What drugs are used to treat TB?
· 'Directly observed therapy' (DOT) is one component of a wider WHO strategy called 'Directly Observed Therapy Short course' (DOTS). This strategy incorporates wide ranging health system improvements, political commitment to improving TB programmes, improved TB laboratory services, free TB drugs for all TB patients, and accurate documentation and …
How to cure tuberculosis?
DOT is a way of helping people during their treatment. Instead of being sent home with your tablets, you might visit your local hospital or pharmacy, or a nurse can come to your home. This means you have someone to chat to, and they can make sure you take your treatment correctly. Who can DOT help? DOT is available to anyone with TB in the UK.
What is the treatment for TB disease?
Abstract. Directly Observed Therapy Shortcourse (DOTS) is composed of five distinct elements: political commitment; microscopy services; drug supplies; surveillance and monitoring …
Can tuberculosis be cured?
· DOTS Therapy is focused on eradicating tuberculosis all over the world. Directly Observed Therapy Shortcourse (DOTS) is an international protocol for handling infectious …
What is Dot medicine?
Directly observed therapy (DOT) is used to ensure the person receives and takes all medications as prescribed and to monitor response to treatment. DOT is widely used to manage tuberculosis (TB) disease. In HIV treatment, DOT is sometimes called directly administered antiretroviral therapy (DAART).
How many months of treatment does TB DOTS have?
Directly Observed Treatment (DOT) TB treatment takes at least six months, patients need to take many tablets each day and side effects are common.
Which drugs are given in DOTS?
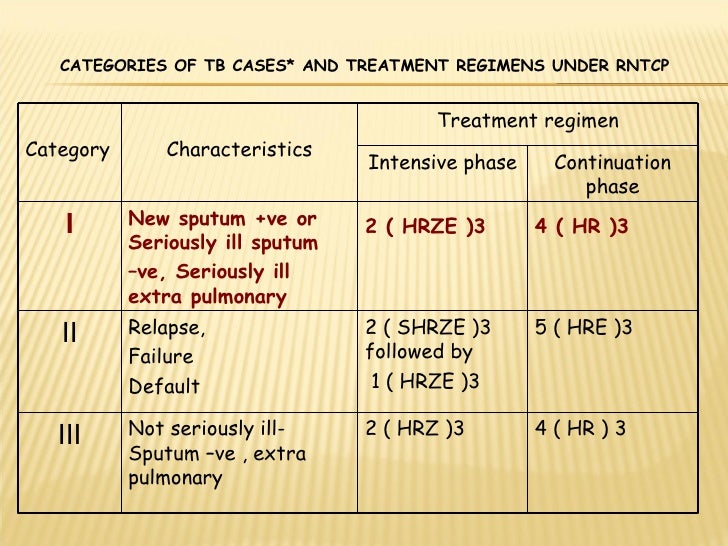
DOTS involved treatment with a four drug regimen. These were isoniazid (INH), Rifampicin (Rif), Prazinamide (PZA) and Ethambutol (EMB) for 6-9 months.
Why is DOTS therapy for patients with pulmonary TB implemented?
DOT was launched by WHO in 1992 [47], and has long been accepted as an effective strategy to promote patient adherence to anti-TB treatment, thus helping to cure most TB cases, to prevent the spread of TB in the community, and to prevent drug-resistant TB [48].
What are the 3 types of tuberculosis?
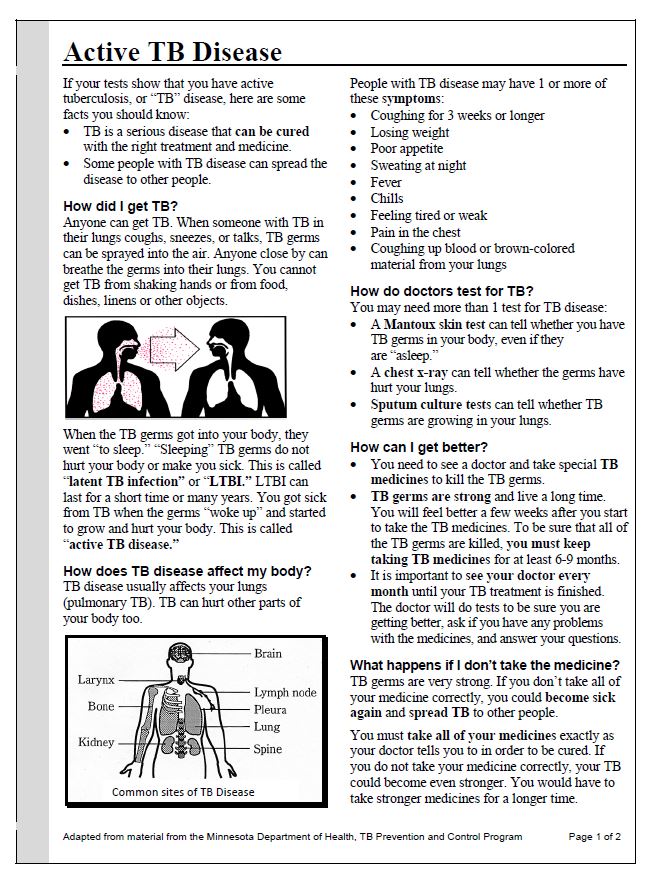
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that usually infects the lungs. It may also affect the kidneys, spine, and brain. Being infected with the TB bacterium is not the same as having active tuberculosis disease. There are 3 stages of TB—exposure, latent, and active disease.
How many stages of TB treatment are there?
The standard six month course of treatment consists of two phases. The first phase lasts two months and is called the intensive phase. The second phase lasts four months and is called the continuous phase.
What is the full form of dot?
Functions of DoT | Department of Telecommunications | Ministry of Communication | Government of India. दूरसंचार विभाग Department of Telecommunications.
What is first line treatment for TB?
Of the approved drugs, isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), ethambutol (EMB), and pyrazinamide (PZA) are considered first-line anti-TB drugs and form the core of standard treatment regimens (Figure 6.4) (Table 6.2). Rifabutin (RBT) and rifapentine (RPT) may also be considered first- line drugs under certain circumstances.
What is the fastest way to cure TB?
The usual treatment is:2 antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin) for 6 months.2 additional antibiotics (pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for the first 2 months of the 6-month treatment period.
What is DOTS and how is it used?
DOTS: Stands for Directly Observed Treatment, Short-course. DOTS is a strategy used to reduce the number of tuberculosis (TB) cases. In DOTS, healthcare workers observe patients as they take their medicine.
What are the five main components of DOTS?
Abstract. Directly Observed Therapy Shortcourse (DOTS) is composed of five distinct elements: political commitment; microscopy services; drug supplies; surveillance and monitoring systems and use of highly efficacious regimens; and direct observation of treatment.
What is DOT in medicine?
Directly observed treatment (DOT) Taking many different tablets each day can be difficult. There might also be a lot of other pressures on you. The good news is that there is help – it’s called directly observed treatment – or DOT for short.
What is a dot?
What is DOT? DOT is a way of helping people during their treatment. Instead of being sent home with your tablets, you might visit your local hospital or pharmacy, or a nurse can come to your home. This means you have someone to chat to, and they can make sure you take your treatment correctly.
Can you take Dot in the UK?
DOT is available to anyone with TB in the UK. If you are finding it difficult to take your tablets regularly, DOT could work well for you.
Is DOT good for TB?
People who have DOT find it really helps them stay motivated. DOT also makes sure that your TB is cured completely. DOT is very successful and is used in over 180 countries around the world. It is saving hundreds of thousands of lives.
What is a dot?
Directly Observed Therapy Shortcourse (DOTS) is composed of five distinct elements: political commitment; microscopy services; drug supplies; surveillance and monitoring systems and use of highly efficacious regimens; and direct observation of treatment. The difference in the way the term 'DOTS' as defined by WHO and interpreted by many observers ...
What does "dots" mean?
WHO generally uses the term to mean the five components of DOTS. But the word 'DOTS' is an acronym for Directly Observed Therapy Shortcourse.
Is DOTS an end in itself?
DOTS is not an end in itself but a means to an end. In fact it has two purposes, to ensure that the patient with tuberculosis (TB) completes therapy to cure and to prevent drug resistance from developing in the community.
What is DOTS therapy?
DOTS Therapy is focused on eradicating tuberculosis all over the world.
How effective is DOTS therapy?
Many nations are struggling with rising tuberculosis rates, but DOTS therapy will only be an effective treatment if the nation is willing to follow through on treatment. The next step is improved case detection, which involves constructing high quality, reliable labs, as well as improving bacteriology techniques. The third element is standardized treatment, which goes hand in hand with better patient care and commitment. This therapy is only effective under supervision.
Can you observe a patient while taking a DOTS?
Patients undergoing DOTS therapy will be observed while they take medication.
What is DOTS in medical terms?
Directly Observed Therapy Shortcourse (DOTS) is an international protocol for handling infectious diseases, most commonly tuberculosis. DOTS therapy uses a battery of drugs in a prescribed order to eradicate tuberculosis and avoid the creation of drug-resistant strains of the disease. Drug-resistant tuberculosis began to emerge in the 1980s, and was recognized as a global public health risk. Drug resistant forms of the disease often appeared in response to incorrectly applied therapies, and the World Health Organization, in cooperation with other public health agencies, developed DOTS therapy, adopting it in 1991.
Is tuberculosis a contagious disease?
Tuberculosis is generally considered to be a highly contagious disease.
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
What is drug resistant TB?
Drug-resistant TB is caused by TB bacteria that are resistant to at least one first-line anti-TB drug. Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR TB) is resistant to more than one anti-TB drug and at least isoniazid (INH) and rifampin (RIF).
How is treatment completion determined?
Treatment completion is determined by the number of doses ingested over a given period of time.
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
What is a dot in TB?
Directly Observed Treatment, or DOT for short, is a highly successful way of supporting people to complete their treatment. DOT involves TB nurses, outreach volunteers or trained volunteers meeting regularly with patients to watch them take their medication. This may take place at the patient’s home, in a clinic or pharmacy, or even a local shop. DOT ensures that the right medication is taken in the right doses, at the right time, for as long as it’s required.
How effective is TB treatment?
TB treatment is effective. Worldwide, nearly 90% of cases of TB and 48% of cases of drug-resistant TB are cured.
What is drug resistant TB?
Drug-resistant TB requires a longer course of treatment, with different combinations of drugs that can have more side effects. A patient will be tested to find out the exact course of treatment that should work for them.
Can you change TB medication?
Patients should always discuss any side effects with their doctor, as it may be possible to change TB medication. If you would like to find out more about the side effects of specific drugs, please download our leaflet About your TB drugs.
Can TB go away?
With any medication, it is possible to experience side effects. Most are nothing to worry about and will go away. The TB nurse or doctor should advise patients of these before they start treatment.
How long does it take for TB to get better?
Patients may begin to feel better within two weeks of beginning treatment, and people with pulmonary TB normally become non-infectious during this time. However, it’s vital that patients complete their treatment, so that the TB bacteria are completely killed off in the body. This prevents symptoms from returning and the risk of bacteria becoming drug resistant.
How long does TB treatment last?
TB treatment lasts at least six months. Treatment for TB is usually a mixture of four antibiotics:
What is a dot in TB?
DOT is a component of case management that helps ensure patients adhere to therapy. It is the method whereby a trained health-care worker or another trained designated person watches a patient swallow each dose of anti-TB drugs and documents it. DOT is the preferred core management strategy recommended by CDC for treatment of TB disease and, if resources allow, for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) treatment. DOT can reduce the development of drug resistance, treatment failure, or relapse after the end of treatment. Good case management, which includes establishing a relationship with the patient and addressing barriers to adherence, facilitates successful DOT.
What are the drugs that treat TB?
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of TB disease (Table 6.2). In addition, the fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and gatifloxacin), although not approved by the FDA for TB disease, are commonly used to treat TB disease caused by drug-resistant organisms or for patients who are intolerant of some first-line drugs. Rifabutin, approved for use in preventing Mycobacterium avium complex disease in patients with HIV infection but not approved for TB disease, is useful for treating TB disease in patients concurrently taking drugs that interact with rifampin (e.g., certain antiretroviral drugs). Amikacin and kanamycin, nearly identical aminoglycoside drugs used in treating patients with TB disease caused by drug-resistant organisms, are not approved by the FDA for treatment of TB.
Can you breastfeed with TB?
Breast-feeding should not be discouraged for women being treated with first-line anti-TB drugs, because the small concentrations of these drugs in breast milk do not produce toxicity in the nursing newborn. Conversely, drugs in breast milk should not be considered to serve as effective treatment for TB disease or for LTBI in a nursing infant. Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) supplementation (25 mg/day) is recommended for all women taking INH who are either pregnant or breast-feeding. The amount of pyridoxine in multivitamins is variable, but generally less than the needed amount.
What is the role of health care providers in TB?
Health-care providers are responsible for deciding whether to restart a complete course of treatment or to continue as intended. These decisions should be based on when the interruption occurred and the duration of the interruption.
How long is the TB continuation phase?
The continuation phase of treatment is given for either 4 or 7 months. The 4-month continuation phase should be used in patients with uncomplicated, noncavitary, drug-susceptible TB, if there is documented sputum conversion within the first 2 months. The 7-month continuation phase is recommended only for
What are the four drugs that are included in the initial treatment regimen?
Four drugs— INH, RIF, PZA, and EMB — should be included in the initial treatment regimen until the results of drug-susceptibility tests are available. Each of the drugs in the initial regimen plays an important role. INH and RIF allow for short-course regimens with high cure rates. PZA has potent sterilizing activity, which allows further shortening of the regimen from 9 to 6 months. EMB helps to prevent the emergence of RIF resistance when primary INH resistance is present. If drug-susceptibility test results are known and the organisms are fully susceptible, EMB need not be included. For children whose clarity or sharpness of vision cannot be monitored, EMB is usually not recommended except when the risk of drug resistance is high or for children who have “adult-type” (upper lobe infiltration, cavity formation) TB disease.
What is the recommended treatment regimen based on?
The recommended treatment regimens are based, in large part, on evidence from clinical trials and are rated on the basis of a system developed by the U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) (Table 6.3).
What is the test for TB?
Sputum tests. If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria. Sputum samples can also be used to test for drug-resistant strains of TB.
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
What test can confirm active tuberculosis?
Blood tests can confirm or rule out latent or active tuberculosis. These tests measure your immune system's reaction to TB bacteria.
