
Background: The role of Cartridge based Nucleic Acid Amplification test (CBNAAT) in the diagnosis of lymphnode TB
Tuberculosis
A contagious infection caused by bacteria that mainly affects the lungs but also can affect any other organ.
Can cbnaat be used to diagnose TB in head and neck?
Apr 16, 2018 · CBNAAT provides a promising role in early diagnosis of TB in head and neck. Its high sensitivity and less time taking procedure makes it an excellent tool for timely diagnosis of such cases. Keywords: CBNAAT, Extra-pulmonary TB, …
Are automated Naats effective in the diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB)?
Tuberculosis of head and neck has been an under diagnosed entity due to large number of smear negative cases, which results in missing out the positive cases, further increasing the burden of TB. The role of cartridge- based nucleic acid amplification test (CBNAAT) with a potential to diagnose TB and rifampicin resistance within 2 h is promising.
What does cbnaat stand for?
Nov 24, 2020 · Every year, 10 million people fall ill with tuberculosis (TB). Despite being a preventable and curable disease, 1.5 million people die from TB each year. TB is the leading cause of death of people with HIV and also a major contributor to antimicrobial resistance.TB disease is curable. It is treated by a standardized course of treatment usually including 4 antibacterial …
What is the initial treatment for tuberculosis (TB) (TB)?
3.3 TB treatment and treatment coverage. Without treatment, the death rate from tuberculosis (TB) is high. Studies of the natural history of TB disease in the absence of treatment with anti-TB drugs (conducted before drug treatments became available) found that about 70% of people with sputum smear-positive pulmonary TB died within 10 years of being diagnosed, as did about …
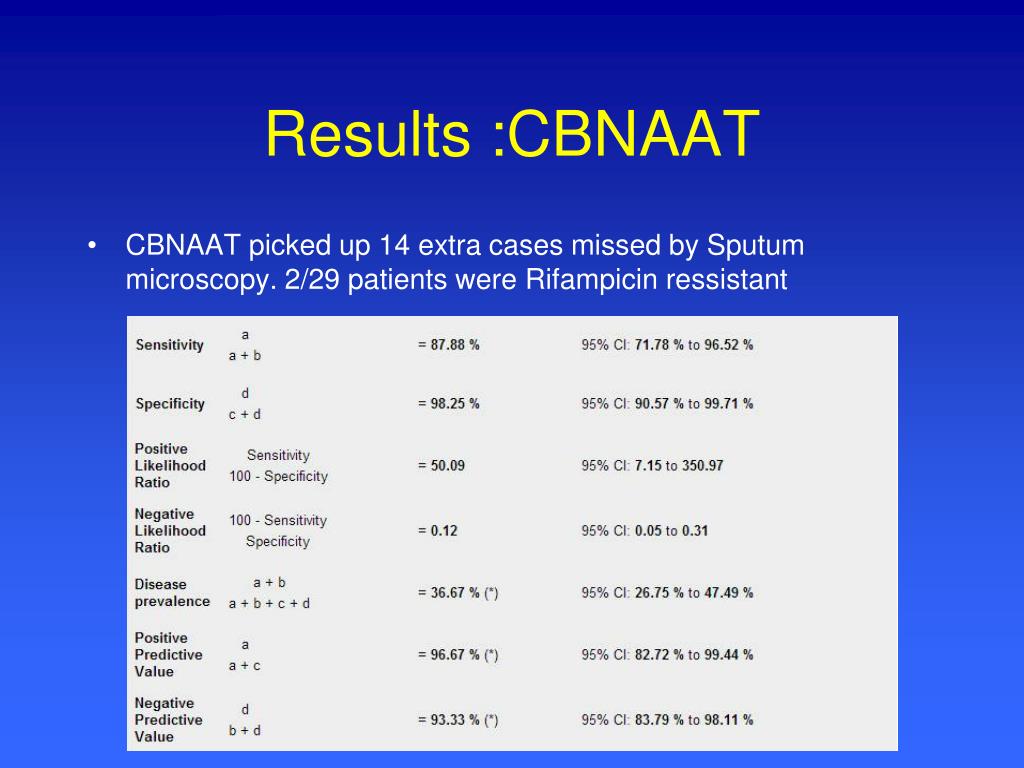
Why do we do Cbnaat?
What is sputum Cbnaat?
What is the difference between GeneXpert and Cbnaat?
What sample is required for Cbnaat?
What is Cbnaat test for TB?
What is Cbnaat for Covid?
What is the other name of TB Gold test?
Is GeneXpert a PCR test?
WHO is GeneXpert?
How accurate is Cbnaat test?
How is NAAT test performed?
Which test is best for tuberculosis?
How long does it take to cure TB?
Treatment. TB is a treatable and curable disease. Active, drug-susceptible TB disease is treated with a standard 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs that are provided with information and support to the patient by a health worker or trained volunteer. Without such support, treatment adherence is more difficult.
Is TB a disease?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable. TB is spread from person to person through the air. When people with lung TB cough, sneeze or spit, they propel the TB germs into the air.
Which countries have the highest TB burden?
In 2019, the 30 high TB burden countries accounted for 87% of new TB cases. Eight countries account for two thirds of the total, with India leading the count, followed by Indonesia, China, the Philippines, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh and South Africa.
How many countries have TB?
Eight countries account for two thirds of the total, with India leading the count, followed by Indonesia, China, the Philippines, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh and South Africa. Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) remains a public health crisis and a health security threat. A global total of 206 030 people with multidrug- or rifampicin-resistant TB ...
How many lives have been saved from TB?
An estimated 60 million lives were saved through TB diagnosis and treatment between 2000 and 2019. Ending the TB epidemic by 2030 is among the health targets of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs.
How many people have TB?
People infected with TB bacteria have a 5–10% lifetime risk of falling ill with TB.
How much risk of TB is there?
People infected with TB bacteria have a 5–10% lifetime risk of falling ill with TB. Those with compromised immune systems, such as people living with HIV, malnutrition or diabetes, or people who use tobacco, have a higher risk of falling ill.
Screening
Diagnosis
- In July 2021, WHO released the WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 3: Diagnosis – rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detection 2021 update (3).Three new classes of nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) are now endorsed by WHO: 1. moderate complexity automated NAATs, which are recommended for the initial detection of TB and resistan...
Treatment
- In April 2021, WHO convened a guideline development group (GDG) to review data from a trial conducted in 13 countries that compared 4-month rifapentine-based regimens with a standard 6-month regimen in people with drug-susceptible TB (6). The GDG considereda 4-month regimen composed of rifapentine, isoniazid, pyrazinamide and moxifloxacin that met the non-inferiority c…
Comorbidities, Vulnerable Populations and People-Centred Care
- In May to June 2021, WHO convened a GDG to review updated evidence on the management of TB in children and adolescents (aged 0–9 and 10–19 years, respectively). A rapid communication thatsummarizes the main updates to guidance on the management of TB in children and adolescents was released by WHO in August 2021 (8). The communication includes new inform…
Other Actions to Support TB Policy Guidance
- To exchange views on emerging areas where there is a need for global TB policy guidance, in March 2021, WHO convened a consultation on the translation of TB research into global policy guidelines, attended by scientists, public health experts, partners,civil society and countries (9). In June 2021, WHO launched a TB Knowledge Sharing Platform to bring all WHO TB guidelines, op…
Who Is Most at Risk?
Global Impact of TB
- TB occurs in every part of the world. In 2020, the largest number of new TB cases occurred in the WHO South-East Asian Region, with 43% of new cases, followed by the WHO African Region, with 25% of new cases and the WHO Western Pacific with 18%. In 2020, 86% of new TB cases occurred in the 30 high TB burden countries. Eight countries accounted for two thirds of the new TB case…
Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Common symptoms of active lung TB are cough with sputum and blood at times, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever and night sweats. WHO recommends the use of rapid molecular diagnostic tests as the initial diagnostic test in all persons with signs and symptoms of TB as they have high diagnostic accuracy and will lead to major improvements in the early detection of TB …
Treatment
- TB is a treatable and curable disease. Active, drug-susceptible TB disease is treated with a standard 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs that are provided with information and support to the patient by a health worker or trained volunteer. Without such support, treatment adherence is more difficult. Since 2000, an estimated 66 million lives we...
TB and HIV
- People living with HIV are 18 (Uncertainty interval: 15-21) times more likely to develop active TB disease than people without HIV. HIV and TB form a lethal combination, each speeding the other's progress. In 2020, about 215 000 people died of HIV-associated TB. The percentage of notified TB patients who had a documented HIV test result in 2020 was only 73%, up from 70% in 2019. In th…
Multidrug-Resistant TB
- Anti-TB medicines have been used for decades and strains that are resistant to one or more of the medicines have been documented in every country surveyed. Drug resistance emerges when anti-TB medicines are used inappropriately, through incorrect prescription by health care providers, poor quality drugs, and patients stopping treatment prematurely. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosi…
Catastrophic Cost
- WHO’s End TB Strategy target of “No TB patients and their households facing catastrophic costs as a result of TB disease”, monitored by countries and WHO since WHA67.1 End TB Strategy was adopted in 2015, shows that the world did not reach the milestone of 0% by 2020. According to the results of 23 national surveys on costs faced by TB patients and their families, the percentag…
Investments in TB Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment and Research
- US$ 13 billion are needed annually for TB prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care to achieve global targets agreed on UN high level-TB meeting. 1. Investments in TB prevention, diagnosis and care for tuberculosis in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) accounting for 98% of reported TB cases, fall far short of what is needed. Less than half (41%) of the global TB funding target is …
Global Commitments and The Who Response
- On 26 September 2018, the United Nations (UN) held its first- ever high-level meeting on TB, elevating discussion about the status of the TB epidemic and how to end it to the level of heads of state and government. It followed the first global ministerial conference on TB hosted by WHO and the Russian government in November 2017. The outcome was a political declaration agree…