What is enzyme wash on denim?
Apr 19, 2021 · Denim bleaching; Enzyme wash; Acid wash; Fig: Different samples of denim wash. ENZYME WASHING [7] The cellulose enzymes are used in washing. They act on the cotton yarn and there by facilitate the abrasions of the indigo dyeing from the yarn surface. The cellulose hydrolyses cellulose, yielding soluble produce such as a short-chain polysaccharides and …
How to de-Pilling denim with matzyme?
Aug 24, 2021 · The enzyme treatment was carried at different amount of cellulose enzyme (50gm, 100gm and 150gm), temperature of 40-60 o C and treatment time of 40-50 minute. The denim fabric is then washed and softened with cationic softener at cold for 10-15 minute. Enzyme treated fabric was squeezed in a hydro extractor machine to remove excess water and then …
What chemicals are used in washing denim?
Oct 30, 2020 · Cellulase enzyme fastens the abrasion by a process known as ‘bio stone washing’. The use of these enzymes allows the denim garment washing procedure to be carried out under mild conditions without the use of pumice stones and other harsh chemical agents. As a result of this process, different visual effects may also be fused on fabrics.
What is the best cellulase to remove color from denim?
May 01, 2010 · Cellulase enzymes are natural proteins which are used in denim garment processing to get stone wash look on to the denim garments without using stones or by …

How do denim enzymes work?
The enzymes used are cellulase enzymes, specifically acting on the cellulose part, mainly on the surface of the fabric. This gives the desired look and at the same time, removes hairiness from surface thus giving a smooth and soft feel.Jan 28, 2018
Which enzyme is used for denim washing?
CellulasesCellulases are the most successful enzymes used in the textile industry (Kuhad et al., 2011). Cellulases are used in the biostoning of denim garments (jeans) and biopolishing of cotton and other cellulosic fabrics (Bera et al., 2015).
How are enzymes used in denim jeans?
Used for stone washing of jeans, the enzymes break off small fiber ends on the yarn surface, thereby loosening the dye so the jeans get that vintage look. Enzymes are added to water when the denim fabric is washed during the manufacturing process.Oct 3, 2017
What is the purpose of enzyme wash?
Enzyme wash is a process that gives denim a softer and worn-in look by breaking down the cellulose molecules naturally found in indigo dyes. Cellulose is a type of sugar that make up the walls of plant cells, making denim stiffer after it is dyed.
Is enzyme washing eco friendly?
Enzyme washing is considered more sustainable than stone washing or acid washing because it is more water efficient.
How do you wash an enzyme at home?
In a spray bottle or other container, mix one part enzyme cleaner with 20 parts water. Shake or stir to combine. This mixture can be used to wash cars, wash floors, and for other jobs around the house that don't require a super-powered cleaner. Make an all-purpose cleaner.
What is indigo wash?
Indigo denim wash features Kurin's patented Deep Indigo™ technology, which removes dirt and debris, kills bacteria, and eliminates odour— all while ensuring as little dye as possible bleeds off your precious jeans/raw denim clothing, helping you achieve great fades without compromising on smell and hygiene.
What is a rinse wash jean?
A rinse wash is exactly what it sounds like, a quick rinse of water to help remove any excess dye. Typically a process for dark wash jeans, this simple treatment helps preserve as much rich color as possible.
What is back staining in denim?
Back staining is a phenomena of the re-deposition of discharged indiogo from the process bath to fabric.As a result bluish color evenly distributed all over the back side of the denim fabric or white pocket fabric.Sep 11, 2015
What is an enzyme presoak?
Laundry enzyme presoaks are a pre-washing stain removal treatment used to break down protein stains like grass, blood, and baby formula so they can be more efficiently removed during the regular wash cycle. A presoak is necessary when clothes are heavily soiled or stained with oil, protein or tannin stains.Jun 25, 2021
What does enzyme washed linen mean?
'Enzyme washing is a laundering process which uses enzymes to soften and finish fabric; providing jeans and other garments with a worn-in look and feel. The use of enzymes comes with various benefits both economically and environmentally.Mar 12, 2020
What are the disadvantages of using enzymes in washing powders?
(Source: Enzyme Technical Association.) A disadvantage of using enzymes in laundry detergent is that some people experience allergic or other reactions to traces of detergent on laundered clothing. Another is that protease enzymes will damage protein fibres in fabrics such as silk and wool.
What happens when cellulases hydrolyze the fiber?
When the cellulases partly hydrolyze the surface of the fiber, the blue indigo is released, aided by mechanical action, from the surface and light-weight areas appear. Figure 3: Bio-washing/bio-stoning of denim with cellulase enzymes. One of the issues related to the denim bio-stoning is back-staining.
What is cellulase for denim?
A range of cellulase for denim finishing, having their own distinctive properties, is available in the market. The first commercial cellulase enzyme introduced in the market was extracted from the Trichoderma family, a fungus which has the longest history in cellulase research.
What enzyme is used to fasten denim?
Cellulase enzyme fastens the abrasion by a process known as ‘bio stone washing’. The use of these enzymes allows the denim garment washing procedure to be carried out under mild conditions without the use of pumice stones and other harsh chemical agents.
What is stonewashed jeans?
Jeans which is manufactured from denim fabric, is one of the world’s most popular clothing item. The famous “stonewash look” has been traditionally achieved by removing the indigo dye using a local process in which a pumice stone is added to the washing drum for the abrasion of the garment.
How to get blue jeans to fade?
In the traditional stonewashing technique, which is done by pumice stone, the blue denim is faded out by an abrasive action of the stones on the garment surface. This process removes some of the indigo dye.
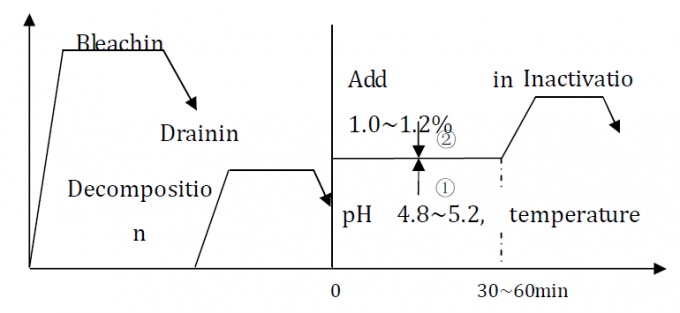
What pH is used for cellulase enzymes?
The temperature and the pH used are quite specific to the type of cellulase enzyme employed. Usually neutral cellulases at pH 6–7 is applied, while acid cellulases are applied at a pH 4.5–5.5. However, the result is a greater extent of back staining, as it is more penetrative.
What is the color of denim?
Traditionally, denim is woven with cotton in twill weave (warp face), in which the warp is blue, and the weft is white. Dyeing of denims is usually performed with pure indigo, or indigo dye mixed with a sulphur dye to decrease the costs which is caused by the expensive indigo dye.
What is protease used for?
In treating natural fibres composed of proteins, like silk and wool, protease can be used. On wool, with some protease base enzymatic preparations, interesting effects can be achieved which have some commercial importance, such as: – Softening and modification of hand characteristics. – Anti-pilling and surface cleaning.
What are the advantages of bioscouring?
Advantages of the Bio-scouring : – Saving of water and energy. – Lower environmental impact and easier to treat wastewater. – Better compatibility with other processes, machinery and materials. – Lesser attacks on the fibre structure, loss of weight and resistance, with improved quality of the article.
What enzymes are used to eliminate hydrogen peroxide?
catalase for elimination of hydrogen peroxide after bleaching, amylase for desizing processes, pectinase for bioscouring of raw cotton, protease for the treatment of wool and silk and. laccase for oxidation of dyes such as indigo. ENZYMATIC DESIZING : Enzymes are bio-chemicals which a specific action on only one type of compound ...
What are the functions of a cellular catalyst?
They are present in all living cells which carry out vital functions in the metabolic process, of growth and cellular reproduction, transforming and conserving energy. They are biological catalysts capable of notably accelerating the chemical reactions which occur in living organisms.
How to shrink wool?
1) Limit the typical tendency of wool to “shrink and felt”. 2) Solve dimensional stability problems. 3) Provide “machine wash” characteristics for the fabric. 4) Eliminate the negative properties emerging in fabric care processes (e.g. hygroscopic expansion) 5) Enhance the fabric colouring.
What are the roles of enzymes in textiles?
Role of Enzymes in Textile Wet-Processing. Enzymes are proteins formed by long linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They are present in all living cells which carry out vital functions in the metabolic process, of growth and cellular reproduction, transforming and conserving energy. They are biological catalysts capable of notably ...
What is the enzyme that kills hydrogen peroxide?
ENZYMATIC PEROXIDE KILLING : Matzyme VHK is a catalase enzyme derived from the submerged fermentation of a genetically modified strain of Aspergillus niger. It has been proven to be highly effective in catalyzing the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water. 2H2O2 VHK O2 + 2H2O.
What are the most successful enzymes used in the textile industry?
Cellulases are the most successful enzymes used in the textile industry ( Kuhad et al., 2011). Cellulases are used in the biostoning of denim garments (jeans) and biopolishing of cotton and other cellulosic fabrics (Bera et al., 2015 ). Traditional stonewashing of denim garments involves the amylase-mediated removal of starch coating (desizing) and treatment (abrasion) of jeans with pumice stone in large washing machines ( Menon and Rao, 2012 ). Cellulases are used in the biostoning of denim garments for producing softness and the faded look of denim garments, replacing the use of pumice stones which were traditionally employed in the industry ( Kuhad et al., 2011 ). The enzymes act on the cellulose fiber to release the indigo dye used for coloring the fabric, producing the faded look of denim. Humicola insolens cellulase is most commonly employed in biostoning, although use of acidic cellulose from Trichoderma along with proteases was found to be equally good ( Zhao et al., 2013a,b ).
What is the third largest enzyme in the world?
Cellulases are currently the third largest industrial enzyme, in terms of commercial value, because of their use in cotton processing (stonewashing denim), paper recycling, as detergent enzymes, in juice extraction and as animal feed additives. However, cellulases will become the largest volume industrial enzyme, if ethanol, butanol, or some other fermentation product of sugars, produced from biomass, becomes a major transportation fuel, as seems likely. Currently, all industrial cellulases are almost produced from aerobic cellulolytic fungi, such as Hypocrea jecorina ( T. reesei) or Humicola insolens. This is due to the ability of these organisms to produce extremely large amounts of crude cellula se (as much as 130 g l −1 ), the high specific activity of their crude cellula se on crystalline cellulose, relative to other crude cellulases , and the ability to genetically modify these strains, so as to tailor the set of enzymes they produce to give optimal activity for specific uses. Research to increase the activity of T. reesei cellulases in degrading pretreated biomass have identified a family 61 enzyme from another organism that increases activity several fold. This is a surprising result as the studied family 61 cellulases have low activity and T. reesei produces several family 61 enzymes.
What is the color of denim jeans called?
Indigo, known as the ‘King of Colors,’ is the deep blue dye used to dye denim jeans. Its importance in world terms is immense and has been for thousands of years. Even today, indigo contributes around one-tenth of the total international dye market.
How does laccase help dyeing?
Laccases can improve the dyeing efficiency and reduce the cost of the dyeing process by in situ oxidation of inexpensive precursors after their adsorption by the fabric, and aid textile bleaching by avoiding back staining by degrading the released dyestuff after dyeing or by bleaching the textile fibers from natural dyes or impurities ( Vasil’eva et al., 2008). Some of the first developed commercial laccase formulations are used for denim fabric finishing (fading of indigo-dyed denim) to give the characteristic gray cast (Galante and Formantici, 2003; Pezzella et al., 2015 ). Laccases have also been used for functional modification of molecules on textile fabrics such as cotton or wool, improving properties as water repellence or resistance ( Lantto et al., 2004; Guimarães et al., 2011; Pezzella et al., 2015 ). In situ polymerization of catechol and p -phenylenediamine catalyzed by laccase on different fabrics can yield colored low-conductive fabrics with good fastness behavior after washing ( Su et al., 2019a ). Moreover, this polymerization reaction has been used for coating wood, cotton and polyethylene terephthalate fabrics to provide antimicrobial properties against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. These enzyme-treated textile fabrics are of special interest in hospitals to reduce the spread of nosocomial diseases ( Su et al., 2019b ).
What is the process of denim?
The desirable abraded look is traditionally obtained in a wet process whereby the garment is washed along with pumice stones (1–2 kg per pair of jeans). This process is called stonewashing or denim wash. Denim is cotton twill-weave fabric with an indigo-dyed warp and a raw white weft. The stonewash effect is due to abrasion of the fabric, which locally removes the surface-bound indigo dye and reveals the white interior of the yarn. The disadvantages of the traditional stonewashing process are reduced fabric strength as a result of abrasion, damage caused to the washing drum and the need for disposal of big loads of pumice dust (reviewed by Heine and Höcker, 1995; Kochavi et al., 1990 ). Enzymes such as cellulases have been used for finishing of denim garments since the 1980s. Cellulases primarily attack the surface of the fiber, since enzymes cannot access the interior of the tightly packed cellulose chains ( Cavaco-Paulo, 1998 ). This mode of action is particularly suitable for finishing of indigo-dyed denim garments. Cellulases, together with the mechanical action of the washing machine, remove the surface-bound dye, resulting in a washed-out appearance ( Kochavi et al., 1990; Tyndall, 1990 ). The advantages of the enzyme-based denim wash are less damage to the garment and the machinery, improved quality of waste water (due to the absence of stone dust) and increased productivity as a result of a higher garment load.
Why are enzymes used in textiles?
The use of enzymes in the textile industry allows the development of environmentally friendly technologies in fiber processing and strategies to improve the final product quality. The consumption of energy as well as increased awareness of environmental concerns related to the use and disposal of chemicals into landfills, water, or release into the air during chemical processing of textiles are the principal reasons for the application of enzymes in finishing of textile materials ( O’Neill et al., 2007 ).
