
What is cognitive behavioral therapy and do I need It?
Cognitive behavioral therapy is used to treat conditions such as depression, anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorders, and addictions. But it is also an option for treating physical conditions such as chronic pain, tinnitus and rheumatism. It can help to relieve the symptoms. Cognitive behavioral therapy requires the patient's commitment and own initiative.
Does cognitive behavioral therapy really work?
Cognitive behavioral therapy has been scientifically proven to be effective in treating symptoms of depression and anxiety in children and adolescents. A 2018 meta-analysis of 41 studies found that CBT helped to improve symptoms in people with anxiety and anxiety-related disorders, including obsessive-compulsive disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy, and how does it help?
In addition to depression or anxiety disorders, CBT can also help people with:
- bipolar disorder
- borderline personality disorder
- eating disorders – such as anorexia and bulimia
- obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
- panic disorder
- phobias
- post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- psychosis
- schizophrenia
- sleep problems – such as insomnia
What is the difference between cognitive and behavioral therapy?
Co-authors from the Jacobs School’s Division of Behavioral Medicine are:
- Rebecca S. Firth, division administrator and research coordinator.
- Gregory D. Gudleski, PhD, research assistant professor. ...
- David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
- G. ...
- Imaging Genetics Center, Mark and Mary Stevens Institute for Neuroimaging and Informatics, Keck School of Medicine at University of Southern California.
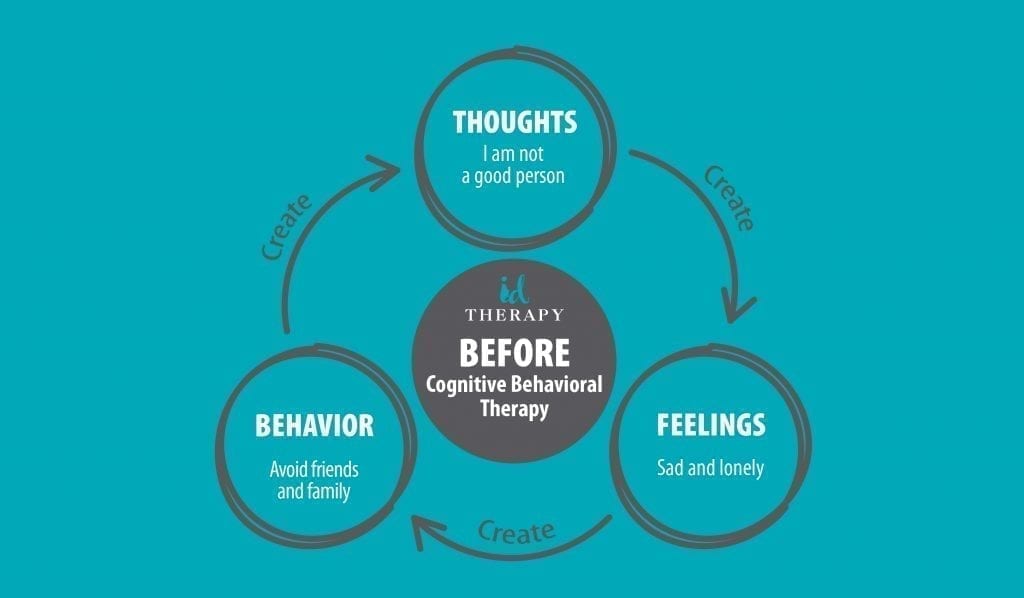
What is an example of cognitive behavioral therapy?
What are examples of cognitive behavioral therapy? Examples of CBT techniques might include the following: Exposing yourself to situations that cause anxiety, like going into a crowded public space. Journaling about your thoughts throughout the day and recording your feelings about your thoughts.
What does cognitive behavioral therapy involve?
CBT treatment usually involves efforts to change thinking patterns. These strategies might include: Learning to recognize one's distortions in thinking that are creating problems, and then to reevaluate them in light of reality. Gaining a better understanding of the behavior and motivation of others.
What are the 5 components of cognitive behavioral therapy?
Intended for both trainees and practitioners in the mental health professions, the book details the five basic components of the therapy in practice: developing an individualized case formulation, session structuring, activity scheduling, the thought record, and the schema change method.
Who is CBT not suitable for?
Due to the structured nature of CBT, it may not be suitable for people with more complex mental health needs or learning difficulties. As CBT can involve confronting your emotions and anxieties, you may experience initial periods where you are more anxious or emotionally uncomfortable.
How long does cognitive behavioral therapy take?
A highly effective psychotherapy called cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) focuses on how our thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes can affect our feelings and behavior. Traditional CBT treatment usually requires weekly 30- to 60-minute sessions over 12 to 20 weeks.
What are the three main goals in cognitive therapy?
Goals of Cognitive Therapy Include:the promotion of self-awareness and emotional intelligence by teaching clients to “read” their emotions and distinguish healthy from unhealthy feelings.helping clients understand how distorted perceptions and thoughts contribute to painful feelings.More items...
What is the difference between cognitive therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy?
First, cognitive therapy focuses on the present while CBT places more emphasis on the past and the future. In cognitive therapy, clients learn how to change thoughts in the current moment. But in CBT, they analyze their past behaviors to help them practice more positive ones in the future.
What are the differences between cognitive therapy and behavioral therapy?
Cognitive Therapy – This type of therapy challenges thoughts, , which leads to better behavior and mood. Behavioral Therapy – This type of therapy uses behavioral approaches to change or alter behaviors for improved outcomes.
Who can benefit from CBT?
Children and adults with various mental health conditions might benefit from CBT. However, certain individuals are more likely to see positive effe...
How long does CBT take for patients to see results?
CBT is generally considered short-term therapy, ranging from about 5-20 sessions for acute cases. However, for patients with chronic conditions, CB...
Do you need a special certification to administer CBT?
No, but you do need to be a licensed mental health professional. Organizations like the National Association of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapists (NA...
Who can provide CBT?
Only licensed mental health professionals like psychologists, social workers, and professional counselors can provide CBT as a treatment for a ment...
Overview
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common type of talk therapy (psychotherapy). You work with a mental health counselor (psychotherapist or therapist) in a structured way, attending a limited number of sessions. CBT helps you become aware of inaccurate or negative thinking so you can view challenging situations more clearly and respond to them...
Why It's Done
- Cognitive behavioral therapy is used to treat a wide range of issues. It's often the preferred type of psychotherapy because it can quickly help you identify and cope with specific challenges. It generally requires fewer sessions than other types of therapy and is done in a structured way. CBT is a useful tool to address emotional challenges. For example, it may help you: 1. Manage sympt…
Risks
- In general, there's little risk in getting cognitive behavioral therapy. But you may feel emotionally uncomfortable at times. This is because CBT can cause you to explore painful feelings, emotions and experiences. You may cry, get upset or feel angry during a challenging session. You may also feel physically drained. Some forms of CBT, such as exposure therapy, may require you to confr…
How You Prepare
- You might decide on your own that you want to try cognitive behavioral therapy. Or a doctor or someone else may suggest therapy to you. Here's how to get started: 1. Find a therapist.You can get a referral from a doctor, health insurance plan, friend or other trusted source. Many employers offer counseling services or referrals through employee assistance programs (EAPs). Or you ca…
What You Can Expect
- Cognitive behavioral therapy may be done one-on-one or in groups with family members or with people who have similar issues. Online resources are available that may make participating in CBT possible, especially if you live in an area with few local mental health resources. CBT often includes: 1. Learning about your mental health condition 2. Learning and practicing techniques s…
Results
- Cognitive behavioral therapy may not cure your condition or make an unpleasant situation go away. But it can give you the power to cope with your situation in a healthy way and to feel better about yourself and your life.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.