
What are the long term effects of ECT treatment?
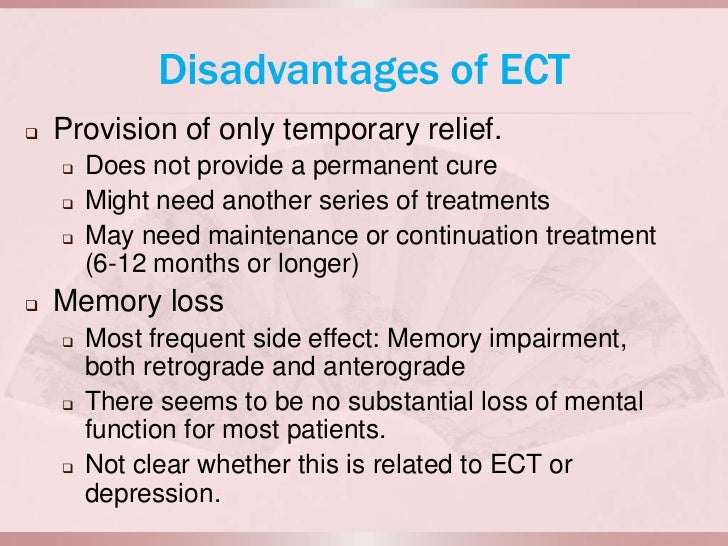
longer-term side effects. Many people experience memory loss after having ECT. Some people find this only lasts for a short time and their memories gradually return as they recover from ECT.
What are the pros and cons of ECT?
“While ECT can sometimes cause people to lose some past memories, we’ve become much better at mitigating that, and it’s less common and much less severe,” said Seiner, explaining unilateral placements of electrodes and the use of “ultra-brief pulses” better emulate how the brain works, so clinicians can induce seizures with less electricity and fewer side effects.
What are the long term effects of ECT?
What are the long term side effects of ECT? Side effects of ECT can include slight memory loss, adverse reactions to anesthesia, hyper- and hypotension, and ongoing heart issues throughout life. Though these side effects are rare and can often be prevented through proper pre-diagnosis, they do add to the controversy of ECT therapy.
What are the dangers of ECT?
“ECT (electroconvulsive treatment) damages the brain and mind. In many cases, it results in huge permanent gaps in memory for important life events, educational background, and professional skills. The individual may even lose his or her identity.
See more

What are the benefits and risks of ECT?
Pain relief and anti-nausea medication can help reduce these unwanted effects. Complications of ECT are rare, and unlikely to be life threatening. As with any procedure performed under anesthesia, there is a risk of serious heart problems or other reactions to anesthesia.
What does an ECT do to the brain?
During ECT, a small amount of electrical current is passed through the brain while the patient is under general anesthesia. This current causes a seizure that affects the entire brain, including the parts that control mood, appetite, and sleep.
What is the success rate of ECT therapy?
Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total of six to twelve sessions. Some patients may need more or fewer treatments. These sessions improve depression in 70 to 90 percent of patients, a response rate much higher than that of antidepressant drugs.
Can ECT change your personality?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
Does ECT destroy brain cells?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
Who is a good candidate for ECT?
People who have had ECT before and responded well are good candidates for ECT. Other first-line indications for the procedure include people who are catatonic or suffering from a form of depression known as psychotic depression (depression associated with delusions and hallucinations).
Is ECT worth the risk?
Risk Assessment of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Clinical Routine: A 3-Year Analysis of Life-Threatening Events in More Than 3,000 Treatment Sessions. Background: Extensive research has reported that electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be highly effective in approximately 80% of patients suffering from depression.
When should ECT not be used?
The following strategies should not be used routinely: augmentation of an antidepressant with a benzodiazepine for more than 2 weeks as there is a risk of dependence. augmentation of an antidepressant with buspirone*, carbamazepine*, lamotrigine* or valproate* as there is insufficient evidence for their use.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity ...
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why it's done. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, ...
How often do you get ECT?
In the United States, ECT treatments are generally given two to three times weekly for three to four weeks — for a total of six to 12 treatments. Some doctors use a newer technique called right unilateral ultrabrief pulse electroconvulsive therapy that's done daily on weekdays.
How long after ECT can you drive?
However, some people may be advised not to return to work, make important decisions, or drive until one to two weeks after the last ECT in a series, or for at least 24 hours after a single treatment during maintenance therapy.
Is it safe to take ECT?
Risks. Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: Confusion. Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer.
When is ECT used?
ECT is generally used when severe depression is unresponsive to other forms of therapy. Or it might be used when patients pose a severe threat to themselves or others and it is too dangerous to wait until medications take effect. Although ECT has been used since the 1940s and 1950s, it remains misunderstood by the general public.
How does ECT work?
With ECT, an electric current is briefly applied through the scalp to the brain, inducing a seizure. In addition, alternative therapies such as yoga and hypnosis sometimes work for mild depression.
How often is ECT given?
The confusion typically lasts for only a short period of time. ECT is usually given up to three times a week for a total of two to four weeks.
What is brain stimulation?
Brain stimulation techniques such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), for example, can be used to treat major depression that hasn't responded to standard treatments. The least invasive of these techniques is called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), in which a magnetic field is created by a device held above the head, ...
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
When medication fails to ease the symptoms of clinical depression, there are other options to try. Brain stimulation techniques such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), for example, can be used to treat major depression that hasn't responded to standard treatments.
What is experimental therapy?
Experimental therapies are treatments that are not regularly used by doctors. Their safety and effectiveness are still being studied. Some experimental therapies currently being investigated for treatment of depression include: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in women: Depression is more common in women than in men.
What are some examples of alternative therapies?
Examples of alternative therapies include acupuncture, guided imagery, chiropractic treatments, yoga, hypnosis, biofeedback, aromatherapy, relaxation, herbal remedies, and massage. In general, alternative therapies by themselves are reasonable to use for mild but not more severe forms of clinical depression.
How safe is ECT?
It reduced the mortality rate to around 1 in 10,000 patients – a probability lower than that of general anaesthetic itself. As one doctor from Chicago Medical School wrote in 1997, “To put the mortal risk with ECT in proper perspective, it is only necessary to note that ECT is about 10 times safer than childbirth.”.
How was the ECT machine used?
In 1944, Emil Gelny, a psychiatrist at two mental hospitals in Lower Austria and a member of the Nazi Party, modified an ECT machine for use in the T4 euthanasia programme of the mentally ill. As World War Two was coming to a close, he added four more electrodes to an ECT machine, allowed the current to flow for minutes (not milliseconds), and murdered 149 patients whose lives were regarded as “not worth living”. Although far more people died from lethal doses of drugs or by malnutrition, Gelny’s work would cast an understandably dark shadow over ECT’s future.
How does electroconvulsive therapy help?
Electroconvulsive therapy helps patients with their symptoms in more than 80% of cases – but its stigma means it may not be helping the people it could. Eighty years ago at the University of Rome La Sapienza, doctors sent 100 volts of electricity through the head of a 39-year-old man. A week earlier, he had been found by ...
When did ECT fall out of favour?
Despite such advances, ECT would fall out of favour after the 1960s. “It was as if penicillin had somehow vanished from the medical armamentarium and a generation’s memory of its very existence had been somehow erased,” wrote Edward Shorter and David Healy, two medical historians, in 2007.
What was used instead of curare in the 1950s?
In the 1950s, succinylcholine chloride, or ‘sux’, was used instead of curare and combined with a general anaesthetic. Today, the treatment looks far different than what Plath once described.
Who was the scientist who used cardiazol to induce epileptic fits?
After hearing about cardiazol, Ugo Cerletti , the chair of the Department of Mental and Neurological Diseases at the University of Rome La Sapienza, thought he knew of a better way to induce convulsions. He had been using short, sharp bursts of electricity to induce epileptic-like fits in his study animals for years.
Can ECT cure a patient?
ECT is far from perfect. It can’t cure a patient, for example, and has to be performed every few months in order to prevent the original symptoms from returning. And there are risks of memory loss (often temporary), headaches, and jaw pain.
What is ECT therapy?
ECT, formerly called electroshock therapy , has been used to treat several psychiatric conditions since 1938. In its early use, people undergoing the treatment often experienced damage to teeth and bones and significant pre-treatment anxiety.
Why is ECT effective?
The reason for the effectiveness of ECT is unknown. The electric pulse is thought to trigger an immediate increase in dopamine and serotonin, the body’s main neurotransmitters associated with depression. ECT also causes a release of important hormones and of natural mood-elevating chemicals, known as endorphins.
What is ECT given for?
ECT is given under anesthesia in both outpatient and inpatient hospital settings. Between 70 and 90 percent of patients experience a rapid improvement in symptoms. It may also help people who are acutely ill with mania, psychosis, catatonia, agitated dementia, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidal thoughts.
How often does ECT treatment last?
ECT may help people whose depression has not responded to other treatment. In the U.S., treatment usually happens three times a week, and a treatment cycle can last from 6 to 12 treatments.
How long does an ECT pulse last?
ECT delivers a small electric pulse to the brain for 1 to 2 seconds, while an individual is under general anesthesia. This causes brain cells to fire in unison, resulting in a brief seizure. As the individual is asleep and their muscles are relaxed, the only evidence of the seizure is through the brain’s wave activity as seen on a monitor. ...
What is the effect of ECT on the body?
ECT also causes a release of important hormones and of natural mood-elevating chemicals, known as endorphins. Antidepressants stimulate a similar reaction, but it can take. Trusted Source. several weeks and different drug combinations to receive the same effect.
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy is a safe, controlled procedure for depression and other psychological disorders that have not responded to other treatments. A small amount of electric current is passed through the brain in order to cause a brief seizure.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What is the treatment for ECT?
This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
Is ECT effective for mental health?
ECT’s effectiveness in treating severe mental illnesses is recognized by the American Psychiatric Association, the American Medical Association, the National Institute of Mental Health, and similar organizations in Canada, Great Britain and many other countries. Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, ...
Is ECT good for depression?
Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, ...
What Is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)?
During ECT, patients are placed under general anesthesia. Then, electrical currents are passed through the brain to create a mild seizure, which creates changes to the neurons and chemicals in the brain.
What Is ECT Used For?
ECT is an effective treatment for severe depression. Because ECT relieves symptoms quickly, it is used with severe or suicidal depression. It is also used for people whose symptoms of depression have not been relieved by medication.
ECT Side Effects
While modern electroconvulsive therapy has fewer adverse effects than historical use, there are still some that patients may experience. These include:
Other Brain Stimulation Therapies
In addition to ECT, there are several other brain stimulation therapies that are used to treat some mental health disorders.
Is ECT Right For You?
ECT may be a treatment option for you if medications or other forms of therapy haven’t worked well. It can also be an option if a treatment is needed to act quickly to reduce the chances of suicide. If you are currently suicidal, reach out for help:
How effective is ECT for depression?
ECT is the most effective known treatment for depression with remission rates of 50-80% (give or take depending on the study), even for treatment-resistant depression.
How long does it take for ECT to go away?
These cognitive deficits have been shown to go away between 1-6 months after treatment ends.
Is ECT evil?
Are There Actually Pros to ECT? Some people will tell you that ECT is evil and there are no benefits worth the side effects. Some people will tell you that ECT is inhumane and should be banned. Some people say that anyone who gets ECT is submitting to some form of assault. All of this is poppycock.
Can bilateral ECT cause memory loss?
The more ECT you do and the more bilateral ECT you do, the greater your risk of side effects like memory loss . The positive effects of ECT may be short-lived leaving you with the choice as to whether to have ECT again. (Doctors try to prevent this by selecting medication for you when you get better that will keep you better.)
Is unilateral ECT a pro or con?
Yes, it’s that successful and painless for some. One other factor that is an ECT pro and con is that typically, unilateral ECT is tried first (there are fewer side effects) but if that isn’t effective, a stronger form of ECT (bilateral) can be tried. It’s a pro because it’s an option but it’s a con because of the increased side effects.
Is ECT covered by insurance?
ECT seems unbelievably effective in treating catatonia with a success rate of over 90% in those, severe cases. ECT is typically covered by insurance ( I wish that weren’t a factor for people but, let’s face it, it is).
Does ECT cause headaches?
ECT can produce physical pain during the treatment. This is muscular and has to do with the invoked seizure, the anaesthesia or both. Headaches are common. This pain is typically easily treated with over the counter medications or, in some cases, prescribed medication like acetaminophen with codeine.
Overview
Why It's Done
Self help information for family, friends and colleagues
- Loosen tight clothing
- Protect the person from injury
- If they have fallen, place something soft under their head
- Stay with them until they recover fully
Do not:
- Try to restrain the person
- Put anything between their teeth
- Move them, unless they are in danger
- Give them food to eat or drink
Person who have had seizure
- Avoid triggers
- Avoid unprotected heights and unsupervised areas of water
- Seizure lasts less than 5 minutes
- None of the below mentioned incidents occur during the episode
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Seizure lasts longer than five minutes
- Breathing or consciousness doesn't return after the seizure stops
- A second seizure follows immediately
- The seizure happened in water
- High fever
- Heat exhaustion
- Person is pregnant
- Person has diabetes
- Person is injured during the seizure
Risks
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. 2. Treatment-resistant depression,a severe depression that ...
Results
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…