What are the 4 stages of skin cancer?
Apr 21, 2021 · Treatment or removal of a precancerous lesion can prevent skin cancer from developing. 5 Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer, with over 2 million Americans diagnosed annually. BCC appears in the basal cells, the new skin cells produced as others die off.
What is the first stage of skin cancer?
Aug 27, 2021 · Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Chemotherapy for basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis is usually topical (applied to the skin in a cream or lotion).
What is the best treatment for skin cancer?
Jun 18, 2020 · With early detection and treatment, the 5-year survival rate from melanoma is close to 99 percent. You can reduce your risk of skin cancer by limiting or avoiding exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Checking your skin for suspicious changes can help detect skin cancer at an early stage.
Does cured early stages of cancer come back often?
Options might include: Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or nivolumab (Opdivo) Nivolumab combined with relatlimab (Opdualag) Nivolumab or pembrolizumab, plus ipilimumab (Yervoy)
What is considered early treatment for melanoma?
Treatment for early-stage melanomas usually includes surgery to remove the melanoma. A very thin melanoma may be removed entirely during the biopsy and require no further treatment. Otherwise, your surgeon will remove the cancer as well as a border of normal skin and a layer of tissue beneath the skin.Jan 20, 2022
Can skin cancer be treated if detected early?
When skin cancer (non-melanoma or melanoma) is found and treated early, the chances of successful treatment are better. Get regular health checkups and see your doctor if you have any symptoms or are worried about your health.
What is early stage skin cancer?
A large brownish spot with darker speckles. A mole that changes in color, size or feel or that bleeds. A small lesion with an irregular border and portions that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black. A painful lesion that itches or burns.Dec 5, 2020
What is the most common treatment for skin cancer?
Surgery is the primary treatment for most skin cancers. For patients with basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas, a dermatologist or other qualified doctor may perform an outpatient procedure using a local anesthetic.Mar 17, 2022
What does Stage 1 melanoma look like?
Stage 1A means the: melanoma is less than 1 mm thick. outer layer of skin (epidermis) covering the tumour may or may not look broken under the microscope (ulcerated or not ulcerated)
How fast does skin cancer spread?
Melanoma can grow very quickly. It can become life-threatening in as little as 6 weeks and, if untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma can appear on skin not normally exposed to the sun. Nodular melanoma is a highly dangerous form of melanoma that looks different from common melanomas.
What does Stage 1 skin cancer look like?
Early stage skin cancer may resemble a small spot or discolored blemish significantly smaller than the size of a fingernail. It may be reddish or brown, though sometimes white with flaking skin cells surrounded by a small blotch of darker skin.Jun 18, 2020
What happens if skin cancer is not treated?
However, left untreated, BCCs can grow deeper into the skin and damage surrounding skin, tissue, and bone. Occasionally, a BCC can become aggressive, spreading to other parts of the body and even becoming life threatening.
What are the 4 signs of skin cancer?
Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed. Raised growths or lumps, sometimes with a lower area in the center. Open sores (that may have oozing or crusted areas) and which don't heal, or heal and then come back. Wart-like growths.Apr 9, 2020
What are 3 types of treatments used for skin cancers?
Simple excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, curettage and electrodesiccation, and cryosurgery are used to treat basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Laser surgery is rarely used to treat basal cell carcinoma.Aug 27, 2021
Can skin cancer go away?
Melanoma can go away on its own. Melanoma on the skin can spontaneously regress, or begin to, without any treatment. That's because the body's immune system is able launch an assault on the disease that's strong enough to spur its retreat.May 11, 2021
How successful is skin cancer treatment?
Non-surgical treatments, such as freezing (cryotherapy), anti-cancer creams, photodynamic therapy (PDT), radiotherapy and electrochemotherapy, are also used in certain circumstances. Overall, treatment is successful for at least 9 out of 10 people with non-melanoma skin cancer.
What test is needed to determine the stage of skin cancer?
Because superficial skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma rarely spread, a biopsy that removes the entire growth often is the only test needed to determine the cancer stage. But if you have a large squamous cell ...
How to diagnose skin cancer?
To diagnose skin cancer, your doctor may: Examine your skin. Your doctor may look at your skin to determine whether your skin changes are likely to be skin cancer. Further testing may be needed to confirm that diagnosis. Remove a sample of suspicious skin for testing (skin biopsy). Your doctor may remove the suspicious-looking skin ...
Can actinic keratoses be treated?
Small skin cancers limited to the surface of the skin may not require treatment beyond an initial skin biopsy that removes the entire growth.
What is the procedure for removing a tumor?
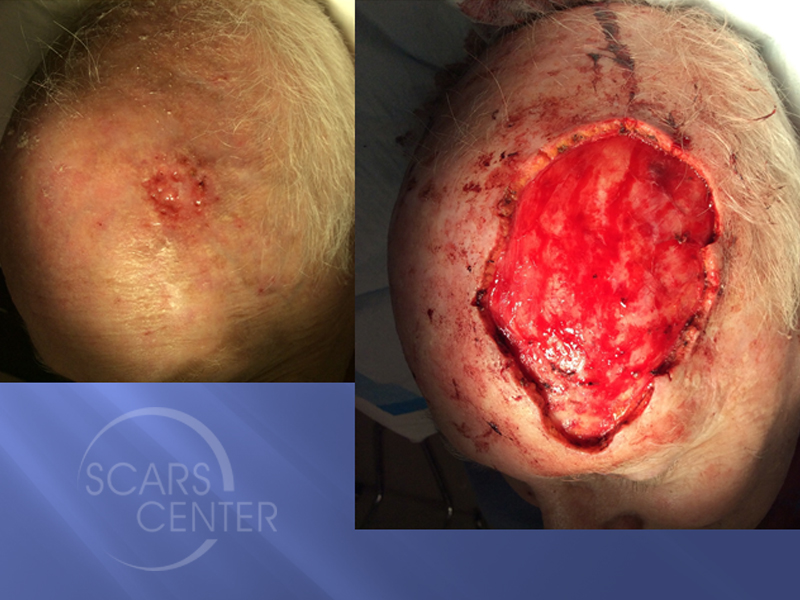
A wide excision — removing extra normal skin around the tumor — may be recommended in some cases. Mohs surgery. This procedure is for larger, recurring or difficult-to-treat skin cancers, which may include both basal and squamous cell carcinomas.
How does Mohs surgery work?
During Mohs surgery, your doctor removes the skin growth layer by layer, examining each layer under the microscope, until no abnormal cells remain . This procedure allows cancerous cells to be removed without taking an excessive amount of surrounding healthy skin. Curettage and electrodesiccation or cryotherapy.
Can radiation therapy be used to remove cancer?
Radiation therapy may be an option when cancer can't be completely removed during surgery. Chemotherapy. In chemotherapy, drugs are used to kill cancer cells. For cancers limited to the top layer of skin, creams or lotions containing anti-cancer agents may be applied directly to the skin.
What is the procedure to remove cancer cells?
Curettage and electrodesiccation or cryotherapy. After removing most of a growth, your doctor scrapes away layers of cancer cells using a device with a circular blade (curet). An electric needle destroys any remaining cancer cells.
How to tell if you have BCC?
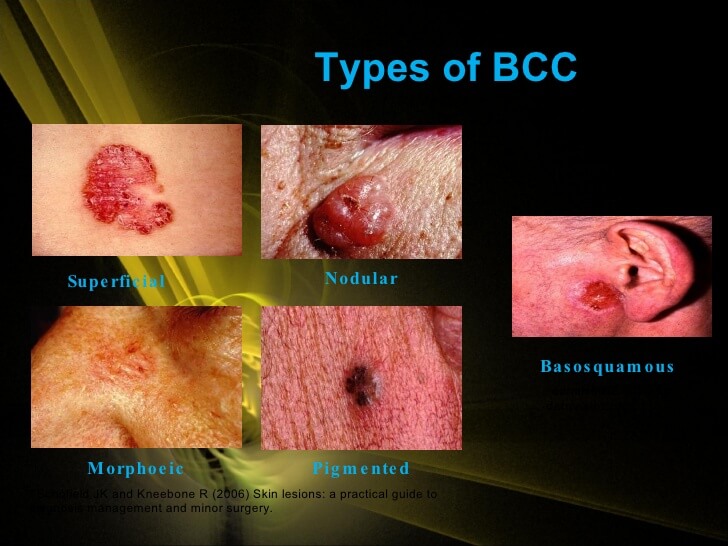
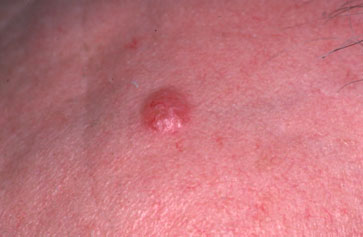
BCC can occur anywhere on the body but is more common in areas exposed to the sun. It is important to know the signs and symptoms of BCC. The main skin changes to look for include: 6 1 A nodule, or bump, that is shiny and can be skin-colored, pink, white, red, or varying shades of brown to black and look similar to a mole 2 An open sore that doesn't heal or one that heals but keeps returning 3 A scaly, rough, raised patch of skin that may be red, itchy, and painful or causes no discomfort at all 4 A scaly patch or growth close to the ear 5 A pink or red growth with an indentation in the center 6 Scar-like shiny and waxy lesions
What causes scaly patches on the face?
Actinic keratosis, also known as solar keratosis, is a condition that produces large, scaly patches of skin caused by chronic exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, such as from sunlight. The patches commonly appear on areas of the body often exposed to the sun, including the face, neck, scalp, hands, shoulders, arms, and back. Fifty-eight million Americans have actinic keratosis, and 5%–10% of the patches become cancerous.
How many people have skin cancer before 70?
Skin cancer is not uncommon, as one in five Americans will develop skin cancer before age 70. 1 Learning to spot the warning signs is vital. When identified early, skin cancer is highly curable.
Where does BCC occur?
BCC can occur anywhere on the body but is more common in areas exposed to the sun.
Can atypical moles be cancerous?
Atypical Moles (Dysplastic Nevi) Atypical moles, or dysplastic nevi, are not cancerous but can develop into skin cancer if left untreated. In most cases, atypical moles appear larger and are more irregular in shape than regular moles. They also may have an uneven border and be of more than one color.
What are cutaneous horns made of?
Cutaneous horns are skin lesions made of keratin (the fibrous protein that makes up your nails and hair) that typically appear in sun-exposed areas of the body. The keratin forms growths that resemble small animal horns. Cutaneous horns can vary in size and shape and are more commonly seen in older adults.
How many people have actinic keratosis?
Fifty-eight million Americans have actinic keratosis, and 5%–10% of the patches become cancerous. The patches that form from actinic keratosis are small, scaly, and dry, and their color varies, appearing as different shades of pink, white, and brown, or resembling the color of one's skin.
Why do we do clinical trials?
Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
What is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. Different types of cancer start in the skin. Skin color and being exposed to sunlight can increase the risk of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, ...
How does chemotherapy stop cancer cells from growing?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing . Chemotherapy for basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis is usually topical (applied to the skin in a cream or lotion).
Where does skin cancer occur?
Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common in skin that is often exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and hands.
Is melanoma more common than squamous cell carcinoma?
Melanoma is less common than basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body. This summary is about basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis.
What is the purpose of skin cancer?
The skin is the body’s largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D.
Where does basal cell carcinoma occur?
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin occur most often in areas of the skin exposed to the sun, such as the nose, ears, lower lip, or top of the hands. Signs of actinic keratosis include the following: A rough, red, pink, or brown, scaly patch on the skin that may be flat or raised.
What does it mean when a biopsy comes back positive?
If your skin biopsy came back positive for melanoma, the most aggressive form of skin cancer, you might hear your melanoma described in stages. Early stage melanoma (0, I, or II) generally means your prognosis is good. From creams to surgery, there are several possible treatment options to undertake, depending on the stage.
How to treat melanoma on face?
Surgery at this stage usually cures the disease. For melanomas on the face, some doctors may instead prescribe a cream containing the drug Aldara (imiquimod).
What is lymph node dissection?
Routine lymph node dissection (removal of lymph nodes near cancer) is an important staging tool in melanomas more than 1 mm thick, even though it has not been shown to improve survival in patients with stage I melanoma. 2 .
How does melanoma spread?
Melanomas spread by way of either the lymphatic system or the bloodstream. When they spread through the lymphatic system, they usually first spread to the lymph nodes that are closest to cancer, and once they spread to a first lymph node, spread down the line to others.
What is stage 0 melanoma?
It is usually treated by surgery (wide excision) to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope.
Where does melanoma come back?
Almost any organ can be affected. Most often, the melanoma will come back in the lungs, bones, liver, or brain. Treatment for these recurrences is generally the same as for stage IV melanoma (see above).
Does melanoma spread to lymph nodes?
The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
What is the best treatment for melanoma?
Radiation therapy to the brain (ster eotactic radiosurgery or whole brain radiation therapy) may help as well. Systemic treatments ( immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemo) might also be tried. As with other stages of melanoma, people with recurrent melanoma may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
Does melanoma come back after treatment?
Treatment of melanoma that comes back after initial treatment depends on the stage of the original melanoma, what treatments a person has already had, where the melanoma comes back, and other factors.
Can melanoma come back after surgery?
Melanoma might come back in the skin near the site of the original tumor, sometimes even in the scar from the surgery. In general, these local (skin) recurrences are treated with surgery similar to what would be recommended for a primary melanoma. This might include a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB). Depending on the results of the SLNB, other treatments might be recommended as well.
Can lymph nodes be dissectioned?
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells, then a lymph node dissection (where all the lymph nodes in that area are surgically removed) will probably be done at a later date. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
What are the signs of melanoma?
A non-cancerous mole is commonly a single shade of brown or tan. If there is a presence of more than one color or uneven distribution of color this can be a warning sign of melanoma. Melanoma can occur in a variety of colors including brown, black, red, blue, or purple. These spots can be flat or raised and can bleed easily. Non-melanoma skin cancer, also known as basal and squamous cell carcinoma, typically appears as small, pearly, or pale bumps or as dark red patches that can be raised, flat or scaly in texture.
How long does it take to get a skin cancer test?
Skin cancer screenings take around 10 minutes and can be lifesaving.
Where is skin cancer most commonly found?
Skin cancer is an abnormal growth of skin cells. Skin cancer can be found anywhere on your body but is most commonly located on the head, neck, arms, and legs.
What is a small bump on the skin called?
These spots can be flat or raised and can bleed easily. Non-melanoma skin cancer, also known as basal and squamous cell carcinoma, typically appears as small, pearly, or pale bumps or as dark red patches that can be raised, flat or scaly in texture.
Is melanoma symmetrical or irregular?
Melanoma lesions are often irregular, or not symmetrical, in shape. A non-cancerous mole is typically symmetrical in shape. If you were to draw a line through the middle of a mole, the two halves should roughly match.
Is a non-cancerous mole a malignant mole?
Non-cancerous moles are typically smaller than malignant ones. If its diameter is greater than a pencil eraser, it may be a sign that it is growing or changing. Larger moles that have been stable for an extended period of time are not typically cause for concern; though continued observation is recommended.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
If the cancer is more advanced, you may be treated by another type of doctor, such as: 1 A surgical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with surgery 2 A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with chemotherapy or other medicines 3 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy
Can basal cell carcinoma be treated with surgery?
Different approaches might be used to treat basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, actinic keratosis, and Bowen disease. Fortunately, most of these cancers and pre-cancers can be cured with fairly minor surgery or other types of local treatments. (Other skin cancers, such as melanoma , lymphoma of the skin , Merkel cell carcinoma , ...
Why is it important to discuss all of your treatment options with your doctor?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include:
What is the difference between a radiation oncologist and a medical oncologist?
A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with chemotherapy or other medicines. A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, nutrition specialists, social workers, ...
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
What are the different types of radiation therapy?
The different types of radiation therapy used to treat SCC are: 1 Superficial radiation therapy: Beams of radiation are directed just beneath the skin, which treats only the tumor. 2 External beam radiation therapy: High-energy beams of radiation are sent into the tumor in order to kill cancer cells. 3 Brachytherapy (bray-key-ther-uh-pee): Radioactive implants are placed inside (or near) the cancer. Also called internal radiation, this therapy is often used to treat prostate cancer.
What is a pathology report?
Also called a pathology report, this report explains what was seen under the microscope, including whether any skin cancer cells were seen. If you have squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the skin, the report will contain the following information when possible: Type of SCC. Stage of the cancer.
What does a board certified dermatologist do?
When you see a board-certified dermatologist, your dermatologist will examine your skin carefully. If your dermatologist finds a spot on your skin that could be any type of skin cancer, your dermatologist will first numb the area and then remove all (or part) of it.
Is radiation therapy a second treatment?
Radiation therapy may be given as a second type of treatment when there is a high risk that the cancer will spread. In this case, radiation therapy often follows surgical removal. If the skin cancer has grown deep or spread, radiation therapy may help a patient feel more comfortable.
What is the procedure called when you have cancer?
This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy . This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform. Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have skin cancer.
Does chemotherapy kill hair cells?
Hair cells and cells in your gastrointestinal (GI) tract also grow quickly and can be killed. When chemotherapy kills these cells, patients develop side effects, such as hair loss and nausea. Other treatments for advanced SCC of the skin: No single treatment is best for everyone who has this advanced cancer.
What type of doctor treats skin cancer?
Your dermatologist or Mohs surgeon can often perform this type of treatment during an office visit. The following describes what to expect from surgical removal and other treatments for this skin cancer: Surgical removal: Three types of surgical removal are used to treat this type of skin cancer.