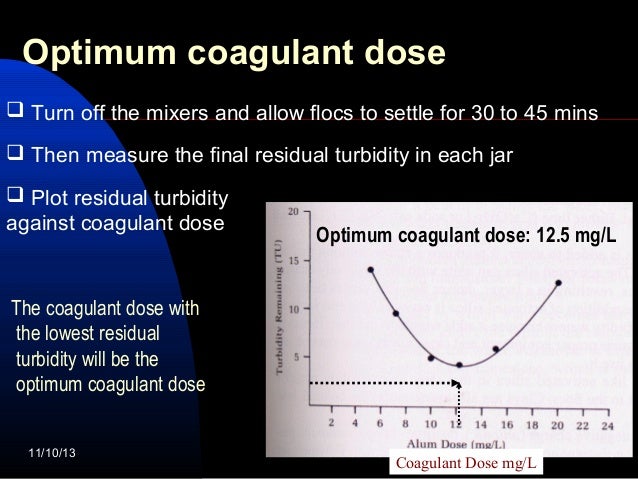
Coagulation water treatment process
- Coagulants. Coagulants are the chemicals that are used to removes tiny particles in water. ...
- Coagulation Mechanism. The colloidal particles carry electrical charges; normally negative charge. ...
- Factors affecting coagulation water treatment. ...
- Coagulation jar test. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is coagulation for water treatment?
Oct 15, 2021 · Ferric sulfate, aluminum sulfate, or ferric chloride, classed as aluminum or iron salts, are common coagulants for water treatment. A coagulant is a chemical that is used to remove suspended solids from drinking water. They are made up of positively charged molecules, which help to provide effective neutralization of water. Advertisement
What are flocculants and coagulants for wastewater treatment?
Jul 14, 2021 · The flocculation process follows coagulation in water treatment. Coagulation is the charge neutralisation of fine particles, and flocculants are the agents that then promote the clumping of these particles together. Flocculants are polymers, materials consisting of long, repeating chains of molecules. They are water-soluble, and will stabilise or enhance the …
Is coagulant and flocculant are same?
Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.
What is the process of water treatment?
May 19, 2021 · Sold in blocks and easily stored, aluminum sulfate has proved a viable option for water coagulation and treatment in third-world countries, as well as in the United States. The optimal pH range of aluminum sulfate is between 5 and 7.5, which means the coagulant performs at its best in slightly acidic or neutral solutions.
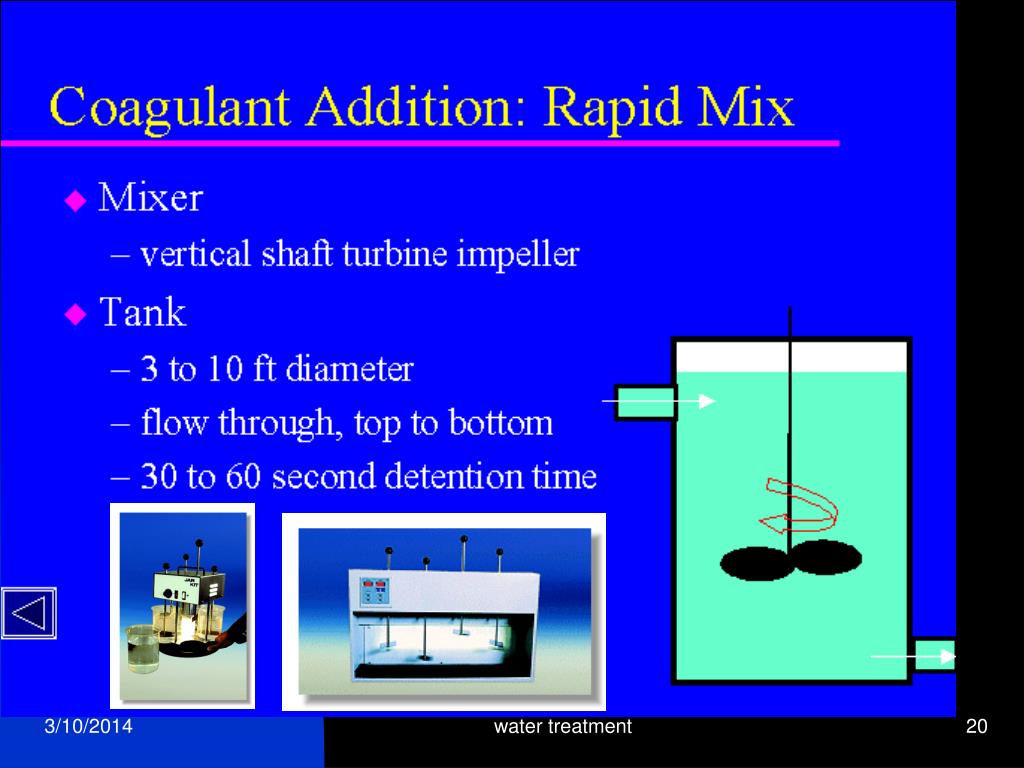
What are the coagulants used in water treatment?
Aluminum sulfate (alum) is the most common coagulant used for water purification. Other chemicals, such as ferric sulfate or sodium aluminate, may also be used. Coagulation is usually accomplished in two stages: rapid mixing and slow mixing.
What is used in coagulant?
The aluminum coagulants include aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride and sodium aluminate. The iron coagulants include ferric sulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric chloride and ferric chloride sulfate. Other chemicals used as coagulants include hydrated lime and magnesium carbonate.
What does the coagulant do?
In water treatment, coagulants are used to remove a wide variety of hazardous materials from water, ranging from organic matter and pathogens, to inorganics and toxic materials, like arsenic, chemical phosphorous and fluoride.
What are the common coagulants?
General and 7 most commonly used coagulants in water treatment plant is under:Alum (aluminum sulfate), Al2(SO4)3. ... Polyaluminum chloride, Al(OH)x(C1)y. ... Ferric chloride, FeCl3. ... Ferric sulfate, Fe2(SO4)3. ... Ferrous Sulfate, FeSO4. ... Sodium Aluminate, Na2Al2O4More items...
What is coagulation in water?
Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.Dec 20, 2019
What does coagulant mean?
Coagulant meaning A substance that brings about coagulation. noun. An agent that causes a liquid or sol to coagulate.
Why is coagulant necessary for purification?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.Jan 23, 2017
Why are coagulants used in waste treatment?
Coagulation in Wastewater Treatment has been used to clarify water since ancient times – as early as 2000BC, when the Egyptians used almonds to clarify river water. There is also evidence to suggest that the Romans were using alum as a coagulant at around 77AD.
What are natural coagulants?
They are mainly composed of polymers of natural origin extracted from plants, algae or animals. Among these are polysaccharides and water soluble substances that act as coagulation and / or flocculation agents.
Which is the best coagulant?
Ferric sulfate works in a similar way to aluminum sulfate, and it is considered to be a highly effective coagulant for industrial usage.May 19, 2021
What is coagulation in water treatment?
Water and wastewater may contain suspended and dissolved impurities that must be removed in order to meet certain water quality criteria. These impurities include:
What are the different types of coagulants used in wastewater treatment?
Types of coagulants used in water and wastewater treatment: Coagulants can be classified as organic coagulants and inorganic coagulants. Organic coagulants are cationic polymers with high molecular weight.
What are coagulants made of?
Organic coagulants include polyamines, polyDADMACS, dicyandiamide and melamine formaldehyde. Inorganic coagulants are mostly based on metallic salts, such as iron sulfate and aluminum sulfate. When they are introduced to the water, they react with the alkalinity of the water and hydrate to form a metal hydroxide.
What are the advantages of organic coagulants?
The major advantage of organic coagulants is that produce much less sludge than inorganic coagulants, due to their higher efficiency . Another advantage is that they do not affect the pH of the treated water. Organic coagulants include polyamines, polyDADMACS, dicyandiamide and melamine formaldehyde.
What is the pH of a coagulant?
Therefore, each coagulant has an optimal pH range in which it works best. For example, Alum works best at a pH of 5.8-6.5, Aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) works at a pH range of 6.5-7.5.
What is the purpose of coagulation?
Coagulation is a chemical process in which a chemical compound, a “coagulant”, is added to the water, in order to destabilize the suspended particles and promote creation of flocs. A ‘Stable colloidal particle’ is a colloidal particle that remains as a separate entity in the water, i.e. in a dispersed state.
What is the term for the adsorption and bridging of electrolytes?
Adsorption and bridging. Precipitation, or sweep-coagulation. Compression of the double layer – when electrolytes are introduced. Higher concentration of electrolytes neutralizes more charges, and as a result the thickness of the double electrical layer is reduced, and particles get closer to each other.
What are Coagulation and Flocculation in Water Treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are two processes that go together in water treatment. They are separate, but they are used one after the other to remove particles in water.
How Coagulation Water Treatment Works
Coagulation water treatment prevents the suspended particles from repelling one another and encourages them to form into clumps, or flocs.
How Flocculation Works
The flocculation process follows coagulation in water treatment. Coagulation is the charge neutralisation of fine particles, and flocculants are the agents that then promote the clumping of these particles together.
How Does Temperature Affect Coagulation in Water Treatment?
Temperature can have a significant effect on coagulation and flocculation.
Is Coagulation Caused by Bacteria in Water Treatment?
Suspended solids in water can be the result of natural causes, arising from organic materials such as algae, or inorganic materials such as sediment or silt.
How to Maximise the Effects of Water Treatment
Coagulation is a long-established water treatment, but it doesn’t remove all bacteria from water systems.
Inorganic coagulants
Inorganic compounds do not have carbon elements in their molecular structure. As such, they are considered to be “artificial” or unnatural. However, just because a coagulant is inorganic does not mean it is environmentally unfriendly, provided it is handled correctly. This also applies to organic coagulants, which are not necessarily eco-friendly.
Organic coagulants
As well as the inorganic coagulant compounds listed above, there are a number of different organic coagulants available on the market. These include substances such as polymers, amines, and acrylamides, all of which can be used to achieve effective coagulation at your facility.
What is Coagulation in Wastewater Treatment?
Coagulation is a somewhat simple chemical process that involves bringing insoluble materials together by manipulating the charges of particles, by adding iron or aluminum salts, such as aluminum sulfate or ferric sulfate, to a wastewater stream.
What Coagulants Are Used In Water Treatment?
In order to use coagulation in your water treatment, you have to apply coagulants to chemically initiate the process. These specialty chemicals should be formulated to meet your specific water quality application based on a particle analysis of your dissolved/suspended solids.
What Are The Common Coagulation In Wastewater Treatment?
Organic coagulants are best used for solid-liquid separation. They are also good options to use when trying to reduce sludge generation. Being organic in nature, these coagulants offer the added benefits of working at lower doses and having no effect on the pH of your water.
ChemREADY: Your Water Treatment Experts
With our chemical expertise and mechanical filtration knowledge, ChemREADY offers total water treatment assistance for industrial processes of any kind.
What Coagulants Are Used In Water Treatment?
In order to use coagulation in your water treatment, you have to apply coagulants to chemically initiate the process. These specialty chemicals should be formulated to meet your specific water quality application based on a particle analysis of your dissolved/suspended solids.
Organic Coagulants
Organic coagulants are best used for solid-liquid separation. They are also good options to use when trying to reduce sludge generation. Being organic in nature, these coagulants offer the added benefits of working at lower doses and having no effect on the pH of your water.
Inorganic Coagulants
Inorganic coagulants are typically cheaper than their organic counterparts, making them a cost-effective solution for a broad range of water treatment applications. They are especially effective when used on raw water with low turbidity.
ChemREADY: Your Water Treatment Experts
With our chemical expertise and mechanical filtration knowledge, ChemREADY offers total water treatment assistance for industrial processes of any kind.
What is a coagulant in water?
A coagulant is used in colored, low pH or alkaline and low turbidity water. The optimum pH it generates helps in water purification. The coagulate dose used in purification produces a hydrolysis process that generates a pH suitable for coagulation.
Why is coagulant added to water?
A coagulant, together with other chemicals, are added in water to aggregate dissolved contaminants and tiny particles into larger particles so that filtration, clarification, or any other solid removal process may be used to remove them.
Can coagulant cause corrosion?
An inappropriate coagulant dose might lead to corrosion due to acidity, hence one must follow guidelines by the governing authority. To improve on filtration, certain guidelines are placed to govern the change of coagulant in any filtration process.
What is a coagulant in water treatment?
Water treatment coagulants are comprised of positively charged molecules that, when added to the water and mixed, accomplish this charge neutralization. Inorganic, organic, or a combination of both coagulant types are typically used to treat water for suspended solids removal. When an inorganic coagulant is added to water containing ...
When to use organic coagulant?
Organic coagulant is generally used when a reduction in sludge generation is desired. Furthermore, blended organic and inorganic chemicals are often more effective than either organic or inorganic chemicals alone. The correct blend can often combine the advantages of using the inorganic coagulant sweep-floc mechanism with ...
What polymers act similarly to inorganic coagulant products?
Melamine Formaldehydes and Tannins. These all-organic polymers act similarly to the inorganic coagulant products in that they not only coagulate the colloidal material in the water, but also contribute their own precipitated floc. This sweep-floc precipitate readily adsorbs organic materials such as oil and grease.
What is the most widely used class of organic coagulation chemicals?
Polyamine and PolyDADMAC. These are the most widely used classes of organic coagulation chemicals. They function by charge neutralization alone, so there is no advantage to the sweep-floc mechanism. Polyamines will generally treat higher turbidity raw water (approximately >20 NTU) effectively.
What are some examples of flocculants?
Examples of ChemTreat flocculants include low-, medium-, and high-molecular weight polymers.
Is sludge hazardous to water?
For influent or raw water applications where the sludge is generally non-hazardous, the penalty for creating more sludge with higher water content is small. For wastewater applications with hazardous sludge, the economic penalty can be significant.
Is ferric chloride a coagulant?
Ferric chloride is generally the least expensive inorganic coagulant, because it is generated as a waste material from steel-making operations (waste “pickle liquor”). However, it is by far the most corrosive and hazardous inorganic coagulant, and its use is limited to facilities equipped to handle it safely.
