What is CLCL 4 used for?
Mar 04, 2022 · Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment can include observation, steroids, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery, or targeted therapy. Learn more about the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of newly diagnosed or recurrent CLL in this expert-reviewed summary.
What is the best treatment for Stage 4 colon cancer?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia in adults. It's a type of cancer that starts in cells that become certain white blood cells (called lymphocytes) in the bone marrow. The cancer (leukemia) cells start in the bone marrow but then go into the blood. In CLL, the leukemia cells often build up slowly.
Is lenalidomide a biologic therapy for leukemia?
Pill with imprint CL 4 is White, Elliptical/Oval and has been identified as Pramipexole Dihydrochloride 0.5 mg. It is supplied by Macleods Pharmaceuticals Limited.
What is CLL (cancer of the blood)?
Oct 02, 2019 · Cesium Chloride is a natural mineral with the touted ability to penetrate the cancer cell and rapidly change its acidic pH to an alkaline pH of about 8. This is theorized to destroy the enzyme A protein that speeds up chemical reactions in the body. systems of the cancer cell and does not allow it to reproduce or survive.

How effective is cisplatin chemo?
In particular, cisplatin's success as a chemotherapy drug against testicular cancer is phenomenal. When used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, its cure rate is more than 90 percent.May 30, 2014
Is cisplatin still used?
Cisplatin, and other platinum-based compounds such as oxaliplatin, and carboplatin are still being used as first-line treatments for patients who have been diagnosed with various types of malignancies, such as lymphomas, breast, testicular, ovarian, head and neck, cervical, and sarcomas [1].Apr 8, 2019
At what stage of cancer is chemotherapy used?
Systemic drug treatments, such as targeted therapy or chemotherapy, are common for stage 4 cancers. Often, a clinical trial may be an option, offering new treatments to help you fight stage 4 cancer.Feb 11, 2022
How effective is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy drugs work better in some cancers than others and while they can be a miracle for some, they fail to work for all patients. Overall response rates are about 15 to 20%.
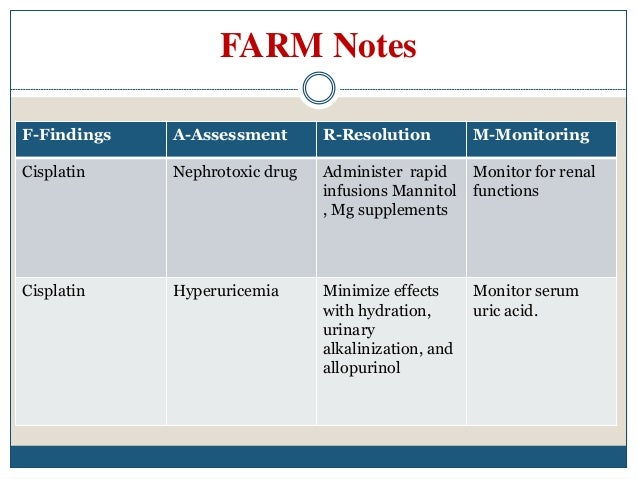
Why is cisplatin so toxic?
Once in the kidney, cisplatin undergoes biotransformation to cysteinyl glycine conjugates and other higher thiols that is believed to cause toxicity. It is also believed that the mechanism of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is the same as the tumor cytotoxicity.Feb 7, 2019
What are the long term side effects of cisplatin?
One of the most common long-term side effects of Platinol (cisplatin), a medication used for many cancers including lung cancer, is ototoxicity (damage to the structures of the ear). Other medications may also cause hearing loss and tinnitus (ringing in the ears).Feb 24, 2022
Is Stage 4 always terminal?
Stage 4 cancer is not always terminal. It is usually advanced and requires more aggressive treatment. Terminal cancer refers to cancer that is not curable and eventually results in death. Some may refer to it as end stage cancer.
What is the life expectancy of Stage 4 cancer?
In most cases, how stage 4 cancer is likely to progress (its prognosis) depends on the type of cancer. Some advanced cancers are very aggressive and fast-growing....Survival Rates.Five-Year Survival Rates for Distant (Stage 4) CancerCancer TypeRelative 5-Year Survival RatePancreatic2.9%11 more rows•Mar 5, 2022
Can you recover Stage 4 cancer?
Treatment for stage IV depends on the location of the cancer and the organs involved. The more widely the cancer has spread from the site where it was first diagnosed, the more difficult it becomes to treat. Patients diagnosed with stage IV or metastatic cancer may not survive long without treatment.Apr 28, 2021
How long does immunotherapy extend life?
In a study led by UCLA investigators, treatment with the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab helped more than 15 percent of people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer live for at least five years — and 25 percent of patients whose tumor cells had a specific protein lived at least that long.
Does immunotherapy extend life?
Immunotherapy works by harnessing the power of your body's own immune system. It attacks metastatic melanoma in a way that can extend lives for months or years -- and in some cases actually get rid of the disease.Dec 7, 2020
Do you lose your hair with immunotherapy?
Hormone therapy, targeted cancer drugs and immunotherapy are more likely to cause hair thinning. But some people might have hair loss. Radiotherapy makes the hair fall out in the area being treated. Hair on other parts of the body is not usually affected.
Who Should Consider Cesium Therapy?
This is an ideal therapy for anyone with terminal malignancy. If you know someone who has been told get your affairs in order you only have 3 to 6...
What Is The Cesium Chloride Cure Rate?
Cesium Chloride is frequently combined with other treatments, such as DMSO, coral calcium, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), ozone, etc. Cesium Chloride is...
Does Cesium Chloride Cause Heart Problems?
I sometimes get asked the question of whether Cesium Chloride causes heart attacks or other heart problems. It seems orthodox medicine is using the...
Evidence For The Protocol on Stage IV Cancer Patients?
The original discoverer of the Cesium Chloride protocol was Dr. A. Keith Brewer. In his research, he used cesium carbonate, an earlier version of t...
Cesium Carbonate vs. Cesium Chloride
Even though there is a common conversion factor for using cesium carbonate (a powder) versus using Cesium Chloride (an ionic liquid), I do not reco...
What is BCL2 inhibitor therapy?
BCL2 inhibitor therapy: This treatment blocks a protein called BCL2 which is found on some leukemia cells. This may kill leukemia cells and make them more sensitive to other anticancer drugs. Venetoclax is a type of BCL2 therapy used to treat symptomatic or progressive, recurrent, or refractory CLL.
Where does CLL spread?
In chronic lymphocytic leukemia ( CLL ), the leukemia cells may spread from the blood and bone marrow to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen. It is important to know whether the leukemia cells have spread in order to plan the best treatment.
What is the name of the cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (also called CLL) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow that usually gets worse slowly. CLL is one of the most common types of leukemia in adults.
What is the disease that causes swollen lymph nodes?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Signs and symptoms of chronic lymphocytic leukemia include swollen lymph nodes and feeling tired. Tests that examine the blood are used ...
What is stage 0 leukemia?
Stage 0. In stage 0 chronic lymphocytic leukemia, there are too many lymphocytes in the blood, but there are no other signs or symptoms of leukemia . Stage 0 chronic lymphocytic leukemia is indolent (slow-growing).
What is PDQ cancer?
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
How does chemo work?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ). Combination chemotherapy is treatment using more than one anticancer drug.
Where do CLL cells grow?
But over time, the cells grow and spread to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
How long can you live with leukemia?
It can take a long time before chronic leukemias cause problems, and most people can live with them for many years. But chronic leukemias tend to be harder to cure than acute leukemias.
What type of leukemia starts with B lymphocytes?
The common form of CLL starts in B lymphocytes. But there are some rare types of leukemia that share some features with CLL. Prolymphocytic leukemia (PLL): In this type of leukemia the cancer cells are a lot like normal cells called prolymphocytes.
What is the difference between lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoma?
The main difference between lymphocytic leukemias and lymphomas is that in leukemia, the cancer cells are mainly in the bone marrow and blood, while in lymphoma they tend to be in lymph nodes and other tissues.
What is the most common type of leukemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia in adults. It's a type of cancer that starts in cells that become certain white blood cells (called lymphocytes) in the bone marrow. The cancer (leukemia) cells start in the bone marrow but then go into the blood. In CLL, the leukemia cells often build up slowly.
How does cancer start?
Cancer starts when cells start to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer and can spread to other parts of the body. To learn more about how cancers start and spread, see What Is Cancer? Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia in adults. It's a type of cancer that starts in cells ...
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the blood-forming cells of the bone marrow?
What is leukemia ? Leukemia is cancer that starts in the blood-forming cells of the bone marrow. When one of these cells changes and becomes a leukemia cell, it no longer matures the way it should and grows out of control. Often, it divides to make new cells faster than normal.
What is cerium chloride?
Cesium Chloride is a natural mineral with the touted ability to penetrate the cancer cell and rapidly change its acidic pH to an alkaline pH of about 8. This is theorized to destroy the enzyme. A protein that speeds up chemical reactions in the body. systems of the cancer cell and does not allow it to reproduce or survive.
What vitamins are taken up by cancer cells?
This uptake was enhanced by Vitamins A and C as well as salts of zinc and selenium. The quantity of cesium taken up was sufficient to raise the cell to the 8 pH range.
Why do cancer cells have low pH?
Cancer cells thrive in this low pH. However, because the cancer cells are burning glucose (and creating lactic acid), energy is pulled from non-cancerous cells. In the “cachexia cycle,” the liver converts the lactic acid back to glucose, which also consumes energy.
What is the lactic acid cycle?
The lactic acid cycle, commonly called “cachexia,” occurs for the following reasons: 1 Cancer cells routinely create lactic acid; 2 This lactic acid is released by the cancer cells and travels to the liver via the bloodstream; 3 The liver converts the lactic acid into glucose; 4 The liver releases glucose and cancer cells may pick up this glucose because cancer cells consume about 15 times more glucose than normal cells.
Why does cesium starve cancer cells?
Cesium starves cancer cells because it limits the uptake of glucose, which cancer cells rely on for sustenance . Without glucose, they end up starving to death. It stops the process of fermentation, the means by which cancer cells metabolize glucose.
Why does the liver release glucose?
The liver releases glucose and cancer cells may pick up this glucose because cancer cells consume about 15 times more glucose than normal cells. Cancer cells convert glucose to lactic acid, lactic acid travels to the liver; the liver converts the lactic acid back to glucose, which then travels back to the cancer cell.
How does fermentation affect cell division?
Theory: The lactic acid produced by fermentation lowers the cell pH (acid/alkaline balance) and destroys the ability of DNA and RNA to control cell division; the cancer cells begin to multiply unchecked. In the absence of oxygen, glucose undergoes fermentation to create lactic acid. This causes the cell pH to drop from between 7.3 to 5.7 depending on the advanced stages of cancer and in metastases.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Radiation Therapy . Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Learn about the types of radiation, why side effects happen, which ones you might have, and more.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps your immune system fight cancer. This page covers the types of immunotherapy, how it is used against cancer, and what you can expect during treatment.
What is stem cell transplant?
Stem cell transplants are procedures that restore blood-forming stem cells in cancer patients who have had theirs destroyed by very high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Learn about the types of transplants, side effects that may occur, and how stem cell transplants are used in cancer treatment.
How many types of cancer treatments are there?
There are many types of cancer treatment. The types of treatment that you receive will depend on the type of cancer you have and how advanced it is. Some people with cancer will have only one treatment. But most people have a combination of treatments, such as surgery with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that targets the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread. Learn how targeted therapy works against cancer and about common side effects that may occur.
What is a biomarker test?
Biomarker testing is a way to look for genes, proteins, and other substances (called biomarkers or tumor markers) that can provide information about cancer. Biomarker testing can help you and your doctor choose a cancer treatment.
What is the procedure that removes cancer from the body?
Surgery. When used to treat cancer, surgery is a procedure in which a surgeon removes cancer from your body. Learn the different ways that surgery is used against cancer and what you can expect before, during, and after surgery.
What is the most common cancer treatment?
Any cancer treatment can be used as a primary treatment, but the most common primary cancer treatment for the most common types of cancer is surgery. If your cancer is particularly sensitive to radiation therapy or chemotherapy, you may receive one of those therapies as your primary treatment. Adjuvant treatment.
Why is cancer treated?
Why it's done. The goal of cancer treatment is to achieve a cure for your cancer, allowing you to live a normal life span. This may or may not be possible, depending on your specific situation. If a cure isn't possible, your treatments may be used to shrink your cancer or slow the growth of your cancer to allow you to live symptom free ...
What is adjuvant therapy?
Adjuvant treatment. The goal of adjuvant therapy is to kill any cancer cells that may remain after primary treatment in order to reduce the chance that the cancer will recur. Any cancer treatment can be used as an adjuvant therapy. Common adjuvant therapies include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and hormone therapy.
What is bone marrow transplant?
A bone marrow transplant, also knowns as a stem cell transplant, can use your own bone marrow stem cells or those from a donor. A bone marrow transplant allows your doctor to use higher doses of chemotherapy to treat your cancer. It may also be used to replace diseased bone marrow. Immunotherapy.
How does cryoablation work?
Cryoablation. This treatment kills cancer cells with cold. During cryoablation, a thin, wandlike needle (cryoprobe) is inserted through your skin and directly into the cancerous tumor. A gas is pumped into the cryoprobe in order to freeze the tissue. Then the tissue is allowed to thaw.
How does radiofrequency ablation work?
Radiofrequency ablation. This treatment uses electrical energy to heat cancer cells, causing them to die. During radiofrequency ablation, a doctor guides a thin needle through the skin or through an incision and into the cancer tissue.
What is the difference between neoadjuvant and palliative?
Neoadjuvant therapy is similar, but treatments are used before the primary treatment in order to make the primary treatment easier or more effective. Palliative treatment. Palliative treatments may help relieve side effects of treatment or signs and symptoms caused by cancer itself. Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and hormone therapy can all be ...
What is stage 1 colon cancer?
Stage I colon cancers have grown deeper into the layers of the colon wall, but they have not spread outside the colon wall itself or into the nearby lymph nodes. Stage I includes cancers that were part of a polyp. If the polyp is removed completely during colonoscopy, with no cancer cells at the edges (margins) ...
Where does stage IV colon cancer spread?
Stage IV colon cancers have spread from the colon to distant organs and tissues. Colon cancer most often spreads to the liver, but it can also spread to other places like the lungs, brain, peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity), or to distant lymph nodes. In most cases surgery is unlikely to cure these cancers.
What does it mean when cancer comes back?
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. The recurrence may be local (near the area of the initial tumor), or it may be in distant organs.
What is the cancer in the colon?
The cancer had blocked (obstructed) the colon. The cancer caused a perforation (hole) in the wall of the colon.
Does stage 3 colon cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Stage III colon cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but they have not yet spread to other parts of the body. Surgery to remove the section of the colon with the cancer (partial colectomy) along with nearby lymph nodes, followed by adjuvant chemo is the standard treatment for this stage. For chemo, either the FOLFOX (5-FU, leucovorin, ...
Can colon cancer spread to lymph nodes?
Many stage II colon cancers have grown through the wall of the colon, and maybe into nearby tissue, but they have not spread to the lymph nodes. Surgery to remove the section of the colon containing the cancer (partial colectomy) along with nearby lymph nodes may be the only treatment needed. But your doctor may recommend adjuvant chemotherapy ...
Can you get rid of liver cancer with chemo?
For tumors in the liver, another option may be to destroy them with ablation or embolization. If the cancer has spread too much to try to cure it with surgery, chemo is the main treatment. Surgery might still be needed if the cancer is blocking the colon or is likely to do so.