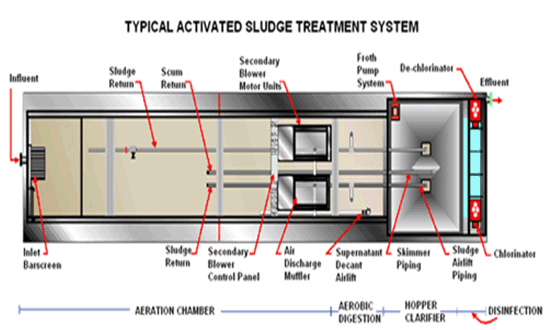
CLARIFIERS FOR WASTEWATER TREATMENT
- Clarifiers Basic Principle: Clarifiers are slowly rotating rake arms, A liquid feed with suspended solids is fed to the clarifier tank.Clear Liquid overflows the top of the tank and is ...
- Characteristics of a Clarifiers. ...
- Clarifier FAQ’S. ...
- Difference Between Primary and Secondary Clarifier:
What is the best method for wastewater treatment?
What is a clarifier in a Wastewater Treatment Plant? Clarifiers are tanks built with a mechanism for continuous removal of solids deposited by the sedimentation while filtering the water. Its general use is to remove the solid particles from the liquid for clarification and thickening .
What is the purpose of a wastewater treatment plant?
The primary clarifying process, also known as sedimentation, is the removal of inorganic solids prior to biological treatment. The following is a step-by-step procedure: 1. Water is introduced into the clarifier tank. 2. Skimmers remove the inorganic materials (scum) floating on the surface. 3.
Does the wastewater treatment plant smell bad?
Dec 24, 2021 · A clarifier in general is extensively used in removing the suspended solids or solid particulates from the liquids for clarification purposes. The method of sedimentation is a vital part of any wastewater treatment. Here the contaminants settle down because of gravity. Thus the clean liquid gets separated.
What is primary treatment of wastewater treatment plant?
Aug 10, 2020 · Here, the clarifier is used to remove treated wastewater from the primary treatment stage. The major task of the secondary clarifier is clarification and thickening. The performance of a wastewater treatment plant depends on the functioning of primary and secondary clarifiers.

What is the principle of a clarifier?
Clarifiers work on the principle of gravity settling. The heavier suspended solids settle in the clarifier due to the quiescent conditions provided in the Clarification zone. The settled solids are swept to the centre well provided for collection of sludge with help of moving scraper blades.
How does a waste water clarifier work?
0:474:03Clarifier basics - How do clarifiers work I Clarifier design - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd are attached to a centrally located shaft. Which is powered by a drive system on the clarifierMoreAnd are attached to a centrally located shaft. Which is powered by a drive system on the clarifier bridge. The removed sludge will either be recycled as Ras returned activated sludge or wasted.
What is the purpose of primary clarifier?
0:5119:13How Primary Clarifiers Work - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe can see now we've got our circular primary clarifier it's called a primary clarifier. BecauseMoreWe can see now we've got our circular primary clarifier it's called a primary clarifier. Because it's the first initial stage of treatment. We refer to this as primary treatment or a primary clarifier
How many types of clarifier are there?
Clarifiers Basic Principle: Bridge support, column support and traction are the three main types of clarifiers, Primary and Secondary clarifiers.
What is the difference between clarifier and Clariflocculator?
Clariflocculator is a combination of flocculation and clarification in a single tank. It has two concentric tanks where inner tank serves as a flocculation basin and the outer tank serves as a clarifier.
Why is chlorine used in wastewater treatment?
The primary goal of chlorination is to disinfect the wastewater and remove any harmful pathogens that are present in the water. Once the wastewater has been properly treated, it can flow naturally into rivers, streams, and oceans without issue.Jul 26, 2021
What is final clarifier?
A gravitational settling tank installed as part of some wastewater treatment plants and placed after the biological treatment step. The tank functions to remove suspended solids. Also referred to as Secondary Clarifier.
What is a secondary clarifier?
secondary clarifiers is to separate biological floc from the treated liquid waste stream. Secondary clarifiers are most often discussed in conjunction with suspended growth biological wastewater treatment systems.
What is a clarifier launder?
Extending from the outer tank wall to the effluent weir, the clarifier launder protects the effluent trough, weir, and other parts of your clarifier launder from sunlight. Preventing windblown debris such as dust and leaves from entering clarifier launder channels. Controlling odors in the launder trough. and more.
What is the difference between primary and secondary clarifiers?
The primary clarifier is designed to dispose of inorganic solids floating at the surface. It also tackles solids settling at the bottom. In this unit, the sludge is less dense. In the secondary clarifier, 100 percent or nearly 100 percent of the sludge, is organic.Feb 15, 2021
What is horizontal flow clarifier?
A horizontal flow primary clarifier treats waste water in which 10%, 60% and 30% of particles have settling velocities of 0.1 mm/s, 0.2 mm/s and 1.0 mm/s respectively.
What is a solids contact clarifier?
Solids contact clarifiers combine the process of mixing, flocculation and sedimentation in a single tank. Recirculation of solids and mixing is accomplished by a radial or axial turbine. Flocculation occurs within the reaction well. Sedimentation occurs in the clarification zone.
How The Clarification Occurs
Coagulation and flocculation reagents, such as polyelectrolytes and ferric are added before the water enters the clarifier to cause finely suspended particles to clump together and form larger and denser particles, called flocs.
Sedimentation Tanks or Secondary Clarifiers
Sedimentation tanks or secondary clarifiers remove flocs of biological growth created in some methods of secondary treatment including activated sludge and rotating biological processes.
What is the SLR of a clarifier?
The solids loading rate (SLR) is the quantity of solids that can be removed by a secondary clarifier per square foot of surface area. An increase above the design SLR will likely result in an increase in solids leaving the clarifier. For secondary clarifiers that follow an activated sludge system the solids loading rate should fall in the range of 12 to 30 pounds of solids per day per square foot of clarifier surface area. Depending on the textbook you reference, you will see a somewhat different range for the SLR.
What are the factors that affect clarifier efficiency?
Clarifier efficiencies are affected by many factors, including: The nature of solids in the wastewater and their source. A large industrial contribution to a municipal wastewater plant will have solids with very different characteristics compared to the solids from a “conventional” municipal plant.
What happens to wastewater in winter?
Temperature can also be a factor during winter when the wastewater temperature drops and long detention times in the clarifier add to the cooling. As the temperature drops the density of the wastewater will increase, slowly the rate at which solids will settle.
What is a clarifier used for?
In water treatment, a clarifier is a settling tank used to remove solid waste particles from water. When the clarifier separates the concentrated impurities, the sludge formed by the process discharges from the bottom of the tank.
When to use a clarifier in a pond?
When the solids are separated from the waste water, the remaining water is slowly removed from the tank and taken to oxidation ponds. A smaller clarifier is also used if the volume of the incoming waste water exceeds the volume of the primary clarifier.
What is added to water before it goes into a clarifier?
Before the waste water goes into the clarifier, it passes through a station called the headworks, where large solids and grit are removed, After this, coagulation and flocculation reagents such as polyelectrolytes and ferric sulfate are often added to the water before it is sent to the clarifier.
Where does the water move in a clarifier?
The water now moves to the primary clarifier tank where it is slowed down to allow the remaining solid waste to settle at the bottom of the tank. A rotating sludge-raking system located at the bottom of the clarifier rakes the settled waste out of the tank, and a rotating rake-skimming system at the top of the tank removes any solids ...
What is the purpose of flocs in a clarifier?
The reagents cause fine suspended particles of waste to clump together, forming larger and denser particles called flocs that allow the waste to settle quickly, allowing the separation of the waste in the clarifier to occur more effectively. The water now moves to the primary clarifier tank where it is slowed down to allow ...
Primary and secondary clarifying
Both the primary and secondary phases of the process rely on clarifier equipment to get the job done in the right way, but each phase has its own objective.
Key types of clarifiers
There are three key types of clarifiers (although, as we will note, clarifiers deployed in the field may be hybrids of more than one type). Read on to discover more about each.
Clarifier tank structures
While we have already covered the main types of wastewater clarifiers, there is something else left to discuss — the structure of the clarifier tank itself. These structures come in two basic types: pre-fab and concrete cylinder.
How does a clarifier work?
The clarifier works by permitting the heavier and larger particles to settle to the bottom of the clarifier. The particles then form a bottom layer of sludge requiring regular removal and disposal. Clarified water then proceeds through several more steps before being sent for storage and use.
What reagents are added to a clarifier?
Before the water enters the clarifier, coagulation and flocculation reagents , such as polyelectrolytes and ferric sulfate, can be added. These reagents cause finely suspended particles to clump together and form larger and denser particles, called flocs, that settle more quickly and stably. This allows the separation of the solids in ...
What is the primary treatment of sewage?
Sedimentation tanks have been used to treat wastewater for millennia. Primary treatment of sewage is removal of floating and settleable solids through sedimentation. Primary clarifiers reduce the content of suspended solids and pollutants embedded in those suspended solids.
How is potable water treated?
Water being purified for human consumption, is treated with floculation reagents, then sent to the clarifier where removal of the flocculated coagulate occurs producing clarified water . The clarifier works by permitting the heavier and larger particles to settle to the bottom of the clarifier.
What is the name of the impurities discharged from the bottom of a wastewater treatment tank?
Concentrated impurities, discharged from the bottom of the tank are known as sludge, while the particles that float to the surface of the liquid are called scum. Three wastewater/sewage clarifiers at the ʻAikahi wastewater treatment plant in Hawaii.
How do tube settler clarifiers work?
Tube settlers are commonly used in rectangular clarifiers to increase the settling capacity by reducing the vertical distance a suspended particle must travel. High efficiency tube settlers use a stack of parallel tubes, rectangles or flat pieces separated by a few inches (several centimeters) and sloping upwards in the direction of flow. This structure creates a large number of narrow parallel flow pathways encouraging uniform laminar flow as modeled by Stokes' law. These structures work in two ways:
Why is sludge formed in clarifiers?
The sludge formed from the settled particles at the bottom of each clarifier, if left for an extended period of time, may become gluey and viscous, causing difficulties in its removal. This formation of sludge, promotes anaerobic conditions and a healthy environment for the growth of bacteria.
