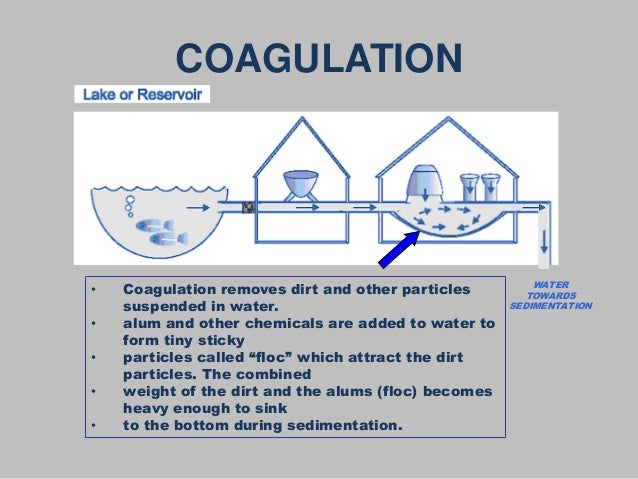
What is coagulation and flocculation in wastewater treatment?
What is coagulation and how is it used in water treatment?
- Works to treat particles that are suspended in the water — not just those which have already formed non-suspended solids.
- Forms clumps or flocs that can be removed from the water relatively simply.
- Cost-effective, as the chemicals required in coagulation are not difficult or expensive to obtain.
What is conventional water treatment process?
conventional treatment processes in detail. 1. Raw water basins slow the water’s velocity after it passes through the intake structure, allowing heavy sediment and grit to settle to the bottom of the basins before the water enters the treatment plant. 2. Chemical coagulants are added to react with the remaining small particles in the water to form particles large enough to settle out.
What is coagulation process?
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot.It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair.
What are flocculants and coagulants for wastewater treatment?
Removal of Inorganics
- Arsenic removal. Arsenic is a commonly occurring toxic element and long term exposure to arsenic is injurious to health.
- Fluoride removal. In 1975, the EPA named fluoride as a contaminant in the National Interim Primary Drinking Water Regulations.
- Chemical Phosphorus Removal. ...
What is coagulation and flocculation process in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are two separate processes, used in succession, to overcome the forces stabilising the suspended particles. While coagulation neutralises the charges on the particles, flocculation enables them to bind together, making them bigger, so that they can be more easily separated from the liquid.
What is used in coagulation in water treatment?
Aluminum sulfate (alum) is the most common coagulant used for water purification. Other chemicals, such as ferric sulfate or sodium aluminate, may also be used.
Why do we do coagulation in water treatment?
safe drinking water. It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect.
What is coagulation or flocculation?
Coagulation is the destabilization of colloidal particles brought about by the addition of a chemical reagent called as coagulant. Flocculation is the agglomeration of destabilized particles into microfloc and after into bulky floccules which can be settled called floc.
What is coagulation process?
Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.
What is the principle of coagulation?
At a glanceWorking PrincipleSuspended particles are destabilised by addition of a clarifying agent leading to the neutralisation of their charges. Particles thus agglomerate (flocs formation) and are able to decant.Main strengthRemoves solids and improves filtrationMain weaknessContinuous input of chemicals required6 more rows•May 24, 2019
What is the function of coagulant?
Coagulants and flocculation processes are used to remove colloidal impurities: suspended particles such as bacteria, clay, silts, and organic matter from the contaminated water. This produces large flock aggregates that can be removed from the water in subsequent clarification/filtration processes.
What is coagulation and its types?
Coagulation is one of the common methods used by water treatment plants to provide safe, clean drinking water to public water customers. This method is often used alongside processes including filtration, disinfection and sedimentation to remove select contaminants from water.
What chemicals are used in coagulation?
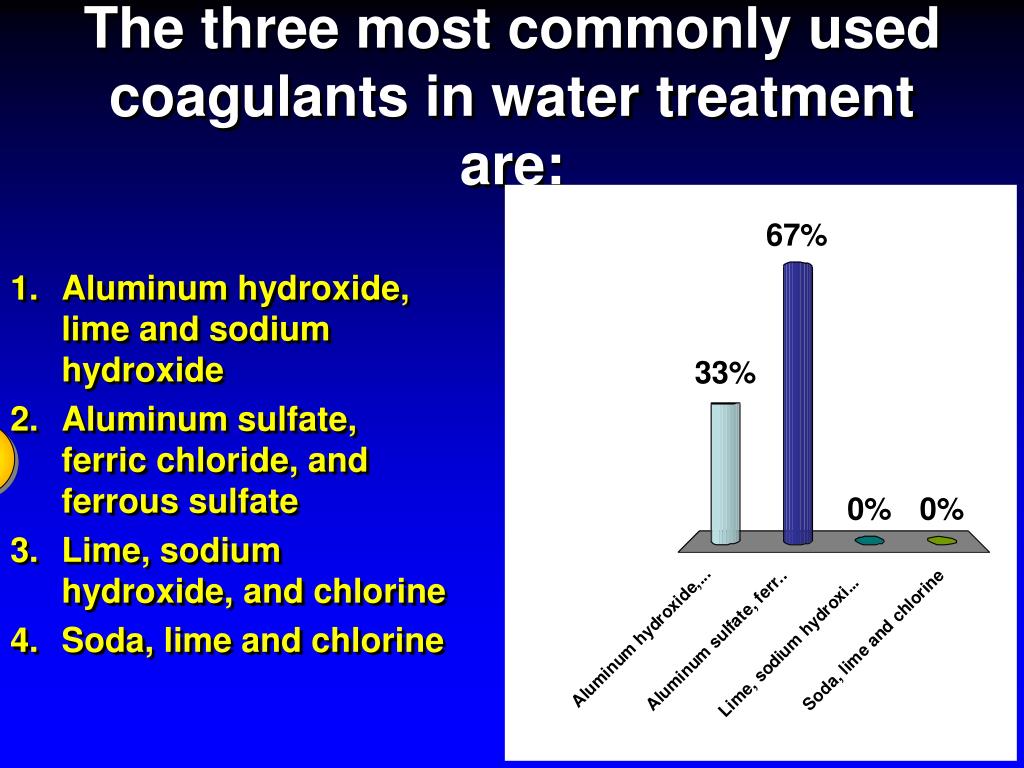
Traditional chemical coagulation uses aluminum and iron coagulants. The most common aluminum coagulants are aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride, and sodium aluminate. Iron coagulants include ferric sulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric chloride, and ferric chloride sulfate [4].
Is coagulation same as precipitation?
Coagulation is the formation of larger aggregates from solid substances, that is, no change in phase. Precipitation, the formation of solid, undissolved species, implies a phase transition. In chemical terms, coagulation and precipitation are distinctly different processes.
What kind of process is coagulation filtration?
precipitative processCoagulation/filtration is a precipitative process. The most widely used coagulants for water treatment are aluminum and ferric salts, which hydrolyze to form aluminum and iron hydroxide particulates, respectively.
What is the difference between coagulation and sedimentation?
Answer: sedimentation is the separation of a suspension of solid particles into a concentrated slurry and a supernatant liquid, either to concentrate the solid or to clarify the liquid while coagulation is the precipitation of suspended particles as they increase in size (by any of several physical or chemical.
What is a Coagulant for Water Treatment?
Ferric sulfate, aluminum sulfate, or ferric chloride, classed as aluminum or iron salts, are common coagulants for water treatment.
How Does Coagulation Treatment Work?
Coagulation treatment is usually carried out before sedimentation and filtration. During the process, a coagulant is added to water, and its positive charge neutralizes the negative charge of suspended contaminants.
What Is Removed During Coagulation?
Coagulation is most effective at removing suspended solids and natural organic matter like gravel, sand, algae, clay, iron, protozoa, and even bacteria. Many of these contaminants can give water an unpleasant taste when present in large quantities, and can also give water a brown or orange color.
What Are the Most Common Types of Coagulants?
The most commonly used chemical for coagulation is aluminum sulfate. Ferric sulfate, ferric chloride, or sodium aluminate are also popular types of coagulants.
How to Choose a Coagulant for Water Treatment
The type of coagulant used by your local water treatment facility will usually depend on availability and affordability. With aluminium sulfate being available, affordable and highly effective, it is the preferred choice for public water treatment around the world.
About the author
Brian Campbell is the founder of WaterFilterGuru.com, where he blogs about all things water quality. His passion for helping people get access to clean, safe water flows through the expert industry coverage he provides. Follow him on twitter @WF_Guru or contact him by email [email protected]
How is coagulation affected by pretreatments?
Coagulation is affected by the type of coagulant used, its dose and mass; pH and initial turbidity of the water that is being treated; and properties of the pollutants present. The effectiveness of the coagulation process is also affected by pretreatments like oxidation.
What is the difference between coagulation and flocculation?
Coagulation (water treatment) In water treatment, coagulation flocculation involves the addition of compounds that promote the clumping of fines into larger floc so that they can be more easily separated from the water. Coagulation is a chemical process that involves neutralization of charge whereas flocculation is a physical process ...
What is the SCD for coagulant dose?
The SCD measures the net surface charge of the particles and shows a streaming current value of 0 when the charges are neutralized ( cationic coagulants neutralize the anionic colloids ). At this value (0), the coagulant dose can be said to be optimum.
What force causes colloidal particles to cling together?
Once the repulsive charges have been neutralized (since opposite charges attract), van der Waals force will cause the particles to cling together (agglomerate) and form micro floc.
Why do colloidal particles settle slowly?
In a colloidal suspension, particles will settle very slowly or not at all because the colloidal particles carry surface electrical charges that mutually repel each other. This surface charge is most commonly evaluated in terms of zeta potential, the electrical potential at the slipping plane. To induce coagulation, a coagulant (typically a metallic salt) with the opposite charge is added to the water to overcome the repulsive charge and "destabilize" the suspension. For example, the colloidal particles are negatively charged and alum is added as a coagulant to create positively charged ions. Once the repulsive charges have been neutralized (since opposite charges attract), van der Waals force will cause the particles to cling together (agglomerate) and form micro floc.
Is coagulation a physical process?
Coagulation is a chemical process that involves neutralization of charge whereas flocculation is a physical process and does not involve neutralization of charge. The coagulation-flocculation process can be used as a preliminary or intermediary step between other water or wastewater treatment processes like filtration and sedimentation.
What is the purpose of coagulation water treatment?
The purpose of coagulation water treatment process is to removes the colloidal particles from water. The water may contain suspended matter, small or large solid particles. Sedimentation and filtration processes can removes most of the solid particles but the small particles that are remains in colloidal suspension cannot removes.
What is the process of coagulation?
The process of consolidation of colloidal particles by neutralizing the charges with a coagulant, so that they can remove from the treated water by sedimentation or filtration is called coagulation. It is a vital part for drinking water and wastewater treatment.
What is a coagulant?
Coagulants. Coagulants are the chemicals that are used to removes tiny particles in water. We used different types of coagulants in coagulation water treatment process. Generally, we can categories the common type of coagulant into two groups, aluminium base and iron base.
What is the name of the chemical that neutralizes the negative charges on colloidal particles?
This chemical is known as coagulant. The positive charges of the coagulant neutralize the negative charges on the colloidal particles. As a result the particles are able to coagulate into coarse formations which are easily removable. The process of consolidation of colloidal particles by neutralizing the charges with a coagulant, ...
What are the factors that affect the coagulation of water?
The process of coagulation of water depends on various factors like pH of the medium, temperature of water, coagulant feed concentration, coagulant dosage, type of coagulant, mass and initial turbidity. Moreover it is also depends on pre-treatment and type of pollutants present.
What is the pH of alum coagulant?
pH affects on the activities of coagulants. The optimum pH for alum coagulation is 6 to 7.5 whereas 5.0 to 8.0 are for iron. If the alkalinity is lower or higher, then the floc does not form properly. As a result, more coagulant is consumed. In this case, it is beneficial to correct the pH by adding acid or base.
Why is alum added to water?
Usually a metallic salt like alum is added as a coagulant to create positively charged ions. Normally 5-10% solution of coagulant is used.
What is coagulation in water treatment?
Coagulation water treatment is the first step in chemical wastewater treatment. Instead of passing over particles that would otherwise slip through the filter and fall too slowly to be trapped as sediment, coagulation clumps them together so they are more easily removed. Most of us know coagulation from anatomy class.
When was coagulation water used?
Yet coagulation water treatment is far from being a new process. In fact, it was in use by the Egyptians as early as 2,000 B.C. Later the Romans used the coagulation process in water treatment, as did the English in the 18th century.
What is a flocculant?
Flocculants are lightweight, medium weight and heavy polymers that cause the destabilized clumps of particles to agglomerate and drop out of the solution, removing them from the filtered water. The weight used depends on the type of particle.
Why is flocculation so popular?
Coagulation and flocculation processes have become more and more popular due to the increasingly stringent filtration requirements for industrial and municipal water treatment and wastewater treatment facilities levied by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA.)
Is alum a good coagulant?
It’s the same principle with wastewater treatment. In coagulation treatment, a harmless chemical such as alum causes all of the particles to give off a positive charge and thus clump together, making them easier to filter. Coagulation is especially useful in removing the chemical phosphorus from water. Yet coagulation water treatment is far ...
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
Why are pathogens removed from water?
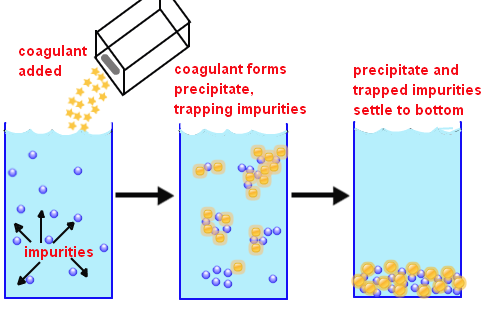
Usually, the pathogens that are removed from the water are removed because they are attached to the dissolved substances that are removed by coagulation. In the picture below, the coagulants have been added to the water, and the particles are starting to bind together and settle to the bottom.
What is the most widely used water treatment technology?
Many water treatment plants use a combination of coagulation, sedimentation, filtration and disinfection to provide clean, safe drinking water to the public. Worldwide, a combination of coagulation, sedimentation and filtration is the most widely applied water treatment technology, and has been used since the early 20th century.
What is added to ferric chloride?
If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added. And if aluminum sulphate is used, aluminum and sulphate are added. The majority of municipal water treatment plants use aluminum sulphate as the coagulation chemical. Generally, water treatment facilities have the coagulation process set up so that the coagulant chemicals are removed with ...
What is residual water?
Residuals are the by-products that remain in the water after substances are added and reactions occur within the water. The particular residuals depend on the coagulant that is used. If ferric sulphate is used, iron and sulphate are added to the water. If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added.
What is slow sand filtration?
that are used. Slow sand filtration removes bacteria, protozoa and viruses, and produces. essentially clean water, though it is still advisable to use a disinfectant as a precautionary. measure.
What Coagulants Are Used In Water Treatment?
In order to use coagulation in your water treatment, you have to apply coagulants to chemically initiate the process. These specialty chemicals should be formulated to meet your specific water quality application based on a particle analysis of your dissolved/suspended solids.
Organic Coagulants
Organic coagulants are best used for solid-liquid separation. They are also good options to use when trying to reduce sludge generation. Being organic in nature, these coagulants offer the added benefits of working at lower doses and having no effect on the pH of your water.
Inorganic Coagulants
Inorganic coagulants are typically cheaper than their organic counterparts, making them a cost-effective solution for a broad range of water treatment applications. They are especially effective when used on raw water with low turbidity.
ChemREADY: Your Water Treatment Experts
With our chemical expertise and mechanical filtration knowledge, ChemREADY offers total water treatment assistance for industrial processes of any kind.
The role of coagulation in wastewater treatment
In the wastewater treatment process, coagulants play a critical role in dealing with sludge. Often used in combination with other mechanical filtering processes and treatment chemicals, using coagulants helps to thicken the sludge into a form which allows the solids and other particles which are contaminating the water to be easily removed.
The history behind coagulation in the treatment of wastewater
The idea of using coagulation as a way to clean up dirty water is nothing new. There is evidence that the Ancient Egyptians were adding almonds to water in rivers as an attempt to clean it up as early as 2,000 BC. The Romans even added a chemical called alum to water as a coagulant as early as the 8 th century.
How does coagulation work?
In simple terms, coagulation describes a chemical reaction. It involves adding a special chemical product called a coagulant, something like iron or aluminium salts to the wastewater, which then affect the electrostatic charge associated with the small particles suspended in the water.
Where can coagulation be used?
Coagulation can be used in a range of different situations, to deal with specific pollutants affecting your water and causing it to become contaminated. Coagulation is particularly effective against:
How coagulation aids mechanical filtration
The main idea behind using coagulation as a treatment for wastewater is to create a state in the water that allows effective mechanical filtration of the effluent. This involves the formation of flocs or clumps of solid material.
What are the different types of wastewater coagulants?
Coagulation doesn’t happen by itself, and in order to kick-start the process you have to add special coagulant chemicals into the wastewater treatment system. The exact combination of chemicals you’ll use will typically depend on the type and concentration of contaminants that are affecting your effluent streams, and the chemical composition.
Organic coagulants
For solid-liquid separation, one of the best options to think about first is the use of organic coagulation. Organic coagulants are also effective when trying to reduce the total volume of sludge which is created as part of the treatment process.
What is the process of separating flocculated materials from water?
The process traditionally utilizes an anode and a cathode, stimulated by a DC power source to destabilize the charges. This operation separates flocculated materials from water, allowing those materials to be removed, leaving clear water.
What is the name of the coagulating agent formed when aluminum hydrolyzes?
Hydroxides: e.g., aluminum hydroxide (a polymeric hydroxide formed when aluminum hydrolyzes) is an excellent coagulating agent. Oxyhydroxides.
How is a floc formed?
Floc formed as a result of coagulation entraps and bridges colloidal particles remaining in the aqueous medium. Electrolyzed water produces small bubbles of oxygen at the anode and hydrogen at the cathode. The bubbles attract flocculated particles and float flocculated materials to the surface.
What are the benefits of electrochemical processes?
An electrochemical process offers outstanding benefits when compared to other technologies: 1 Can treat both process and waste water 2 Treats a wide range of contaminants 3 Operation uses safe, simple equipment 4 Typically, no need for chemical treatment 5 Can typically reuse electrocoagulation-treated waters, minimizing waste
Overview
In water treatment, coagulation and flocculation involve the addition of compounds that promote the clumping of fine floc into larger floc so that they can be more easily separated from the water. Coagulation is a chemical process that involves neutralization of charge whereas flocculation is a physical process and does not involve neutralization of charge. The coagulation-flocculation pr…
Factors
Coagulation is affected by the type of coagulant used, its dose and mass; pH and initial turbidity of the water that is being treated; and properties of the pollutants present. The effectiveness of the coagulation process is also affected by pretreatments like oxidation.
Mechanism
In a colloidal suspension, particles will settle very slowly or not at all because the colloidal particles carry surface electrical charges that mutually repel each other. This surface charge is most commonly evaluated in terms of zeta potential, the electrical potential at the slipping plane. To induce coagulation, a coagulant (typically a metallic salt) with the opposite charge is added to the water to overcome the repulsive charge and "destabilize" the suspension. For example, the c…
Determining coagulant dose
The dose of the coagulant to be used can be determined via the jar test. The jar test involves exposing same volume samples of the water to be treated to different doses of the coagulant and then simultaneously mixing the samples at a constant rapid mixing time. The microfloc formed after coagulation further undergoes flocculation and is allowed to settle. Then the turbidity of the sampl…
Limitations
Coagulation itself results in the formation of floc but flocculation is required to help the floc further aggregate and settle. The coagulation-flocculation process itself removes only about 60%-70% of Natural Organic Matter (NOM) and thus, other processes like oxidation, filtration and sedimentation are necessary for complete raw water or wastewater treatment. Coagulant aids (polymers that bridge the colloids together) are also often used to increase the efficiency of the …
See also
• Electrocoagulation
• Industrial wastewater treatment
• Industrial water treatment