What is DNase I used for?
DNase and cystic fibrosis • DNase reduces sputum viscosity (stickiness) • DNase is effective and safe at all stages of lung disease • DNase is effective with long term use • Probably protects against the damaging effects of lung inflammation Recommendation • DNase should be used as soon as possible ...
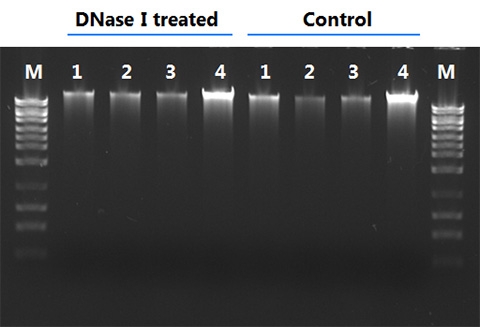
Does the DNase treatment degrade RNA samples?
Apr 28, 2021 · DNase short for Deoxyribonuclease is the class of enzymes having unmatched importance in both in vivo and in vitro experiments. Cleaving DNA either, on ends or in between is the function it performs. Consequently, it releases tension during DNA replication in vivo. DNase cleaves the DNA for various gene manipulation and gene editing experiments.
What is DNase 1 demystified?
DNase I Demystified DNase I is a versatile enzyme that nonspecifically cleaves DNA to release 5'-phosphorylated di-, tri-, and oligonucleotide products (1). A powerful research tool for DNA manipulations, DNase I is used in a range of molecular biology applications. Some of its uses include: 1. Degradation of contaminating DNA after RNA isolation,
How much RNA can be treated with DNase I?
I. DNase Treatment of RNA Samples Prior to RT-PCR 1. Set up the DNase digestion reaction as follows: RNA in water or TE buffer 1–8μl RQ1 RNase-Free DNase 10X Reaction Buffer 1μl RQ1 RNase-Free DNase (see Note 1) 1u/μg RNA Nuclease-free water to a final volume of 10μl 2. Incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes.

What does DNase treatment do?
DNA-free™ DNase Treatment & Removal Reagents contain RNase-free DNase, and an optimized DNase digestion buffer, to ensure safe, complete removal of contaminating DNA from any RNA sample.
Is DNase treatment necessary?
When working with blood, DNase treatment is essential. Unlike other eukaryotic cells, e.g., cell lines, blood cells contain more DNA than RNA.Jul 8, 2021
How long does DNase treatment take?
Each of these inactivation or removal methods has its drawbacks. Heat inactivation: Probably the most common method of DNase inactivation is heat treatment, typically for 5 minutes at 75°C.
Why is DNase used?
DNASE 1. Deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I, encoded by DNASE1) is a specific endonuclease facilitating chromatin breakdown during apoptosis. DNase I activity is important to prevent immune stimulation, and reduced activity may result in an increased risk for production of antinucleosome antibodies, a hallmark of SLE.
Do you need DNase for RNA extraction?
For removal of genomic DNA from RNA samples, a DNase I treatment is recommended. The DNAse I enzyme is classified as an endonuclease which is able to digest single and double-stranded DNA into single bases or oligonucleotides.Dec 22, 2017
Can DNase digest RNA?
Many researchers inactivate DNase I by heat denaturation at 75ÐC for 10 min. However, this method, too, can prove deleterious for the RNA sample, since heating RNA in the presence of divalent cations, contained in DNase digestion buffer, can cause enzyme-independent degradation of the RNA.
How can DNase contamination be prevented?
PREVENTING CONTAMINATION One of the most efficient safeguards to prevent contamination is the separation of pre- and postamplification areas and equipment. Use a dedicated set of pipettes, preferably with aerosol-resistant (barrier) tips, in the pre-amplification area.
Is DNase a protein?
This structure provides insight into the catalytic mechanism and evidence that DNase II is a member of the same protein structural family as phospholipase D (PLD), phosphatidylserine synthase (PSS), tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (TDP) and the endonuclease Nuc from Salmonella typhimurium ('bacterial nuclease').Mar 29, 2017
How much DNase should I use?
Use 0.01 to 1 mg/ml DNase I. For each cell type, the working concentration must be determined individually. For optimal enzyme activity, add 5 mM Mg2+. DNase I is prepared from bovine pancreas.
Is DNase a digestive enzyme?
DNase I is a digestive enzyme, secreted by the pancreas, that degrades DNA into shorter nucleotide fragments. Many other endonucleases and exonucleases cleave DNA, including the restriction enzymes and enzymes involved in DNA repair and replication.
What is the difference between DNase and RNase?
In the laboratory, DNase I is required to remove DNA from samples used in mRNA expression assays, whereas RNase A is used to remove RNA from samples used for DNA analysis. DNase and RNase are important for modifying and metabolizing nucleic acid chains and can be used as disease markers [4–13].Jul 11, 2014
What happens to DNA molecules treated with DNase?
What would first happen to DNA molecules treated with DNase? The two strands of the double helix would separate. The phosphodiester bonds between deoxyribose sugars would be broken. The purines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
How does DNase work?
Structurally, two adjacent nucleotides are joined by the phosphodiester linkage and form a chain of nucleotides- a polynucleotide chain . DNase hydrolyzes the phosphodiester bond and breaks or cleaves the DNA either on ends or in-between. Cleaving produces 3’- hydroxyl and 5’ phosphate ends or vice versa, which depends on the type of DNase.
Why is DNase important?
DNase has significant importance in genetic engineering as nearly all experiments of gene manipulations are not possible without it. Commercially available DNase are powerful enough to cleave DNA even at the right location.
What is the DNase?
Definition, Structure, Function and Types. “DNase is the group of DNA enzymes and a type of nuclease applicable for hydrolytic cleaving of the DNA. It is used in varied biological applications in order to perform various experiments.”. Deoxyribonuclease abbreviated as DNase is the class of enzymes having unmatched importance in both in vivo ...
What is the function of DNase?
Deoxyribonuclease abbreviated as DNase is the class of enzymes having unmatched importance in both in vivo and in vitro experiments. Cleaving DNA either, on ends or in between is the function it performs. Consequently, it releases tension during DNA replication in vivo. DNase cleaves the DNA for varied gene manipulation and gene editing experiments.
What is the name of the gene that cleaves DNA?
DNase is a class of nuclease that cleaves or cut DNA at precise or random locations. It’s a type of protein, performs the catalytic reaction; the gene for DNase is DNASE. For different DNases, varied DNASE genes are located on different chromosomes. Each one is different in terms of length and number of exons as well.
When was the first method to measure the activity of DNase?
The spectrophotometric method described by Kunitz was the first method to measure the activity of DNase in 1950. To honor the original researcher, the unit to measure the activity of DNase is named “Kunitz”.
What is the role of DNase I in autoimmune disease?
8. The physiological role of DNase I is to reduce autoimmune reactions by digesting major extracellular nucleoproteins. Systemic lupus erythematosus, a kind of autoimmune disease is caused by a mutation in the DNASE1 gene, which reduces the activity of the DNase enzyme, gradually.
What is the function of DNase I?
DNase I is a versatile enzyme that nonspecifically cleaves DNA to release 5'-phosphorylated di-, tri-, and oligonucleotide products (1). A powerful research tool for DNA manipulations, DNase I is used in a range of molecular biology applications. Some of its uses include:
How sensitive is RT-PCR?
RT-PCR has the ability to amplify a single molecule from a complex heterogeneous mixture; in fact, RT-PCR is so sensitive that when more than 40 cycles of PCR are performed, just about any reaction will produce a band in the "minus-RT" control reaction, indicating contaminating DNA.
Does DNase I cleave DNA?
Although DNase I is commonly perceived to cleave DNA nonspecifically, in practice it does show some sequence preference. For example, the enzyme is sensitive to the structure of the minor groove, and favors cleavage of purine-pyrimidine sequences. However, DNase I will cut at all 4 bases in heterogeneous dsDNA, ...
What is DNA free dnase removal?
DNA-free™ DNase Treatment & Removal Reagents contain RNase-free DNase, and an optimized DNase digestion buffer, to ensure safe, complete removal of contaminating DNA from any RNA sample. Also included is a unique DNase Removal Reagent which, after digestion, eliminates DNase in minutes — no more messy phenol extractions or heat inactivation procedures which can cause RNA loss or degradation.#N#DNA, contaminating RNA preparations, can serve as a template in PCR to produce a false positive signal from RT-PCR. Although false positives are easily identified by looking at the outcome of a "minus-RT" control, eliminating the DNA is not trivial. Here we discuss the problem of genomic DNA contamination in RT-PCR, the best methods to detect and remove it, and an innovative way to remove DNase I after DNase I treatment.
What is DNA free reagent?
DNA-free DNase Treatment & Removal Reagents are one of Ambion's latest tools designed to simplify RNA preparation for RT-PCR. With DNA-free, genomic DNA contamination can be removed from any RNA preparation without incurring RNA loss or risk of degradation. The DNA-free DNase Treatment & Removal Reagents provide RNase-free DNase I and optimized DNase Reaction Buffer for the complete digestion of contaminating DNA in RNA samples. Ambion's DNase I is prepared with ultra pure reagents and is not released for sale until it is shown to be both highly effective at eliminating DNA, and devoid of RNase activity. The 10X DNase Reaction Buffer is designed for optimal DNase I activity. DNA-free also includes a novel DNase Removal Reagent to quickly eliminate the DNase after treatment. This unique reagent effectively removes all traces of DNase and divalent cations from the reaction mixture after DNA digestion is complete. The DNase/cation removal step is fast — taking only three minutes to complete. After DNase digestion, The Removal Reagent is added, the tube flicked to mix, and the solution incubated for 2 minutes at room temperature. DNase and ions are bound by the DNase Removal Reagent which is spun out with a quick centrifugation leaving the RNA in the supernatant ready for RT-PCR. This simple method avoids messy organic extraction or heat inactivation of DNase I that may put your RNA at risk. DNA-free DNase Treatment & Removal Reagents are also available as components of the RNAqueous®-4PCR Kit (see sidebar, "RNA Isolation for RT-PCR").
Can pseudogenes be amplified?
Pseudogenes may exist in your sample that can produce an amplified product of the same size as the expected cDNA product. (Pseudogenes arise from a processed mRNA that is reverse transcribed and then integrated into the genome; no introns are present).
Is there a method to isolate RNA from genomic DNA?
There is no RNA isolation method that consistently produces RNA free from genomic DNA without the use of DNase. To illustrate this, RT-PCR was performed on mouse liver RNA isolated by several different methods:
Popular Answers (1)
I will add to the above with one final comment: Most DNAses apart from Ambions Turbo principle are highly purified and incorporate remnants of RNAses. Irrespective of particular issues with contaminated stop buffer therefore you often see nominal RNA degradation when you DNAse treat RNA with these purified principles.
All Answers (18)
Obviously the problem is the STOP solution, most probably the EDTA solution was prepared with water without DEPC (diethylpyrocarbonate) treatment. Try to prepare your EDTA 5 mM with water treated with DEPC to solve your RNA degradation.
