
Deep Vein Thrombosis
A condition in which the blood clots form in veins located deep inside the body.
Full Answer
What can cause an elevated D dimer?
- disseminated intravascular coagulation
- vaso-occlusive sickle-cell crisis
- acute cerebrovascular accident
- acute myocardial infarction
- unstable angina
- atrial fibrillation
- pneumonia
- vasculitis
- superficial phlebitis
- many cancers including lung, prostate, cervical, and colorectal
Why is a positive D-dimer is not always a blood clot?
Why a Positive D-Dimer Is Not Always a Blood Clot. A blood clot causes a breakdown product called D-dimer . A negative blood result means you don't have a pulmonary embolism. But with increasing age comes an increased likelihood of a positive result, even if there are no blood clots.
When to get a D dimer?
You can expect to experience the following during a blood test, or blood draw:
- You’ll sit in a chair or lie on a medical bed, and a healthcare provider will check your arms for an easily accessible vein. ...
- Once they’ve located a vein, they’ll clean and disinfect the area.
- They’ll then insert a small needle into your vein to take a blood sample. ...
- After they insert the needle, a small amount of blood will collect in a test tube.
What does D dimer tell you?
A D-dimer test is used to find out if you have a blood clotting disorder. These disorders include: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a blood clot that's deep inside a vein. These clots usually affect the lower legs, but they can also happen in other parts of the body.
How is high D-dimer treated?
Statins have proven antithrombotic properties, as suggested by the reduction of several prothrombotic markers, including D-dimer, in patients at high risk of arterial thrombosis.
When is D-dimer treated?
Due to the incidence of false negatives, a D-dimer should only be used in the setting of low suspicion for pulmonary embolism (PE) or low suspicion for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and also known as venous thromboembolism (VTE). It also plays a role in the workup of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
What is the problem if D-dimer is high?
If your results show higher than normal levels of D-dimer, it may mean you have a clotting disorder. But it cannot show where the clot is located or what type of clotting disorder you have. Also, high D-dimer levels are not always caused by clotting problems.
How can I lower my D-dimer naturally?
Some foods and other substances that may act as natural blood thinners and help reduce the risk of clots include the following:Turmeric. Share on Pinterest Rowan Jordan/Getty Images. ... Ginger. ... Cayenne peppers. ... Vitamin E. ... Garlic. ... Cassia cinnamon. ... Ginkgo biloba. ... Grape seed extract.More items...
How long does it take for D-dimer to return to normal?
In our experience, we observed that after complete clinical recovery from COVID-19, restoration of wellbeing, and normalization of molecular swab, 20% of patients had substantially elevated levels of D-dimer, which returned progressively to normal after about two weeks of treatment with prophylactic doses of enoxaparin ...
Does Covid cause elevated D-dimer?
D-dimer elevation is often observed in patients with acute COVID-19 due acute lung injury itself or due thromboembolic complications that occur frequently in COVID-19.
How do they treat blood clots?
Blood-thinning medications are commonly used to prevent blood clots from forming or getting bigger. Thrombolytic medications can break up existing clots. Catheter-directed treatments, such as percutaneous transcatheter treatment, are done by inserting a catheter into a blood vessel in the groin.
What kind of infection causes elevated D-dimer?
Conclusions. In conclusion, D-dimer levels are commonly elevated in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Significantly higher levels are found in those with critical illness and may be used as a prognostic marker for in-hospital mortality.
How do u prevent blood clots?
Preventing Blood ClotsWear loose-fitting clothes, socks, or stockings.Raise your legs 6 inches above your heart from time to time.Wear special stockings (called compression stockings) if your doctor prescribes them.Do exercises your doctor gives you.Change your position often, especially during a long trip.More items...
Which fruit is good for blood clots?
Citrus Fruit Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for staying healthy and citrus fruits are an excellent way to include it in your diet. Citrus fruit such as oranges, grapefruit, and lemons contain many antioxidants that can lower inflammation, prevent blood clots, and improve blood circulation.
What vitamin helps blood clots?
Vitamin K helps to make four of the 13 proteins needed for blood clotting, which stops wounds from continuously bleeding so they can heal. People who are prescribed anticoagulants (also called blood thinners) to prevent blood clots from forming in the heart, lung, or legs are often informed about vitamin K.
What medication is used to dissolve blood clots?
Anticoagulants, such as heparin, warfarin, dabigatran, apixaban, and rivaroxaban, are medications that thin the blood and help to dissolve blood clots.
What is the D-dimer in blood?
One of those leftovers is called D-dimer. It’s part of a protein. Normally, with a little time, it goes away. But you can get high levels of D-dimer in your blood if you have a major clot like with deep vein thrombosis ( DVT ). With DVT, you have a clot deep in one of your veins, usually in your legs, and it can lead to serious problems.
Why do you need a D-dimer test?
To rule out DVT and other conditions: The D-dimer test is most useful when your doctor thinks something else is causing your symptoms and wants to quickly rule out these causes: DVT, which may give you swelling, pain, or redness in your leg.
What does it mean when your D-dimer levels drop?
If D-dimer levels drop, it’s a sign that the treatment is working. What Happens During the Test? You don’t need to do anything special to get ready for a D-dimer test. Your doctor uses a thin needle to take a small amount of blood.
Can a positive D-dimer test show a blood clot?
In this case, the test is only helpful if you’re not too likely to have blood clots. A positive D-dimer test doesn’t mean you have a blood clot. Other tests will be needed to check for that. If your odds of having a clot are higher, you’ll need different tests. You have higher odds of a clot with:
Why is D-dimer used?
Its main use, therefore, is to exclude thromboembolic disease where the probability is low. D-dimer levels are used as a predictive biomarker for the blood disorder, disseminated intravascular coagulation and in the coagulation disorders associated with COVID-19 infection. A four-fold increase in the protein is an indicator ...
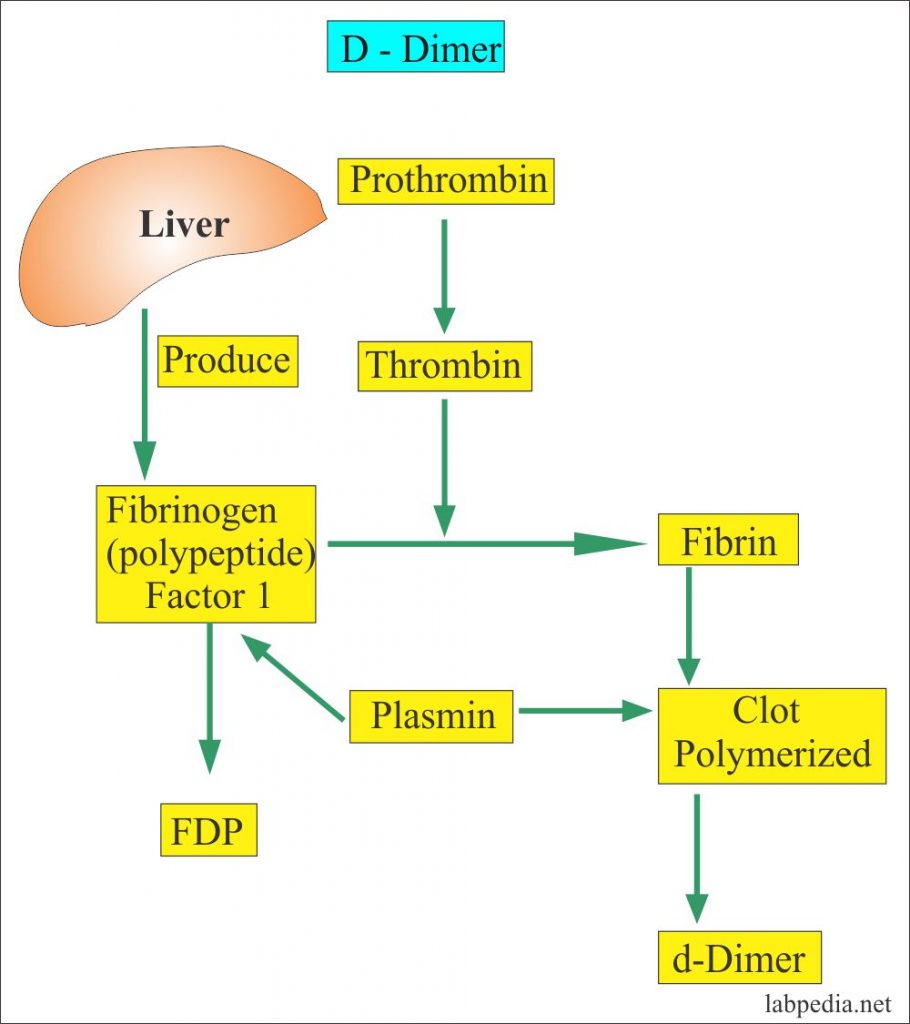
What is a D dimer?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross-link.
How much is 1.0 mcg/mL of d-dimer?
The molecular weight of the fibrinogen molecule is about twice the size of the D-dimer molecule, and therefore 1.0 mcg/mL FEU is equivalent to 0.5 mcg/mL of d-dimer.
How to determine D-dimer concentration?
D-dimer concentration may be determined by a blood test to help diagnose thrombosis . Since its introduction in the 1990s, it has become an important test performed in people with suspected thrombotic disorders, such as venous thromboembolism.
Why are D-dimers not present in plasma?
D-dimers are not normally present in human blood plasma, except when the coagulation system has been activated, for instance because of the presence of thrombosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation. The D-dimer assay depends on the binding of a monoclonal antibody to a particular epitope on the D-dimer fragment.
What does it mean when D-dimer levels drop?
During the course of stay D-dimer levels decline, indicating that there is no longer increased coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Is DIC a separate organ failure?
Consequently, prevention of new or worsening organ dysfunction is a primary goal in the treatment of patients with severe sepsis. DIC can be seen as a separate organ failure, which might be prevented. Anticoagulation leads to lowering levels of D-dimer in patients with thromboembolic diseases.
Is DIC a beneficial outcome?
Various studies in patients with DIC clearly showed that a decrease in DIC severity is associated with beneficial outcome, whereas a worsening DIC to overt DIC is associated with organ failure and death.
Is D-dimer present in fibrinogen?
D-dimer, which is present in the degradation products, is not present in fibrinogen or the fibrin monomer. Therefore, plasma levels of D-dimer are specific for the plasmin-catalyzed degradation of the fibrin polymer. Thereby D-dimer plasma levels specifically reflect the turnover of the coagulation system.
Why does the D-dimer go up?
Other health problems can also cause the D-dimer level to go up. Therefore, the D-dimer test is not the only test used to diagnose a disease or condition. It is usually used with other blood tests and imaging scans. If the D-dimer test is positive, then you might be sent for imaging.
What does a positive D-dimer test mean?
A positive test means the D-dimer level in the body is higher than normal and suggests someone might have blood clots.
What blood thinners are used for DVT?
The most commonly used injectable blood thinners for DVT are enoxaparin (Lovenox) and fondaparinux (Arixtra). After taking an injectable blood thinner for a few days, your doctor may switch you to a pill. Examples of blood thinners that you swallow include warfarin (Jantoven) and dabigatran (Pradaxa).
How to treat DVT?
DVT is most commonly treated with anticoagulants, also called blood thinners. These drugs don't break up existing blood clots, but they can prevent clots from getting bigger and reduce your risk of developing more clots. Blood thinners may be taken by mouth or given by IV or an injection under the skin.
What to do if you can't take medicine to thin your blood?
If you can't take medicines to thin your blood, you might have a filter inserted into a large vein — the vena cava — in your abdomen. A vena cava filter prevents clots that break loose from lodging in your lungs. Compression stockings. These special knee socks reduce the chances that your blood will pool and clot.
Can you take blood thinners with IV?
Certain blood thinners do not need to be given first with IV or injection. These drugs are rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis) or edoxaban (Savaysa). They can be started immediately after diagnosis. You might need to take blood thinner pills for three months or longer.
What is an abnormal D-dimer?
Abnormal D-dimer values are indicators of acute diseases or medical conditions that call for immediate action. The physician may request for a series of tests such as CT scan, lung scintigraphy or ultrasound of the leg veins to check if there indeed a thrombus that occurred. An abnormal D-dimer value can be a red flag for DIC (or disseminated intravascular coagulation) and PE (or pulmonary embolism).
What is the normal D-dimer level?
The normal amounts for D-dimer in the blood should be around 0.5 mg/l of blood or 500 ng/ml of blood. A normal D-dimer test result will reveal a negative result, which indicates that thrombosis has not occurred. People who yield negative or normal D-dimer test results are most likely not suffering from any acute medical condition or disorder that can trigger abnormal blood clotting formation and break down. D-dimer normal values are a good indication that the treatment given to a patient suffering from disseminated intravascular coagulation is working; while an elevated D-dimer value signifies the opposite.

Overview
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross-link, hence forming a protein dimer.
D-dimer concentration may be determined by a blood test to help diagnose thrombosis. Since its introduction in the 1990s, it has become an important test performed in people with suspected t…
Principles
Coagulation, the formation of a blood clot or thrombus, occurs when the proteins of the coagulation cascade are activated, either by contact with a damaged blood vessel wall and exposure to collagen in the tissue space (intrinsic pathway) or by activation of factor VII by tissue activating factors (extrinsic pathway). Both pathways lead to the generation of thrombin, an enzyme that turns the soluble blood protein fibrinogen into fibrin, which aggregates into proteofib…
Indications
D-dimer testing is of clinical use when there is a suspicion of deep venous thrombosis (DVTl), pulmonary embolism (PE) or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
For DVT and PE, there are possible various scoring systems that are used to determine the a priori clinical probability of these diseases; the best-known is the Wells score.
• There exists a significant correlation between increased plasma D-dimer level with an increase…
Interpretation
The following are reference ranges for D-dimer:
D-dimer increases with age. It has therefore been suggested to use a cutoff equal to patient’s age in years × 10 µg/L (or x 0.056 nmol/L) for patients aged over 50 years for the suspicion of venous thromboembolism (VTE), as it decreases the false positive rate without substantially increasing the false negative rate.
History
D-dimer was originally described in the 1970s and found its diagnostic application in the 1990s.
External links
• D-dimer - Lab Tests Online