Contraindications Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) Hypersensitivity to insulin or its excipients (inactive co-ingredients) Warnings and Precautions Hypoglycemia may occur and is the most common side effect of insulin treatment. Severe, life-threatening allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur.
What is really contraindicated with diabetes?
Dec 27, 2017 · Insulin pump use may be contraindicated in the following clinical situations: Patient has history of serious psychological or psychiatric condition(s).1 Patient has sensory or gestural impairment.2 Patient is unable or unwilling to perform MDI injections (≥3–4 daily), frequent SMBG (≥4 daily), and carbohydrate counting.1 Active progressing retinopathy.3 …
Can prolonged use of insulin damage the kidneys?
Dec 26, 2017 · Obese patients may require 2 U/kg/day. 40-60 % of the daily dose is given as basal insulin with 1 or 2 injections of intermed Contra Indications Insulin is contraindicated in hypoglycaemia, severe allergy to porcine or bovine insulins.Patients who are hypersensitive to a single species insulin can be changed to Human insulin.
What are the precautions for insulin?
Jul 16, 2021 · Contraindications Though there are no absolute contraindications to insulin therapy, the dose of insulin needs to be adjusted and monitored in numerous settings. Insulin dosing requires adjustment in patients with renal impairment and liver failure, as insulin metabolism occurs in the liver, excreted in the urine.
Which medication is contraindicated with Coumadin?
Adequate treatment of insulin dependent diabetes with insulin, properly implemented and accurately indicated, ensures good control which guarantees a favourable effect on the clinical course of diabetes. The main advantage of treatment is to maintain a stable insulinaemia during the interprandial pe …
What drugs are contraindicated with insulin?
These include:Salicylates (aspirin)Sulfa antibiotics.Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.Angiotensin II receptor blockers.Beta-blockers.Alcohol.Octreotide.More items...•Apr 5, 2021
What are the contraindications of regular insulin?
You should not use insulin regular if you are allergic to insulin, or if you are having an episode of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Regular insulin is not approved for use by anyone younger than 2 years old. This medicine should not be used to treat type 2 diabetes in a child of any age.May 27, 2020
What should you not do when taking insulin?
Do rotate the place where you inject insulin Try not to inject your insulin in the same exact place on your body every time. This is to prevent a condition called lipodystrophy. In lipodystrophy, the fat under the skin either breaks down or builds up and forms lumps or indentations that can obstruct insulin absorption.Sep 21, 2018
What is insulin side effects?
Human insulin may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site.changes in the feel of your skin, skin thickening (fat build-up), or a little depression in the skin (fat breakdown)weight gain.constipation.
What are the 5 types of insulin?
The 5 types of insulin are: rapid-acting insulin. short-acting insulin. intermediate-acting insulin....Rapid-acting insulinFiasp and NovoRapid® (insulin aspart)Humalog® (insulin lispro)Apidra® (insulin glulisine).
When should you not take Lantus?
You should not use Lantus if you are allergic to insulin, or if you are having an episode of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or diabetic ketoacidosis (call your doctor for treatment). Lantus is not approved for use by anyone younger than 6 years old, and some brands are for use only in adults.Mar 25, 2022
Can you take insulin without eating if blood sugar is high?
Take insulin, but don't eat: Rapid-acting and short-acting insulin injections should be taken just before or with meals. Your blood sugar rises after meals. Taking rapid-acting or short-acting insulin without eating could lower your sugar to a dangerous level.Mar 8, 2022
How long should you wait to eat after taking insulin?
With regular insulin, you inject the insulin and then wait 30 to 60 minutes before eating. Many people find it hard to time their meals around regular insulin injections. Sometimes they end up eating too soon or too late. Then they don't achieve the best blood sugar control.Aug 17, 2020
What are the side effects of insulin?
Hypersensitivity to insulin or its excipients (inactive co-ingredients) Hypoglycemia may occur and is the most common side effect of insulin treatment. Severe, life-threatening allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur. Hypokalemia (low blood potassium) may occur because insulin stimulates movement of potassium from blood into cells.
What is the generic name for insulin?
Generic Name: insulin (IN-su-lin) Brand Name: Examples include BD Ultrafine and Novofine Insulin is used for: Injecting insulin (and other solutions as determined by your doctor) into a preselected site of the body. Do NOT use insulin if: you are allergic to any ingredient in insulin Contact your doctor or health care provider right away if any of these apply to you. Before using insulin: Some medical conditions may interact with insulin. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have any medical conditions, especially if any of the following apply to you: if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding if you are taking any prescription or nonprescription medicine, herbal preparation, or dietary supplement if you have allergies to medicines, foods, or other substances Some MEDICINES MAY INTERACT with insulin. However, no specific interactions with insulin are known at this time. Ask your health care provider if insulin may interact with other medicines that you take. Check with your health care provider before you start, stop, or change the dose of any medicine. How to use insulin: Use insulin as directed by your doctor. Check the label on the medicine for exact dosing instructions. Carefully attach the needle to your insulin pen as you have been shown. Prepare and inject your insulin following the procedure you have been shown. Do not remove the cap from the needle until you are ready to give the injection. Do not recap the needle after the injection. You may accidentally stick yourself trying to recap the needle. Do not share pen or cartridge devices with another person. Sharing these devices may pass infections from one person to another. This includes infections you may not know you have. Keep this product, as well as syringes and needles, out o Continue reading >>
How long does insulin glargine stay in the body?
After injection into the subcutaneous tissue, the acidic solution is neutralized, leading to formation of microprecipitates from which small amounts of insulin glargine are slowly released, resulting in a relatively constant concentration/time profile over 24 hours with no pronounced peak.
What is the purpose of insulin in diabetes?
Adequate insulin dosage permits patients with diabetes to effectively utilize carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Regardless of dose strength, insulin enables carbohydrate metabolism to occur and thus to prevent the production of ketone bodies by the liver.
Can insulin be administered intravenously?
Some insulins (for example, regular insulin) also may be administered intravenously. The dose is individualized for each patient. A combination of short or rapid acting and intermediate or long acting insulin typically are used Some patients may develop resistance to insulin and require increasing doses.
Do Type 2 diabetics need insulin?
Patients with Type 2 diabetes (especially in early stages) still produce their own insulin or just need help processing the insulin that is in their body- due to resistance, for example. Type 1 patients produce no insulin therefore they NEED insulin to survive. There is no other option.
Is insulin a substitute for diabetes?
Insulin of course is the first line drug in case of Type 1 Diabetes (T1 DM), previously called juvenile diabetes. There is no substitute here and oral hypoglycemic agents are contraindicated because the deficiency of Insulin here is absolute.Insulin ought to be the drug of choice.
What are the side effects of insulin?
Common side effects of insulin include hypoglycemia, headache, weight gain, rash, itching, flu-like symptoms, lipoatrophy, and reaction at the site of injection. Warnings, precautions, and drug interactions should be reviewed prior to taking insulin.
What causes insulin to be reduced?
Hepatic ( liver) impairment may reduce the insulin requirement. Renal (kidney) dysfunction may reduce the insulin requirement. Illness, emotional disturbance, or other stress may alter the insulin requirement. Intravenous administration increases the risk of hypoglycemia and hypokalemia.
How does insulin affect blood glucose levels?
Insulin lowers blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake primarily by skeletal muscle cells and fat, and by inhibiting glucose production and release by the liver. Insulin inhibits lipolysis (breakdown of fat), proteolysis (breakdown of proteins), and gluconeogenesis (manufacture of glucose).
What is insulin made of?
Human insulin preparations and regular insulin are made by recombinant DNA technology . Examples of preparations of insulin include rapid ...
What happens if you don't produce enough insulin?
Patients with diabetes are insensitive to insulin and do not produce enough insulin which leads to hyperglycemia and symptoms of diabetes. Exogenous insulin preparations replace insulin in diabetics, increasing the uptake of glucose by cells and reducing the short and long term consequences of diabetes.
How to report a drug problem to the FDA?
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088 . Medically Reviewed on 10/28/2019.
Where is insulin administered?
Insulin usually is administered by subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall, thigh, buttocks (gluteal region), or upper arm. Injection sites should be rotated within the same region. Some insulins (for example, regular insulin) also may be administered intravenously. The dose is individualized for each patient.
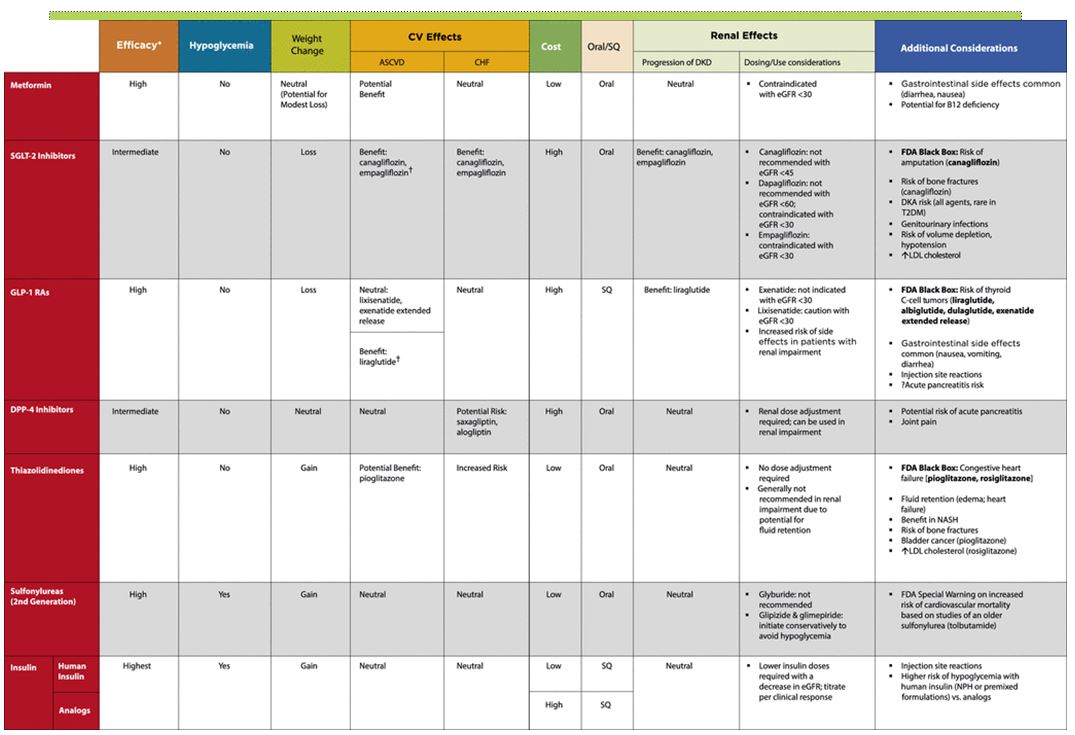
What are the factors to consider when selecting another agent in lieu of metformin?
There are numerous factors to consider when selecting another agent in lieu of metformin including, but not limited to, overall efficacy in A1creduction, adverse effect profile, cost, and patient preference.
What is the best medication for diabetes?
The American Diabetes Association/European Association for the Study of Diabetes recommend a sulfonylurea, meglitinide, pioglitazone, or dipeptidyl pep tidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitor when metformin cannot be used.3They also recommend using a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist if weight loss is warranted.
Can you take metformin with gastrointestinal problems?
Patients may initially receive metformin but not be able to tolerate common side effects, mainly its gastrointestinal adverse effects. Likewise, some practitioners may be cautious in using metformin in patients at risk for but who do not necessarily currently have specific contraindications to its use.
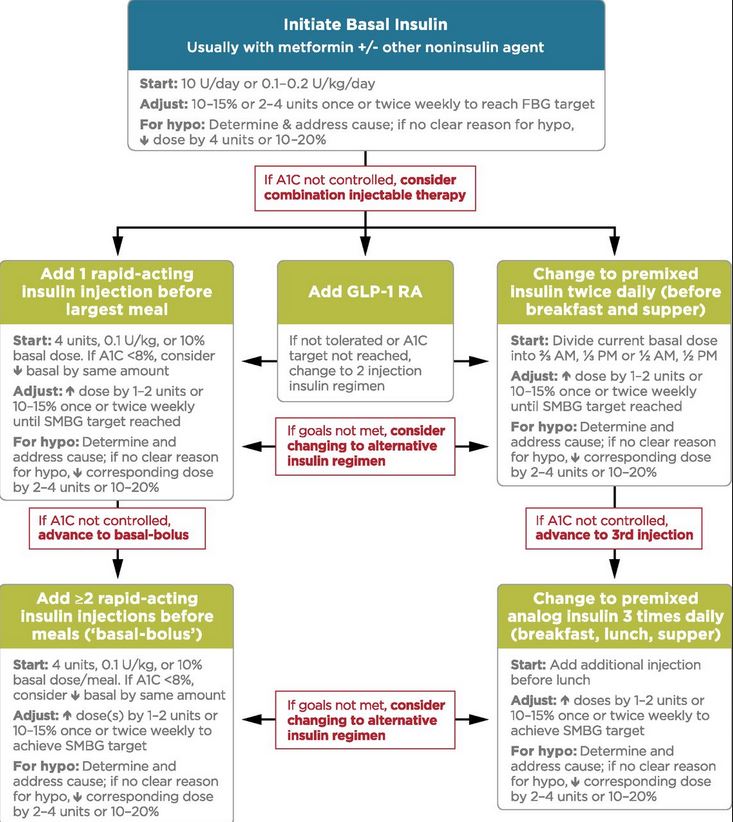
Can basal insulin be used twice a day?
If fasting glucose concentrations are the only glycemic problem, use of a once-daily or twice-daily basal insulin should suffice. However, if post-prandial glucose excursions in addition to increased fasting glucose occur together, a combination of basal and bolus insulin or a fixed insulin combination is warranted.
Can metformin be used for renal impairment?
If a patient cannot receive metformin due to significant renal impairment (creatinine clearance <45 mL per minute), use of canagliflozin should also be avoided. DPP-4 inhibitors. Over the past few years, there have been numerous DPP-4 inhibitors approved for use in the treatment of hyperglycemia associated with T2DM.
What is a contraindication for surgery?
Contraindication. A contraindication is a specific situation in which a drug, procedure, or surgery should not be used because it may be harmful to the person . There are two types of contraindications: Relative contraindication means that caution should be used when two drugs or procedures are used together.
Can you take aspirin and warfarin together?
For instance, a person who takes warfarin to thin the blood should not take aspirin, which is also a blood thinner. This is an example of a relative contraindication.
Is isotretinoin safe for pregnancy?
For example, isotretinoin, a drug used to treat acne is absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy due to the risk of birth defects. Certain decongestants are contraindicated in people with high blood pressure and should be avoided.
What happens if you have too much insulin?
Insulin shock occurs when you have too much insulin in your blood. This can lead to hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar. Insulin shock may occur if someone: Insulin shock is a diabetic emergency. If left untreated, it can lead to diabetic coma, brain damage, and even death.
Why do people take insulin shots?
High blood glucose can cause eye and foot problems, heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and nerve damage. Insulin shots help people with diabetes use glucose more efficiently. Taking an insulin shot before eating helps the body absorb and use glucose from the food. The result is a more balanced and healthy blood sugar level.
What to eat after taking insulin shot?
Eat after taking your insulin shot. Always ask your doctor how to use a new medication. Eat a snack if your blood sugar is under 100 milligrams per deciliter before exercise or if you’re planning on doing more exercise than normal. Keep a carbohydrate snack with you when exercising.
What to do if your blood sugar isn't increasing?
If your blood sugar isn’t increasing, try eating another 15 grams of carbohydrates, followed by a meal. If you blood sugar is not increasing after repeating this step again, contact your doctor or visit the emergency room. Plummeting blood sugar can also cause: Insulin shock can also happen in the middle of the night.
How does insulin work?
How insulin works. When we consume food or beverages that contain carbohydrates, your body converts them into glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar that fuels the body, giving it the energy it needs to perform everyday functions. Insulin is a hormone that works like a key.
What happens if your blood sugar drops below normal?
If your blood sugar drops a bit below normal, you may experience mild to moderate symptoms, including: dizziness. shaking. sweating/clamminess. hunger. nervousness or anxiety. irritability. rapid pulse. At this stage, you can usually take immediate steps to recover.
How to treat hypoglycemia?
If you or someone near you begins to experience insulin shock, take these steps: Call 911 , particularly if the person is unconscious. Treat as outlined above unless the person is unconscious.