such as epilepsy and sleep disorders, or for identifying the presence of a brain tumor.
When was EEG invented?
First invented in 1929, EEG now comes in a variety of forms and is used for diverse purposes, including diagnostic tests, scientific research, brain mapping, and a growing number of consumer applications. Image 2: On the left, a child wearing semi-dry water-based EEG cap ( Bitbrain Versatile EEG 32 ).
How to diagnose ADHD?
Doctors diagnosing ADHD will assign the condition to one of three varieties: 1 Inattentive type: symptoms cluster around attention-related issues (e.g., inability to focus on school or work, difficulty organizing tasks, forgetfulness). 2 Hyperactive/impulsive type: symptoms primarily relate to hyperactivity (e.g., excessive fidgeting, speaking at inappropriate times, inability to sit still). 3 Combined type: a combination of the above.
What is ADHD psychiatric?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, or ADHD, is a psychiatric condition characterized by an inability to focus, impulsivity, or excessive movement (hyperactivity). (APA 2017) Despite being a relatively common condition, the neurobiological causes of ADHD have not been fully defined. As such, researchers are working toward techniques ...
What is cognitive rehabilitation?
Cognitive rehabilitation, based on brain-computer interface (BCI) neurotechnology, can help with some psychiatric and psychological conditions besides ADHD, such as depression. In addition, any person without medical needs can also enhance normal cognitive capabilities such as memory or attention.
What are the early symptoms of ADHD?
Early symptoms may include forgetfulness, excessive fidgeting, difficulty taking turns, or carelessness. ( CDC 2021) Though research shows that ADHD is driven partially by genetic factors, the underlying causes of the condition have not been fully characterized.
Who is Caitlin Shure?
Caitlin Shure is a scholar and writer exploring the intersection of neuroscience, technology, and society. Her research investigates the cultural and ethical implications of modern neurotechnology, as well as the historical provenance of these tools.
What is neurofeedback in psychology?
Similarly, neurofeedback signals a convergence of psychiatry and neurology in bioelectrical approaches to treating affective disorders. By stabilizing the brain and rewarding it for holding particular states, neurofeedback acts as a natural anticonvulsant.".
Who is Joel Lubar?
While Joel Lubar, Ph.D., professor of psychology at University of Tennessee in Knoxville, recognizes the shortage of randomized trials on neurofeedback, he told PT that matched-group studies conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki are more appropriate than controlled trials for studying hyperactivity.
Is EEG neurofeedback effective?
Additional research suggests that EEG neurofeedback may be an effective alternative to psychostimulants in the treatment of ADHD if medication is ineffective or has adverse effects or if patients are noncompliant (Rossiter and La Vaque, 1995).
Is neurofeedback a controlled trial?
Although neurofeedback remains an investigational therapy (Baydala and Wikman, 2001), the growing number of case studies on this therapy are compelling enough to warrant controlled clinical trials with adequate sample sizes that can generate replicable data.
Is neurofeedback a good adjunct therapy?
Neurofeedback, a way for patients to learn to create and maintain desirable brainwaves, may be an affective adjunct therapy for many psychiatric disorders. Which procedures are most effective, and what are the benefits and risks?

Why It's Done
A test to monitor the electric sensitivity of the brain and thereby detect disorders if any, using electrodes.
Type: Imaging
Duration: Within a day
Results available: Almost immediate
Conditions it may diagnose: Brain tumor · Stroke · Traumatic brain injury · Encephalitis · Dementia
Is Invasive: Noninvasive
Risks
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
- An EEG can determine changes in brain activity that might be useful in diagnosing brain disorders, especially epilepsy or another seizure disorder. An EEGmight also be helpful for diagnosing or treating the following disorders: 1. Brain tumor 2. Brain damage from head injury …
Results
- EEGsare safe and painless. Sometimes seizures are intentionally triggered in people with epilepsy during the test, but appropriate medical care is provided if needed.
Clinical Trials
- Food and medications
1. Avoid anything with caffeine on the day of the test because it can affect the test results. 2. Take your usual medications unless instructed otherwise. - Other precautions
1. Wash your hair the night before or the day of the test, but don't use conditioners, hair creams, sprays or styling gels. Hair products can make it harder for the sticky patches that hold the electrodes to adhere to your scalp. 2. If you're supposed to sleep during your EEGtest, your doct…
Purpose of Test
- During the test
You'll feel little or no discomfort during an EEG. The electrodes don't transmit any sensations. They just record your brain waves. Here are some things you can expect to happen during an EEG: 1. A technician measures your head and marks your scalpwith a special pencil to indicate wher… - After the test
The technician removes the electrodes or cap. If you had no sedative, you should feel no side effects after the procedure, and you can return to your normal routine. If you used a sedative, it will take time for the medication to begin to wear off. Arrange to have someone drive you home. …
Risks and Contraindications
- Doctors trained to analyze EEGs interpret the recording and send the results to the doctor who ordered the EEG. Your doctor might schedule an office appointment to discuss the results of the test. If possible, bring along a family member or friend to the appointment to help you remember the information you're given. Write down questions to ask your doctor, such as: 1. Based on the r…
After The Test
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
Interpreting Results
Test Overview
- For most people, an EEG is perfectly safe and poses no significant risks. Note that the electrodes used for an EEG only pick up electrical charges; they do not emit electricity and are harmless. In rare instances, an EEG can cause seizures in a person with a seizure disorder, which are brought on by deep breathing or flashing lights or if the person took less or none of their medication for t…
Why It Is Done
- You can resume your normal activities after your test is done. You'll probably want to wash your hair to get rid of any remaining glue. You may find that your scalp is red and irritated in the spots where the electrodes were placed. This should not last long. Your healthcare provider will inform you as to when you may resume medicines you stopped taking before the test, if any.
How to Prepare
- The results of your EEG will be sent to a neurologist to be interpreted, who will convey them to the doctor who ordered your test. This will affect how long you will have to wait: You may hear back from your healthcare provider within a day or so, or it could be as long as week or two. An EEG will come back as either normal or abnormal. In other words, it will show that you did not have abnor…
How It Is Done
- An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test that measures and records the electrical activity of your brain by using sensors (electrodes) attached to your scalp with a paste and connected by wires to a computer. The computer records and displays your brain's electrical activity on the screen or on paper as wavy lines. Certain conditions, such as seizur...
How It Feels
- An electroencephalogram (EEG) may be done to: 1. Help confirm the diagnosis of epilepsy and determine the best treatment option based on seizure type. 2. Identify and locate a suspected brain lesion such as: tumor, inflammation and infection. 3. Evaluate periods of unconsciousness or dementia. 4. Help predict a person's chance of recovery after a change in consciousness. 5. S…
Results
- Before the day of the electroencephalogram (EEG) test, your doctor will need to know what medications you are taking. Avoid foods that contain caffeine (such as coffee, tea, cola, and chocolate) for at least 8 hours before the test. Eat a small meal shortly before the test, because low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) may produce an abnormal test. Since the electrodes are attach…