
What is the maximum number of ECT treatments?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure in which a brief application of electric stimulus is used to produce a generalized seizure. It is not known how or why ECT works or what the electrically stimulated seizure does to the brain. In the U.S. during the 1940’s and 50’s, the treatment was administered mostly to people with severe mental illnesses.
What are the risks of ECT?
Feb 28, 2022 · Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment that involves electrically stimulating the brain. It is used for specific mental health disorders, including severe forms of major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder , that do not respond to other treatments like medication and therapy.
How successful is ECT?
Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT for short, is a treatment that involves sending an electric current through your brain, causing a brief surge of electrical activity within your brain (also known as a seizure). The aim of the treatment is to relieve the symptoms of some mental health problems. ECT is given under a general anaesthetic, so you aren't awake during the treatment.
How much does ECT therapy cost?
Dec 03, 2021 · Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), perhaps better known more crudely as “shock therapy”, is a medical treatment that’s been proven to be one of the most effective for severe depression and several other serious mental illnesses—it works for about 80% of all patients! It’s not like traditional therapy that relies on verbal communication.
How long does ECT last?
Who qualifies for ECT?
Is ECT still used today?
Is electric shock therapy painful?
Does ECT damage the brain?
Does ECT change your personality?
Does ECT worsen anxiety?
Is ECT worth the risk?
Can ECT make you worse?
Can ECT erase your memory?
A group of researchers at Rutgers University led by Dr. Donald J Lewis showed that ECT might be able to specifically erase fear memories. The researchers first made rats associate a tone with a fearful memory by playing this tone as they electrically shocked the rats' feet.Oct 1, 2017
Do they shave your head for ECT?
Does memory come back after ECT?
Is ECT a cure for mental illness?
Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, it is not a cure. To prevent a return of the illness, most people treated with ECT need to continue with some type of maintenance treatment. This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
Is ECT good for depression?
Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, ...
How long does a seizure last after ECT?
This causes a seizure within the brain that lasts for approximately a minute. The patient is asleep for the procedure and awakens after 5-10 minutes, much as from minor surgery. Most insurance plans offering coverage for psychiatric disorders at least partially reimburse the cost of ECT.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
What is TMS in medical terms?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies. It involves the use of rapidly alternating magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Unlike ECT, TMS does not cause a seizure and the patient remains awake through the noninvasive process.
How often is TMS given?
TMS is usually administered four or five times a week for four-to-six weeks. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) was developed as a treatment for seizure disorders but can also be used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure in which a brief application of electric stimulus is used to produce a generalized seizure. It is not known how or why ECT works or what the electrically stimulated seizure does to the brain. In the U.S. during the 1940’s and 50’s, the treatment was administered mostly to people with severe mental ...
Is ECT a long term treatment?
After 60 years of use, ECT is still the most controversial psychiatr ic treatment. Much of the controversy surrounding ECT revolves around its effectiveness vs. the side effects, the objectivity of ECT experts, and the recent increase in ECT as a quick and easy solution, instead of long-term psychotherapy or hospitalization.
How many people are treated with ECT?
Today, ECT is administered to an estimated 100,000 people a year, primarily in general hospital psychiatric units and in psychiatric hospitals. It is generally used in treating patients with severe depression, acute mania, and certain schizophrenic syndromes.
When is ECT administered?
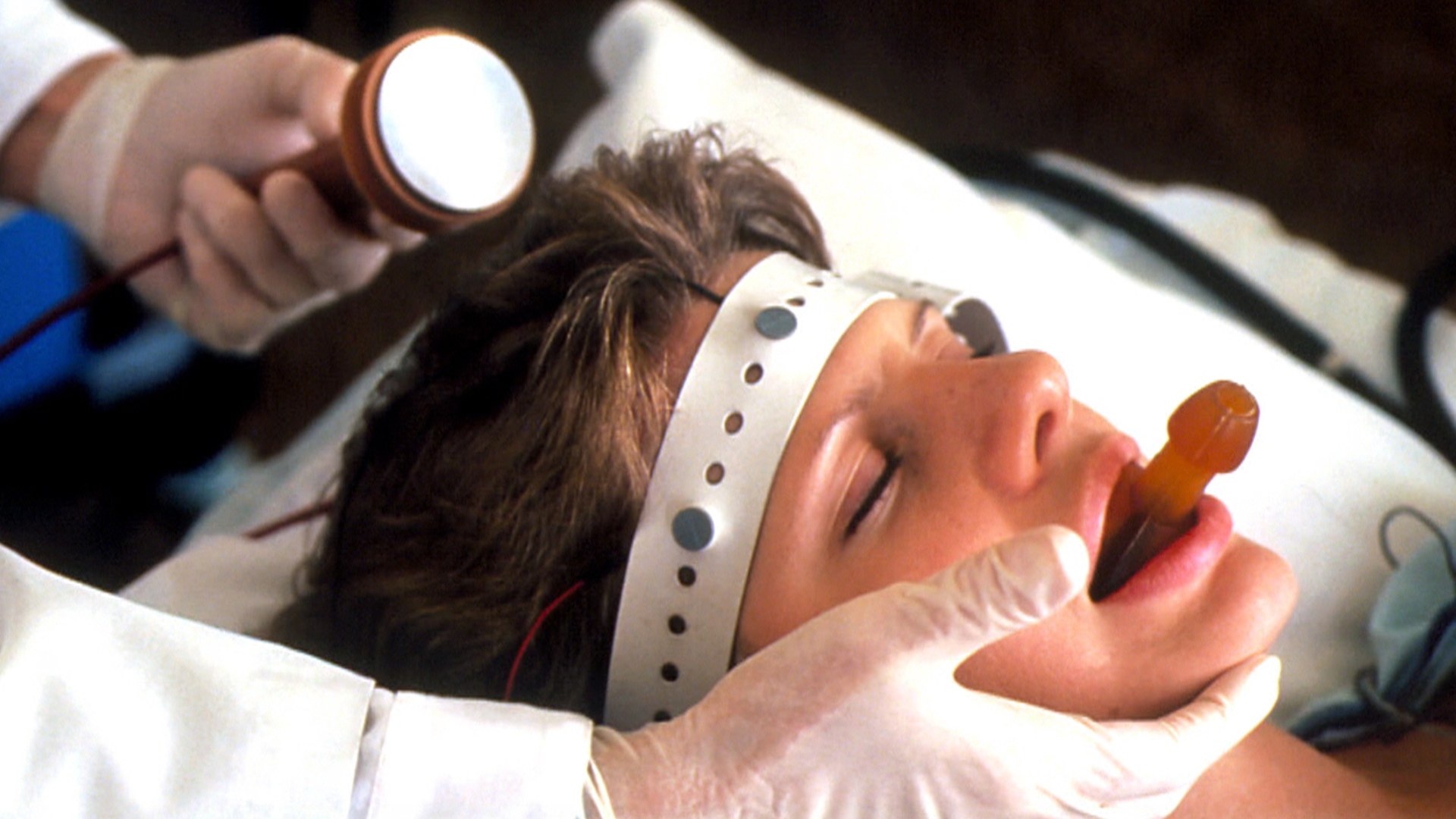
ECT treatment is generally administered in the morning, before breakfast. Prior to the actual treatment, the patient is given general anesthesia and a muscle relaxant. Electrodes are then attached to the patients scalp and an electric current is applied which causes a brief convulsion. Minutes later, the patient awakens confused ...
What is ECT therapy?
What is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT for short, is a treatment that involves sending an electric current through your brain, causing a brief surge of electrical activity within your brain (also known as a seizure).
Why is ECT used?
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends that ECT is only used to achieve quick, short-term improvements if you have: severe or life-threatening depression and your life is at risk so you need urgent treatment.
What are the benefits of ECT?
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends that ECT is only used to achieve quick, short-term improvements if you have: 1 severe or life-threatening depression and your life is at risk so you need urgent treatment 2 moderate to severe depression and other treatments such as medication and talking therapies haven't helped you 3 catatonia (staying frozen in one position, or making very repetitive or restless movements) 4 a severe or long-lasting episode of mania.
Can ECT cause memory loss?
This has sometimes been shown in films and TV shows, which may not reflect how ECT is carried out today. It can sometimes cause memory loss. This is often short-term, but can be longer-lasting as well. See our page on the side effects of ECT for more information.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a treatment for severe symptoms of depression, mania and catatonia. This section explains what ECT is, when it is used and your rights to refuse this treatment.
What is an ECT?
ECT is when electrical currents are passed through your brain to cause seizures or fits. The seizures or fits can be very small and minor. They usually last less than a minute. There are 2 types of ECT. Bilateral ECT. This is when the current is passed through both sides of your head. Unilateral ECT.
What is ECT used for?
ECT uses an electrical current which passes through your brain. The current causes a fit or seizure. Health professionals use ECT to treat severe depression, catatonia or mania. It may be considered to treat schizophrenia, but this is uncommon. Doctors may offer you ECT if other treatments don’t work or your symptoms are very bad.
Can you use ECT for schizophrenia?
Health professionals use ECT to treat severe depression, catatonia or mania. It may be considered to treat schizophrenia, but this is uncommon. Doctors may offer you ECT if other treatments don’t work or your symptoms are very bad. Your doctor may offer you ECT if they think that it will improve your symptoms.
What is ECT in medical terms?
ECT is a treatment for some mental illnesses. ECT is when electrical currents are passed through your brain to cause seizures or fits. The seizures or fits can be very small and minor. They usually last less than a minute. There are 2 types of ECT. Bilateral ECT.
How long does ECT last?
Unilateral ECT. This is when the current is only on one side of your head. ECT will last about 5 to 10 minutes. With extra time for preparation and recovery. Before you get ECT, doctors will give you muscle-relaxing medicine.
How does ECT work?
Doctors are not sure how ECT works. But they think that ECT changes the way the chemicals in your brain work. Changes to these chemicals seem to have a positive effect on some mental health symptoms. It is thought that ECT can make these chemicals work better in your brain.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) ECT is most commonly used to treat depression, but doctors also recommend it to help with schizophrenia. Compared with medications, it starts to work faster (often within a week), especially with older people. ECT can reduce chances of relapse as long as you undergo follow-up treatments.
Does ECT help with schizophrenia?
ECT is most commonly used to treat depression, but doctors also recommend it to help with schizophrenia. Compared with medications, it starts to work faster (often within a week), especially with older people. ECT can reduce chances of relapse as long as you undergo follow-up treatments.
What are the side effects of a VNS?
A VNS procedure comes with risks, such as pain around the surgical cuts, infection, and temporary paralysis of your vocal cords. Some possible side effects are: 1 Hoarseness and voice changes 2 Throat pain and difficulty swallowing 3 Coughing 4 Headaches
What to do if you have schizophrenia?
If you have schizophrenia, your psychiatrist or psychologist probably began your treatment with psychotherapy and medications. But sometimes medications are not successful enough in controlling hallucinations and other symptoms of schizophrenia.
What is the best treatment for schizophrenia?
If you have schizophrenia, your psychiatrist or psychologist probably began your treatment with psychotherapy and medications. But sometimes medications are not successful enough in controlling hallucinations and other symptoms of schizophrenia. In that case, your doctor may recommend brain stimulation therapy to support or replace medications.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
Compared with medications, it starts to work faster (often within a week), especially with older people. ECT can reduce chances of relapse as long as you undergo follow-up treatments. In one study, 77% of people with schizophrenia responded favorably to ECT.
How long does TMS last?
A session of TMS usually lasts 30 to 60 minutes. You may feel a slight knocking or tapping sensation in your head as pulses are administered. Some doctors favor TMS treatment because it focuses on a more specific area of your brain than ECT can, which minimizes side effects. Those side effects can include:
Is ECT a good treatment for schizophrenia?
ECT can be an effective therapy for treatment-re sistant mental health conditions , including depression, schizophrenia, and catatonia. It is a very old psychiatric treatment and has a controversial history. However, doctors recommend ECT for some people because it is low risk and carries few side effects.
How does ECT work?
ECT uses electric currents to stimulate a person’s brain to induce a controlled seizure. Researchers do not exactly know how ECT works, but one theory is that it could regulate neurotransmitter activity. This article looks at how ECT works, whether it is an effective treatment, and its controversial history. It also discusses some alternative ...
What is electro shock therapy?
Electroshock therapy, also known as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for severe major depression, bipolar depression, and other mental health conditions. Psychiatrists may recommend ECT when a person does not respond well to other treatments. ECT uses electric currents to stimulate a person’s brain to induce a controlled seizure.
How long is a brief pulse?
The stimulus usually consists of a brief electrical pulse, which is one in the range of 0.5–2.0 milliseconds (ms) Trusted Source. . Doctors may sometimes use ultra-brief pulses, which are under 0.5 ms. The pulse reaches the brain through electrodes on the head and induces a controlled seizure.
How long does an ECT last?
An ECT session may last for about 1 hour, which includes 15–20 minutes for the procedure and 20–30 minutes of recovery time. A person may receive ECT two or three times a week for a total of between six and 12 sessions. The frequency and number of sessions will differ among individuals depending on the severity of the condition and ...
How many times a week can you get ECT?
A person may receive ECT two or three times a week for a total of between six and 12 sessions. The frequency and number of sessions will differ among individuals depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. After the session, a person must not drive for 24 hours.
Is vagus nerve stimulation effective?
and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), can also be effective treatments for severe depression and other mental health conditions.
Does Ect Work?
- Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. ECT is sometimes used in t…
What Are The Steps Involved When Getting ect?
- Before beginning a series of ECT treatments, a patient should receive a thorough psychiatric assessment, including a medical examination and sometimes a basic blood test and an electrocardiogram (ECG) to check heart health. Informed consent is another important part of the process. A patient must provide written informed consent before ECT is administered. In situati…
What Are The Risks and Benefits?
- Like any medical procedure, ECT is has some risks. ECT treatment has been associated with short-term memory loss and difficulty learning. Some people have trouble remembering events that occurred in the weeks before the treatment or earlier. In most cases, memory problems improve within a couple of months. Some patients may experience longer lastin...
Other Brain Stimulation Treatments
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies. It involves the use of rapidly alternating magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Unlike ECT, TMS does not cause a seizure and the patient remains awake through the noninvasive process. TMS typically only has mild side effects including headaches, …
Resources
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2012. Therapies for Treatment Resistant Depression: A Review of the Research.
- National Institute of Mental Health: Brain Stimulation Therapies
- Mental Health America: Electroconvulsive Therapy
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): ECT, TMS And Other Brain Stimulation Therapies