Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD
Chemical oxygen demand
In environmental chemistry, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) test is commonly used to indirectly measure the amount of organic compounds in water. Most applications of COD determine the amount of organic pollutants found in surface water (e.g. lakes and rivers) or wastewater, making COD a useful measure of water quality.
What is “oxygen demand” in wastewater treatment?
Influent waters entering wastewater plants are high in organics and the wastewater plant must reduce the “organic loading” before discharging water to a receiving body. Oxygen demand is useful for measuring waste loadings, evaluating the efficiency of the treatment process, and ensuring compliance with regulations for the oxygen demand of effluent.
What is the significance of chemical oxygen demand in water?
The Significance of Chemical Oxygen Demand High chemical oxygen demand in water indicates greater levels of oxidizable organic matter and consequently, a lower amount of Dissolved Oxygen (DO). Critical DO depletion due to organic contamination can kill off aquatic life forms. What Are the Differences Between COD & BOD?
How can we reduce dissolved oxygen levels in wastewater?
Removal of organic matter from wastewater using coagulants and flocculants eliminates the ‘food’ necessary for microbes to thrive, thus reducing the competition for dissolved oxygen with marine life.
What are the methods of chemical oxygen demand analysis?
A common method for Chemical Oxygen Demand analysis is Method 410.4. The method involves using a strong oxidizing chemical, potassium dichromate Cr 2 O 72-, to oxidize the organic matter in solution to carbon dioxide and water under acidic conditions. Often, the test also involves a silver compound...

What is chemical oxygen demand?
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a test that measures the amount of oxygen required to chemically oxidize the organic material and inorganic nutrients, such as Ammonia or Nitrate, present in water.
What is chemical oxygen demand and why is it important?
COD is a water quality measure used not only to determine the amount of biologically active substances such as bacteria but also biologically inactive organic matter in water [8]. It is an important and rapidly measured variable for characterizing water bodies, sewage, industrial wastes, and treatment plant effluents.
What causes chemical oxygen demand in wastewater?
COD increases as the concentration of organic material increases. It also increases if inorganic compounds susceptible to oxidation by the oxidant (typically dichromate) are present. Water with high COD typically contains high levels of decaying plant matter, human waste, or industrial effluent.
What does high chemical oxygen demand mean?
High chemical oxygen demand in water indicates greater levels of oxidizable organic matter and consequently, a lower amount of Dissolved Oxygen (DO). Critical DO depletion due to organic contamination can kill off aquatic life forms.
What is significance of COD?
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is the amount of dissolved oxygen that must be present in water to oxidize chemical organic materials, like petroleum. COD is used to gauge the short-term impact wastewater effluents will have on the oxygen levels of receiving waters.
Why is COD important in wastewater?
In wastewater treatment, the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is an important measurement for the amount of oxygen that is required to break down pollutants (organic substances) in water. The chemical oxygen demand can be measured using different methods, direct or indirect.
How do you control COD?
More specifically, utilizing certain types of bacteria can reduce COD. To do this you must first aerate the wastewater in order to provide an environment in which the bacteria can live. Aeration provides oxygen to the bacteria. The bacteria can treat and stabilize the wastewater without the use of chemicals.
How do you treat COD?
You can reduce COD and BOD by adding hydrogen peroxide to the wastewater solution. The hydrogen peroxide will chemically attack the organics in the wastewater, degrading them and reducing the measured COD and BOD.
What is a good COD level?
According to standards of Central Pollution Control Board, permissible value of BOD is 30 mg/l and COD is 250 mg/l. Hope this helps, it mentions standards for India relating to different uses.
How do you test COD in water?
The most common test method is the colorimetric analysis after oxidizing the COD with acid and using indicator compounds, such as hexavalent dichromate. In some instances, however, there are compounds that will interfere with the colorimetric analysis, and titration is required to determine COD levels.
Why is chemical oxygen demand important in wastewater treatment?
A key benefit of knowing the chemical oxygen demand in wastewater treatment is that it helps industrial and municipal clients determine the best method for treatment and the most effective structure for their wastewater treatment facility.
What is the chemical oxygen demand?
What Is Chemical Oxygen Demand? Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is the amount of oxygen required to oxidize all soluble and insoluble organic compounds present in a volume of water. COD value is usually expressed in milligrams per liter of water (mg/L).
How to reduce COD in wastewater?
There are various proven methods for COD reduction in wastewater management. Two of the most common techniques for COD wastewater removal are: 1 Wastewater separation (coagulation and flocculation) 2 COD removal by microbial action.
What does high oxygen demand mean in water?
High chemical oxygen demand in water indicates greater levels of oxidizable organic matter and consequently, a lower amount of Dissolved Oxygen (DO). Critical DO depletion due to organic contamination can kill off aquatic life forms.
What is the best way to remove COD from sewage?
Another efficient technique for COD removal is to introduce bacteria or microorganisms that break down organic compounds present in the wastewater. Microbes in sewage treatment can be aerobic or anaerobic.
Is anaerobic COD removal good for wastewater?
It is a highly beneficial method because the biofuel generated from the process can be utilized as an alternative energy source for power, heating, and drying applications. Anaerobic COD removal is suitable for wastewater with COD > 2000 mg/L.
What to do if COD is elevated in wastewater?
Action: If COD is elevated in wastewater, treatment methods such as aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment, filtration, coagulation and flocculation should be used to remove organic and inorganic material.
Why does COD increase in water?
COD increases as the concentration of organic material increases. It also increases if inorganic compounds susceptible to oxidation by the oxidant (typically dichromate) are present. Water with high COD typically contains high levels of decaying plant matter, human waste, or industrial effluent.
What is COD in water?
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a parameter of water quality used to determine the concentration of organic matter in a water supply.1 COD represents the amount of oxygen needed to allow a strong oxidant to oxidise all the organic matter in the sample. However, the strong oxidants used in COD tests do not discriminate between inorganic and organic compounds; some inorganics will be oxidised while some organics will remain intact.2 Despite its inability to measure the absolute organic carbon concentration perfectly, COD is often sufficient for wastewater treatment applications. These tests also only take a matter of hours rather than days ( Biological Oxygen Demand, or BOD, levels take around five days to measure) and generally provide enough information about water quality to be useful in wastewater treatment. In addition, COD can be used in toxic wastes that would otherwise kill the bacteria used in BOD testing.2
How to determine oxygen demand?
When selecting a method for analyzing oxygen demand, it’s important to consider the following: 1 Specific testing application 2 Oxidant that will be used 3 Completion time 4 Accuracy and precision of the measurement
What happens when wastewater is discharged into the environment?
When treated wastewater is discharged into the environment, it can introduce pollution in the form of organic content to receiving waters. High levels of wastewater COD indicate concentrations of organics that can deplete dissolved oxygen in the water, leading to negative environmental and regulatory consequences.
What is COD in water?
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is the amount of dissolved oxygen that must be present in water to oxidize chemical organic materials, like petroleum. COD is used to gauge the short-term impact wastewater effluents will have on the oxygen levels of receiving waters.
When is it necessary to measure BOD or COD in the influent water?
For compliance, it’s necessary to measure BOD or COD in the influent water as it enters the plant, before mechanical screening processes and at the end of the treatment at the discharge point.
What does TOC measure?
TOC measures organic carbon but different organic carbons will generate different oxygen demand. Measuring TOC alone will not necessarily indicate how much oxygen will be consumed by the organics in the environment. For example, oxalic acid and ethanol produce identical TOC results. However, due to different oxidation states, ...
What is the chemical oxygen demand?
The chemical oxygen demand (COD) is defined as the mass of oxygen needed for the complete oxidation of an organic compound present in water. For the oxidation of glucose (CH2O)6, a representative hydrocarbon, 1 mol O2 mol-1 C is needed according to:
What is the German law regarding wastewater discharge into public sewers?
VO 1989: Indirekteinleiterverordnung; regulation of indirect introduction) and into surface waters (Mindestanforderungen nach §7a, WHG (2002); minimum requirement, §7a, water resource policy law) places a limit on emissions. This will be presented shortly in the next section.
What is the effect of dissolved oxygen on marine animals?
Marine animals such as fish use dissolved oxygen for respiration. However, the balance of DO consumption is quite delicate. When a large number of organic compounds are present in water, microbial activity will proliferate, putting a strain on the aquatic ecosystem. Critical DO reduction will ultimately harm marine life.
What is dissolved oxygen?
Dissolved Oxygen is the amount of gaseous oxygen dissolved in a sample of water. O 2 can be absorbed directly from the atmosphere or indirectly from the by-product of photosynthesis in surrounding plants.
What is the maximum BOD level for wastewater disposal?
Clean Water Act. Typical maximum values range from 10 mg/L for direct environmental disposal and 300 mg/L for disposal to sewer systems .
How does wastewater clarification work?
Wastewater clarification removes organic solids (primary sludge) from the water by utilizing the force of gravity – in other words, the heavier particles settle to the bottom and are removed first. Wastewater clarification is often followed by a chemical separation process.
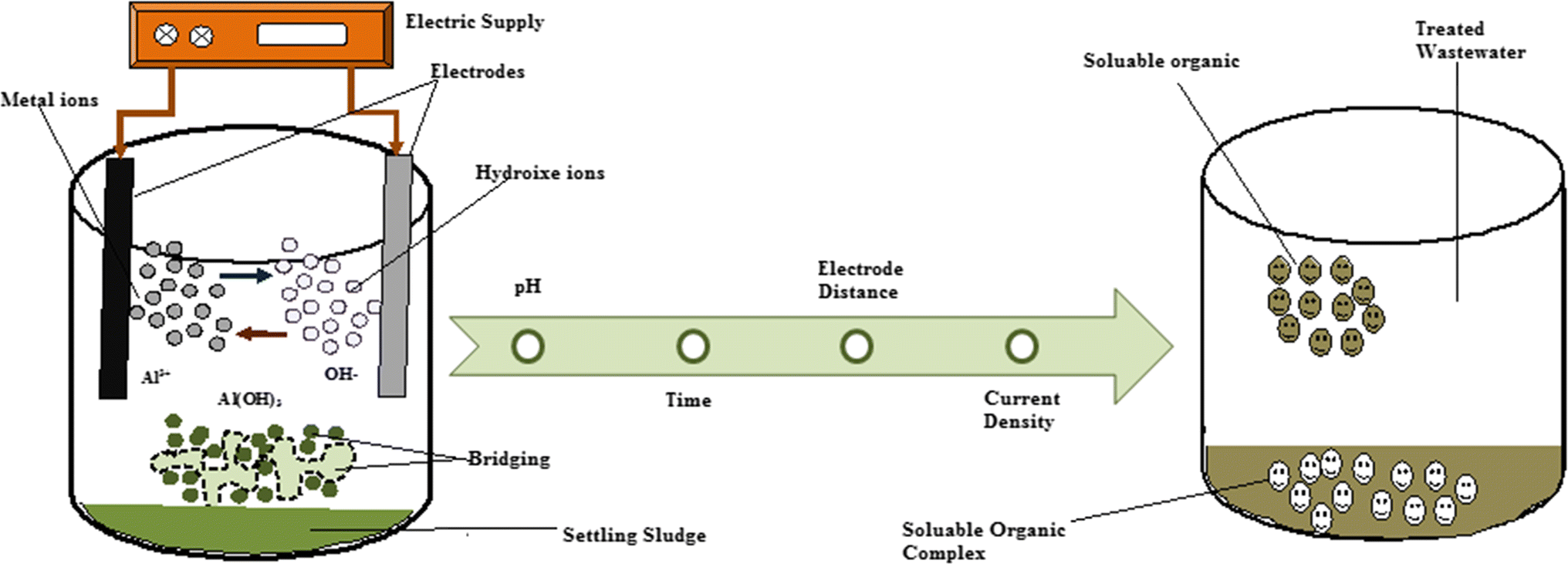
What is the name of the agglomerating agent that is added to wastewater to make it clumps
In coagulation, a non-toxic agglomerating agent such as Ferric Chloride (F e Cl) or alum is added to the wastewater causing the suspended particles to come together to form clumps which can easily be removed from the water by filtration.
Why is groundwater important?
Groundwater is essential in sustaining plant and animal life and as a raw material for many industries . Wastewater is water that has been contaminated from human activity, environmental, or industrial processes and must be treated for reuse or safe disposal. Usually determined alongside chemical oxygen demand (COD) in wastewater treatment, ...
What is flocculation in water?
Flocculation uses a chemical polymer (flocculating agent) to precipitate organic particles out of the water by coalescing to form larger particles or flocs. These larger particles can then be deposited into a sedimentation tank for further treatment prior to disposal.
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) & its significance
1. Definition: Biological oxygen demand indicates “the amount of O 2 required for biological oxidation of organic matter present in wastewater by microorganisms”. BOD is expressed in milligrams per liter of wastes.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
What is chemical oxygen demand COD? How to measure chemical oxygen demand?
Total Organic Carbon (TOC)
Total Organic Carbon determines the total organic matter in wastewater samples as CO 2 with modern instruments.
Coagulation and Flocculation
What are coagulation and flocculation in wastewater treatment? what is the difference between coagulation and flocculation?
Use of Polymer flocculants for industrial waste
When oil is present in the emulsified waste in water, alum and lime are added first to break the emulsion, followed by the polymer. Hot mill wastes could be gravity settled in scale pots, but the effluent from these contains particles between 2-70 microns in diameter.