Why is ECMO treatment so costly?
Dec 17, 2020 · There is insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in adults with COVID-19 and refractory hypoxemia. Rationale. ECMO has been used as a short-term rescue therapy in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) caused by COVID-19 and refractory hypoxemia.
How long can you live on ECMO?
ECMO is only a “life-sustaining treatment.” It does not cure or treat the disease or injury that led to heart and/or lung failure. This means it is a treatment that can prolong life to allow for more time to try to fix the problem. Sometimes patients do not get better while they are on ECMO because their disease or injury cannot be fixed.
Is ECMO considered life support?
Oct 21, 2020 · Adults and children are treated with ECMO for severe heart or lung conditions including: Heart failure. High blood pressure in the lungs, or pulmonary hypertensive crisis. Massive blood clot in the lungs, or pulmonary embolism. Patients awaiting a transplant or ventricular assist device placement. ...
Do people survive ECMO?
Sep 24, 2021 · Cardiac failure — Venoarterial (VA) ECMO can provide acute support in cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest in adults. Assuming that the brain function is normal or only minimally impaired, ECMO is provided until the patient recovers or receives a long-term ventricular assist device as a bridge to cardiac transplantation.

Why do adults need ECMO?
People who need ECMO have a severe and life-threatening illness that stops their heart or lungs from working properly. For example, ECMO is used during life-threatening conditions such as severe lung damage from infection, or shock after a massive heart attack.
How long can a person live on ECMO?
Where once about 60% of such patients survived at least 90 days in spring 2020, by the end of the year just under half of COVID patients on ECMO survived that long.Sep 29, 2021
What qualifies you for ECMO?
Who is eligible to receive ECMO ? At Mayo Clinic only people who are hospitalized may receive ECMO . It might be an option for people who haven't responded to other life-support measures, such as medications or ventilators.Feb 16, 2022
Is ECMO the same as life support?
ECMO is the highest level of life support — beyond a ventilator, which pumps oxygen via a tube through the windpipe, down into the lungs. The ECMO process, in contrast, basically functions as a heart and lungs outside the body.Sep 10, 2021
Can ECMO cause brain damage?
A meta-analysis of 135 adults from 20 separate publications who received ECMO following cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) noted that neurological sequelae were “poorly described in the reviewed literature.”5 At the extreme, brain death occurred in 7% to 21% of cases of ECMO-treated adults in some academic centers.Aug 8, 2011
Does ECMO hurt?
Does ECMO hurt? Generally no. Patients that undergo ECMO are typically already connected to a ventilator through a breathing tube down their mouth or nose and have received pain medications and sedatives.
Who is not a good candidate for ECMO?
Relative contraindications for VA ECMO include: Severe irreversible non‐cardiac organ failure limiting survival (i.e., severe anoxic brain injury) Irreversible cardiac failure if transplantation or long‐term ventricular assist device (VAD) will not be considered. Severe aortic insufficiency.
Can you be awake on ECMO?
Awake ECMO is ECMO without mechanical ventilation in spontaneously breathing patients. These patients are maintained awake through the ECMO run [3]. Many centres in India are still in the early stage of gaining experience with ECMO.Jan 18, 2021
What is the quality of life after ECMO?
The mortality was high in the first three months after treatment (17% of the ECMO survivors died in the first 90 days). This time point served as a cut-off to define late survival. In patients who were alive at 90 days, 87% were alive five years later.Mar 29, 2019
How long can a person be on a ventilator in an ICU?
Some people may need to be on a ventilator for a few hours, while others may require one, two, or three weeks. If a person needs to be on a ventilator for a longer period of time, a tracheostomy may be required.Jun 2, 2020
What is the longest someone has been on ECMO?
Hamm was on ECMO for 147 days, a remarkably long time. Hamm was on ECMO for 147 days, a remarkably long time. (Photography: Steve Wood)Ricky Hamm is no stranger to UAB Hospital. A medevac helicopter pilot, he has been flying ill and injured patients to UAB for 17 years.Jul 16, 2021
What are the chances of survival after being on a ventilator?
On the ventilator Your risk of death is usually 50/50 after you're intubated. When we place a breathing tube into someone with COVID pneumonia, it might be the last time they're awake. To keep the patient alive and hopefully give them a chance to recover, we have to try it.Dec 27, 2021
When is ECMO used?
ECMO is used when life support is needed after surgery, or when you are very ill and your heart or lungs need help so that you can heal. Your doctor will decide when it may be helpful. If you need ECMO, your doctor and trained respiratory therapists will prepare you.
What are the risks of ECMO?
The most common risks that may occur with ECMO include: 1 Bleeding 2 Blood clot (thromboembolism) 3 Blood clotting disorder (coagulopathy) 4 Infection 5 Loss of blood in hands, feet or legs (limb ischemia) 6 Seizures 7 Stroke (part of the brain is damaged by loss of blood or by a blood vessel that bursts)
Where does extracorporeal membrane oxygenation take place?
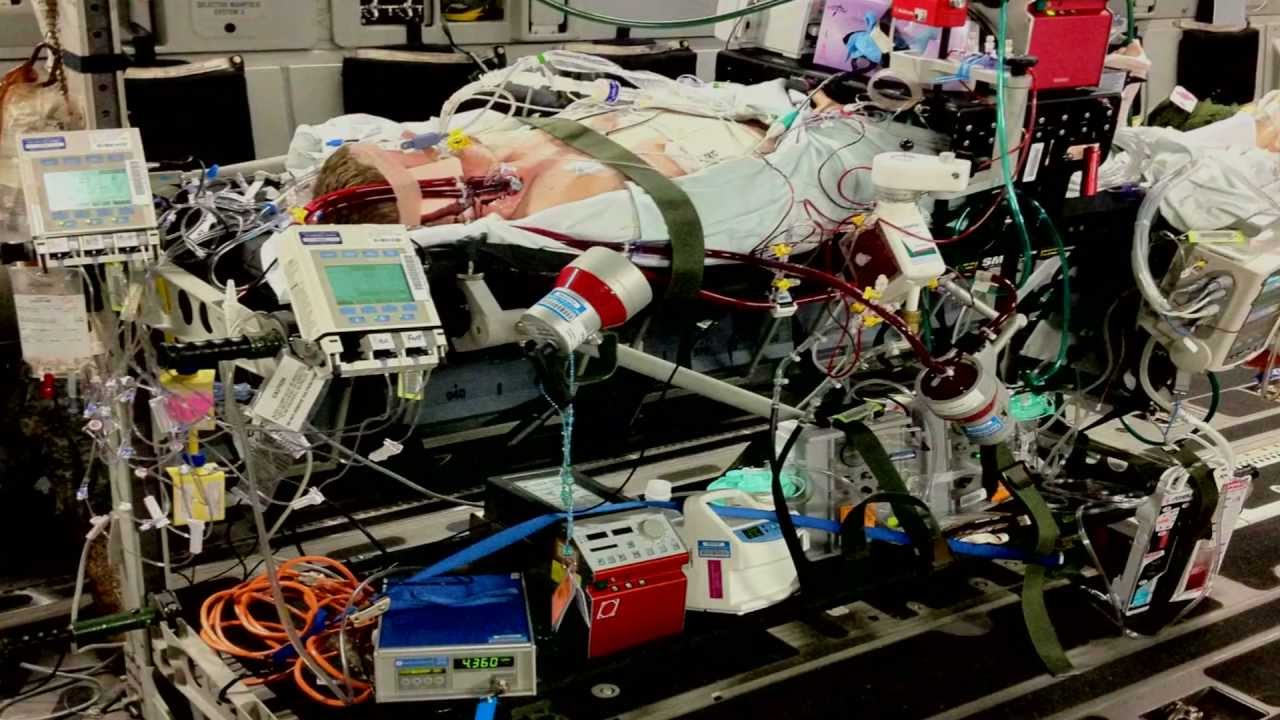
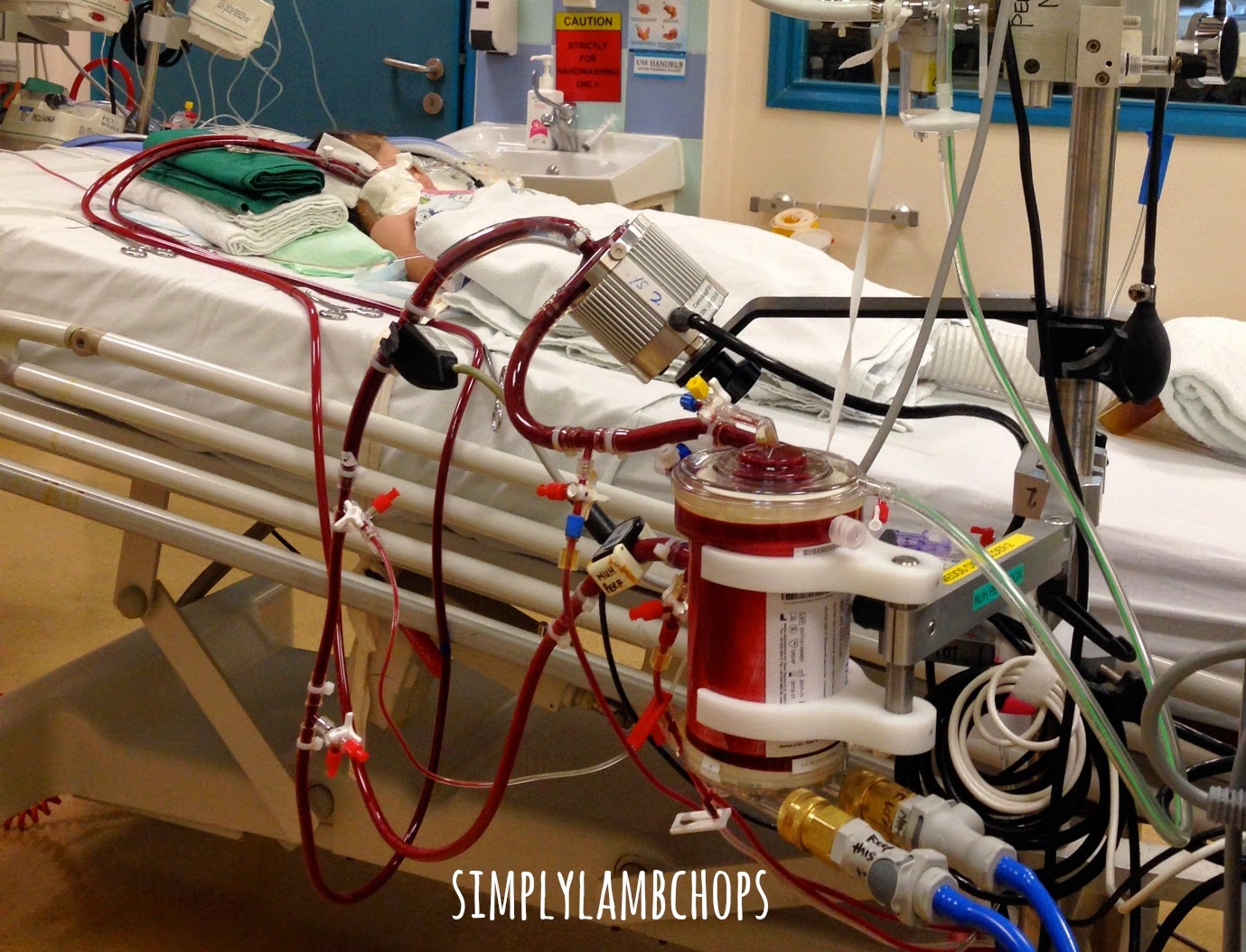
In extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body. Blood flows from the right side of the heart to the membrane oxygenator in the heart-lung machine, and then is rewarmed and sent back to the body.
What is the life threatening response to infection?
Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) Life-threatening response to infection (sepsis) Low body temperature (severe hypothermia) Post-transplant complications. Shock caused by the heart not pumping enough blood (cardiogenic shock) Some lung (pulmonary) conditions in which ECMO may be used include:
Recommendation
There is insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in adults with COVID-19 and refractory hypoxemia.
Rationale
ECMO has been used as a short-term rescue therapy in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) caused by COVID-19 and refractory hypoxemia. However, there is no conclusive evidence that ECMO is responsible for better clinical outcomes regardless of the cause of hypoxemic respiratory failure. 1-4
What is ECMO treatment?
ECMO removes carbon dioxide waste from the blood and returns oxygen-rich blood back to the body. "ECMO is akin to dialysis for the lungs – in that the same way that dialysis cleans the blood of toxins when the kidneys have failed, ...
When to use ECMO?
ECMO is generally used in patients who are younger than 65 and who were previously healthy , Hodgson says: "People who are older, frail or have other medical conditions do not respond as well.". The decision to put a patient on ECMO is painstaking, with assistance from the ELSO COVID-19 Guidelines.
What are the risks of ECMO?
ECMO treatment has major risks, including: 1 The large ECMO cannulas, or tubes, can cause nerve or blood vessel damage. 2 Bleeding can occur as patients are often being managed with anti-clotting medication to prevent clotting within the ECMO circuit. 3 Infection can result whenever tubes are placed in the body.
What is ECMO in medical terms?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation , or ECMO, replaces the function of the heart and lungs. ECMO is helping some COVID-19 patients for whom standard treatments have failed and a mechanical ventilator alone is not enough to safely support their breathing.
How long does it take to recover from ECMO?
It usually takes several days to wean patients, she says. However, she adds, some patients recover quickly and are weaned within 24 hours or so.
What is the function of a drainage cannula?
The drainage cannula sends blood from the patient to the oxygenator. This artificial lung, or membrane, removes carbon dioxide from the blood and adds oxygen, all from outside the body. Pump. Acting as the heart would, the rotating pump sends the oxygen-rich blood back to the patient via the return cannula. Blender.
Can ECMO be used for ARDS?
Currently, Agerstrand says, the use of ECMO for ARDS, whether it's due to COVID-19 pneumonia or regular pneumonia, is reserved for someone who has failed conventional, standard-of-care approaches to mechanical ventilation.
What is ECMO in medical terms?
● Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a type of prolonged mechanical cardiopulmonary support that is usually delivered in the intensive care unit. ECMO should only be performed in centers with the appropriate equipment and expertise. (See 'Introduction' above.)
What is mechanical cardiopulmonary support?
Mechanical cardiopulmonary support is most often applied intraoperatively to facilitate cardiac surgery (ie, cardiopulmonary bypass). However, cardiopulmonary support can also be delivered in a more prolonged fashion in an intensive care unit, although it is less common. Prolonged cardiopulmonary support is called extracorporeal membrane ...
How is oxygenation determined?
Oxygenation is determined by flow rate, whereas elimination of CO 2 can be controlled by adjusting the rate of countercurrent gas flow through the oxygenator [ 50 ].
Where are cannulae placed?
Cannulation — Cannulae are usually placed percutaneously by Seldinger technique. The largest cannulae that can be placed in the vessels are used. For VV ECMO, venous cannulae are usually placed in the right or left common femoral vein (for drainage) and right internal jugular vein (for infusion).
Is UpToDate a substitute for medical advice?
The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your own physician or other qualified health care professional regarding any medical questions or conditions. The use of UpToDate content is governed by the UpToDate Terms of Use. ©2021 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
Why is ECMO used?
ECMO is often used to take stress off the lungs and heart for several days, which theoretically promotes healing. It's used in patients who, if emergently treated, their chances of survival are good, and who would otherwise probably die without ECMO.
What is ECMO in a hospital?
ECMO (AKA extracorporeal life support or ECLS) is a short-term means of providing life support in people who are seriously ill (think lung or heart failure). Specifically, ECMO infuses oxygen into the blood and removes carbon dioxide. 2 It can also provide hemodynamic (blood pressure) support.
What are the components of an ECMO?
Here are the components of a typical ECMO: 1 heat exchanger 2 membrane oxygenator 3 roller or centrifugal pump 4 circuit tubing 5 catheters specific to the site of access (VV ECMO returns blood to the venous system via the superior vena cava or right atrium, and VA ECMO returns blood to the arterial system via the aorta or common carotid artery)
How many people survive ECMO?
Patients who are on ECMO are usually very sick, and not everyone survives the experience. In 2013, ELSO reported that worldwide only 72 percent of people survived ECMO with this statistic being heavily weighed in favor of neonates who have limited lung injury going into the procedure.
What are the adverse effects of ECMO?
Adverse effects of ECMO include severe internal and external bleeding, infection, thrombosis (life-threatening blood clots inside blood vessels ) and pump failure. In order to mitigate the threat of thrombosis, components of ECMO are coated in heparin, a blood thinner.
What is the effect of cardiopulmonary bypass?
An adverse effect of this early form of bypass involved hemolysis or the destruction of blood cells which limited its benefit to a few hours at most.
What is ECMO in medical terms?
Short for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, also called extracorporeal life support or ECLS, ECMO is used as a temporary form of heart lung bypass in patients who have the most severe heart, lung or heart and lung failure.
How does ECMO work?
ECMO works because it allows the lungs to rest and it allows us to minimize the harm that the breathing machine causes.
What is ECMO in ICU?
Short for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, also called extracorporeal life support or ECLS, ECMO is used as a temporary form of heart lung bypass in patients who have the most severe heart, lung or heart and lung failure.
What is an ECMO machine?
The ECMO machine performs the function of the lungs successfully so the lungs can rest and we can use very low settings on the breathing machine. This protects the lungs from additional damage that the high pressures from the breathing machine cause.
What is the survival rate of ECMO?
Centers that do a lot of ECMO, however, may have survival rates above 70%. It's like anything else, if you go to a place that specializes in that area and has significant experience doing a particular complex procedure, then the survival is much better.
When is a tracheostomy needed?
A Tracheostomy may be required if a prolonged weaning off the ventilator is expected . In a critically ill Patient on VV- ECMO for lung failure a prolonged weaning off the ventilator after ECMO has been discontinued is often likely and therefore a Tracheostomy necessary.
Is withdrawal of treatment ethical?
Withdrawal of treatment can be morally and ethically challenging in ECMO Patients. It could get particularly challenging (morally, ethically and clinically) if treatment would be withdrawn on an awake Patient. If your critically ill loved one requires ECMO for lung failure (VV- ECMO) it is less likely that your critically ill loved one is being ...
Overview
- Your loved one may need ECMO when their heart or lungs need help functioning. ECMO is considered when a patient doesn’t respond well to other treatments, like a ventilator. We offer the most treatment options in the area for patients with heart or lung failure. Our team will provide …
Why It's Done
Risks
How You Prepare
- In extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body. Blood flows from the right side of the heart to the membrane oxygenator in the heart-lung machine, and then is rewarmed and sent back to the body. This method allows the blood t…
What You Can Expect
- ECMO may be used to help people who are very ill with conditions of the heart and lungs, or who are waiting for or recovering from a heart transplant. It may be an option when other life support measures haven't worked. ECMOdoes not treat or cure a disease, but can help you when your body temporarily can't provide your tissues with enough oxygen. Some heart conditions in whic…
Results
- The most common risks that may occur with ECMOinclude: 1. Bleeding 2. Blood clot (thromboembolism) 3. Blood clotting disorder (coagulopathy) 4. Infection 5. Loss of blood in hands, feet or legs (limb ischemia) 6. Seizures 7. Stroke (part of the brain is damaged by loss of blood or by a blood vessel that bursts)
Clinical Trials
- ECMO is used when life support is needed after surgery, or when you are very ill and your heart or lungs need help so that you can heal. Your doctor will decide when it may be helpful. If you need ECMO, your doctor and trained respiratory therapists will prepare you.