What is the maximum number of ECT treatments?
What is the maximum number of ECT treatments? The ECT taper from an acute series to a maintenance schedule is generally once a week for 4 treatments, then every 2 weeks for 4 treatments, then every 3 weeks for 4 treatments, then every 4 weeks. There is no limit on how long a patient can receive maintenance ECT provided the treatment is effective.
How many ECT treatments are needed?
Typically the ECT treatment course lasts eight to 12 treatments -- sometimes as few as six, sometimes as many as 15 treatments can occur in a course. Your doctor will determine how many you need depending on your response. After patients have received a course of ECT they're usually placed back on medication.
What are the long term effects of ECT treatment?
longer-term side effects. Many people experience memory loss after having ECT. Some people find this only lasts for a short time and their memories gradually return as they recover from ECT.
Is ECT an Ethical Treatment?
Since ECT is considered to be an established treatment, it can be used as an active comparator in a noninferiority paradigm, avoiding the ethical dilemma of treating very ill patients with a placebo treatment.
What is ECT therapy?
What is the treatment for ECT?
What is ECT in medical terms?
What are the side effects of ECT?
What test is needed for ECT?
When is ECT used?
How many times a week do you get ECT?
See more
About this website
What is the success rate for ECT?
Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total of six to twelve sessions. Some patients may need more or fewer treatments. These sessions improve depression in 70 to 90 percent of patients, a response rate much higher than that of antidepressant drugs.
How is ECT treatment performed?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical procedure that involves passing a mild electric current through your brain, causing a short seizure. This procedure is proven to have strong positive effects on severe, treatment-resistant mental health conditions.
Is ECT life threatening?
The NHS say that ECT is generally safe. The death rate following ECT is less than that for other minor surgical procedures. There is no evidence that having ECT is more dangerous than any other procedure needing a general anaesthetic.
What are the side effects of ECT?
What are the risks and side-effects of ECT?loss of memory about the events immediately before and after ECT.heart rhythm disturbances.low blood pressure.headaches.nausea.sore muscles, aching jaw.confusion.
Are you awake during ECT?
Although you will be asleep during the treatment, the medical team will need to start preparing you for the treatment while you are still awake. The team will: Place sensors called electrodes on your head, so that they can measure the electrical activity in your brain.
Can ECT damage your brain?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
Can ECT change your personality?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
Why is ECT so controversial?
Reasons for Controversy Three reasons are given for the aversion: 1) ECT is considered old-fashioned and politically incorrect; 2) it is forced on the patient; and 3) the memory disturbances are so severe and persistent that no rational human being would undergo this procedure, no matter how well-intended.
Why is ECT a last resort?
ECT is too often considered as a last resort, rather than as a first-line treatment, a status that some states have even written into law. ECT's controversial history and the consequent reluctance of patients to accept it without trying other alternatives may also be a barrier to its increased use.
Can ECT cause death?
Conclusion: The ECT-related mortality rate was estimated at 2.1 per 100 000 treatments. In comparison, a recent analysis of the mortality of general anesthesia in relation to surgical procedures reported a mortality rate of 3.4 per 100 000. Our findings document that death caused by ECT is an extremely rare event.
Does ECT worsen anxiety?
The concern of some psychiatrists is that while ECT may help with depressive symptoms, it could worsen anxiety symptoms, including obsessional thoughts or panic attacks.
Can you feel worse after ECT?
ECT can't prevent future depression, or fix any ongoing stresses or problems that are contributing to how you're feeling. Some people have very bad experiences of ECT, for example because they feel worse after treatment or are given it without consent. You might not want to risk the possibility of getting side effects.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Benefits & Side Effects
For serious depression that does not respond to traditional medications, there are other therapies that may help. WebMD explains electroconvulsive therapy, transcranial magnetic stimulation, vagus ...
The Debate Over Electroconvulsive Therapy | Psychology Today
However, it didn't take long before doctors worldwide started using the procedure systematically as a treatment protocol, not only for mental illness, but also for criminal behavior, memory loss ...
Treatment Guideline for the Use of ECT - Beacon Health Options
ValueOptions July 3, 2007 Page 3 of 6 Pregnancy 1. ECT may be used in all three trimesters of pregnancy. 2. Obstetric consultation should be obtained prior to ECT.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity ...
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why it's done. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, ...
How often do you get ECT?
In the United States, ECT treatments are generally given two to three times weekly for three to four weeks — for a total of six to 12 treatments. Some doctors use a newer technique called right unilateral ultrabrief pulse electroconvulsive therapy that's done daily on weekdays.
How long does it take to get an ECT?
The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
What is the name of the state of intense euphoria, agitation, and hyperactivity that?
Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity that occurs as part of bipolar disorder. Other signs of mania include impaired decision-making, impulsive or risky behavior, substance abuse, and psychosis.
Is ECT safe?
ECT is much safer today. Although ECT may still cause some side effects, it now uses electric currents given in a controlled setting to achieve the most benefit with the fewest possible risks.
Why is ECT effective?
The specific reason for the positive action of ECT is unknown, but this treatment appears to have many effects. There are multiple theories to explain why ECT is effective. One theory suggests that the seizure activity itself causes an alteration of the chemical messengers in the brain known as neurotransmitters. Another theory proposes that ECT treatments adjust the stress hormone regulation in the brain, which may affect energy, sleep, appetite, and mood.
How many times a week can you get ECT?
Treatments are normally administered three times a week on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. A course of ECT normally ranges from six to twelve treatments. The average number of treatments is nine. The number of treatments that you need will be determined by the severity of your symptoms and how rapidly you respond.
How to generate a seizure with a right unilateral treatment?
To generate a seizure with a right unilateral treatment, one electrode is placed on the crown of the head and the other on the right temple. Those receiving the right unilateral treatments may respond somewhat more slowly than those who receive bilateral treatments. This difference is usually no greater than 1 to 2 treatments. Right unilateral treatment is typically associated with less memory side effects. Patients who do not respond to right unilateral treatments may require a switch to bilateral placement.
What is bilateral ECT?
Bilateral ECT treatment involves placing the electrodes on both temples. This treatment may be associated with more acute memory side effects than right unilateral treatments. Bilateral ECT is indicated for severe mental illnesses including depression with psychosis, manic episodes of bipolar disorder, psychosis related to schizophrenia and catatonia.
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
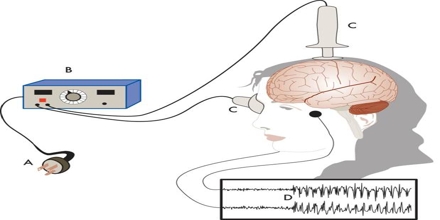
Electroconvulsive therapy involves applying a brief electrical pulse to the scalp while the patient is under anesthesia. This pulse excites the brain cells causing them to fire in unison and produces a seizure.
How many treatments for a syphilis?
It usually takes six treatments before major improvements in your symptoms are noted. However, family members, friends, and caregivers may begin to see mild improvements following the first 3 to 6 treatments. These improvements may include an increase in your activity level, improved sleeping patterns, and a mild increase in your appetite.
Why is ECT used in psychiatry?
Many years ago when psychiatry was less advanced, ECT was used for a much wider range of mental illnesses and sometimes, unfortunately, it was used to control troublesome patients. Patients who went through ECT might also have suffered broken bones before the advent of modern anesthesia and muscle paralytics.
What is ECT treatment?
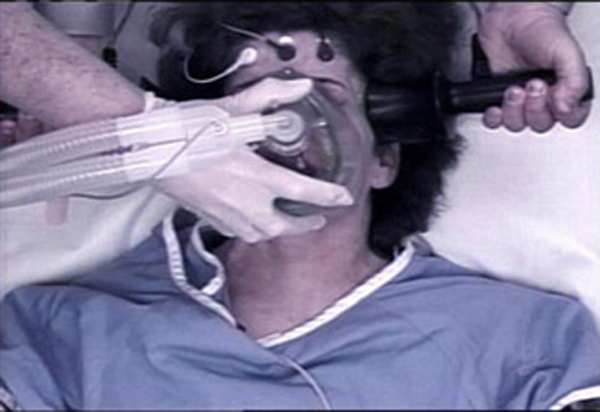
The patient is anesthetized with an intravenous injection and then injected with a drug that causes paralysis, to prevent the jerking motions of a seizure. The heart rate and other vital signs are monitored throughout the ECT treatment. (details on how shock treatment for depression works)
What is Modern ECT Like?
Today, the American Psychiatric Association has very specific guidelines for the administration of ECT. Electroconvulsive therapy is to be used only to treat severe, debilitating mental disorders and not to control behavior. In most states, written and informed consent is required. The doctor must explain in detail to the patient, and / or family, the reasons why ECT is being considered along with the potential electroconvulsive therapy side effects.
How long does an ECT last?
Clinically effective ECT seizures generally last from about 30 seconds to just over a minute. The patient's body does not convulse and the patient feels no pain. During the ECT therapy seizure, there are a series of changes in brain waves on an electroencephalogram (EEG) and when the EEG levels off, this is an indication that the seizure is over. As the patient wakes, they may experience electroconvulsive therapy side effects including: 1 Headache 2 Nausea 3 Temporary confusion 4 Muscle stiffness and pain
How does electroconvulsive therapy work?
It is thought ECT acts by temporarily altering some of the brain's electrochemical processes and helping to create new neurons.
What is ECT in medical terms?
ECT is the procedure of stimulating the brain through the use of an electrical current applied directly to the skull.
How does bilateral ECT work?
In bilateral ECT, electrodes are placed above each temple. For unilateral ECT, one electrode is placed above the temple of one side of the brain and the other in the middle of the forehead. An electrical current is then passed through the brain, inducing a grand mal seizure. Evidence of the seizure may show in twitching toes, an increased heart rate, clenched fists or a chest heave. Because current passes through more of the brain during bilateral ECT, it is more likely to cause cognitive side effects such as short-term memory loss than unilateral ECT.
What is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)?
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a very safe and effective medical treatment for certain psychiatric disorders. It is considered a form of brain neuromodulation. The treatment involves delivery of a small amount of electrical energy to your brain to induce a short seizure. Most people, on average, receive between 6 to 12 treatments for their illness to improve. While ECT will be helpful for many patients, ECT is not a panacea or cure. A response to ECT is never guaranteed.
How many treatments does ECT have?
Most people, on average, receive between 6 to 12 treatments for their illness to improve. While ECT will be helpful for many patients, ECT is not a panacea or cure. A response to ECT is never guaranteed.
What indications or diagnoses might benefit from ECT?
Major Depression including acute depression, moderate to severe depression, treatment-resistant depression, suicidal depression, and psychotic depression
Who can get ECT in California?
Any adult age 18 or older with an appropriate clinical diagnosis and who is capable of giving voluntary informed consent can receive ECT. Others, including adolescents between 13 and 17 years of age, may receive ECT after special reviews and legal procedures are followed. Nobody capable of providing informed consent can be given ECT against their will.
Where is ECT performed?
ECT is performed at the UCLA Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital in the ECT Treatment Suite.
What happens during the ECT consultation?
The patient's current medical and psychiatric history are reviewed. The ECT procedure is explained. The patient's ability to understand their illness, the procedure and possible risks and benefits are evaluated. If a person is considered a candidate for treatment, further work-up and preparation are discussed. The ECT team will coordinate care and treatment with the patient's doctors. Involvement, with patient permission, of family, friends, or significant others is encouraged.
How does ECT work?
ECT is done under medical monitoring and with general anesthesia. Researchers believe that ECT corrects the biological abnormalities that underlie severe psychiatric disorders. More than one treatment, however, is needed to achieve these positive effects. An average of 6 to 12 repeated treatments (also referred to as an "index series") is needed in order to achieve sustained improvement. However, there is no set number and treatments are individualized to the person. Response rates vary depending on the type of illness and other factors. Following a course of treatment, patients feel more like themselves again and are able to work and lead productive lives. Often, family members, doctors, or nurses may notice improvement before the patient.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What is the treatment for ECT?
This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is ECT in medical terms?
ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia. It is typically administered by a team of trained medical professionals that includes a psychiatrist, an anesthesiologist, and a nurse or physician assistant.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
What test is needed for ECT?
Before beginning a series of ECT treatments, a patient should receive a thorough psychiatric assessment, including a medical examination and sometimes a basic blood test and an electrocardiogram (ECG) to check heart health.
When is ECT used?
ECT is typically used when other treatments, including medications and psychotherapy, haven’t worked. ECT is also used for people who require a rapid treatment response because of the severity of their condition, such as being at risk for suicide.
How many times a week do you get ECT?
A patient typically receives ECT two or three times a week for a total of six to 12 treatments, depending on the severity of symptoms and how quickly the symptoms respond to the treatment.

Does Ect Work?
What Are The Steps Involved When Getting ect?
Self help information for family, friends and colleagues
- Loosen tight clothing
- Protect the person from injury
- If they have fallen, place something soft under their head
- Stay with them until they recover fully
Do not:
- Try to restrain the person
- Put anything between their teeth
- Move them, unless they are in danger
- Give them food to eat or drink
Person who have had seizure
- Avoid triggers
- Avoid unprotected heights and unsupervised areas of water
- Seizure lasts less than 5 minutes
- None of the below mentioned incidents occur during the episode
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Seizure lasts longer than five minutes
- Breathing or consciousness doesn't return after the seizure stops
- A second seizure follows immediately
- The seizure happened in water
- High fever
- Heat exhaustion
- Person is pregnant
- Person has diabetes
- Person is injured during the seizure
Other Brain Stimulation Treatments
Resources
- Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, such as bi…
Overview
- Before beginning a series of ECT treatments, a patient should receive a thorough psychiatric assessment, including a medical examination and sometimes a basic blood test and an electrocardiogram (ECG) to check heart health. Informed consent is another important part of the process. A patient must provide written informed consent before ECT is administered. In situations where a person is too ill to make decisions for him or herself, t…
Why It's Done
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies. It involves the use of rapidly alternating magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Unlike ECT, TMS does not cause a seizure and the patient remains awake through the noninvasive process. TMS typically only has mild side effects including headaches, muscle twitches and pain at the stimulation site. TMS is usually administ…
Risks
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2012. Therapies for Treatment Resistant Depression: A Review of the Research.
- National Institute of Mental Health: Brain Stimulation Therapies
- Mental Health America: Electroconvulsive Therapy
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): ECT, TMS And Other Brain Stimulation Therapies
How You Prepare
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions. ECT often works when other treatments are unsucce...
What You Can Expect
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. 2. Treatment-resistant depression,a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. 3. Severe mania,a st…
Results
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people have trouble remembering events that occurred right before treatmen…