Medication
Cardiovascular treatments are for conditions affecting the heart and circulatory system. Common symptoms include: Pain, tightness, or pressure in the chest. Pain or discomfort that radiates down the arm, left shoulder, elbows, jaw, or back. Feeling out of breath at rest, or short of breath all the time. Unexplained fatigue.
Procedures
Despite the many advances in treatment and prevention, cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of premature death and disability in the United States. 1 Nevertheless, 70% of cardiovascular disease is preventable through lifestyle changes alone. 2 Clearly, we have work to do. An integrative approach acknowledges the great value and ...
Nutrition
Treatment plans can vary and depend on the symptoms and the type of cardiovascular disease you have. Cardiovascular disease treatment may include: Lifestyle changes: Examples include making changes to your diet , increasing your aerobic activity and quitting smoking .
What are three ways to prevent cardiovascular disease?
Jun 11, 2021 · Cessation of tobacco use, reduction of salt in the diet, eating more fruit and vegetables, regular physical activity and avoiding harmful use of alcohol have been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
How do you treat cardiovascular disease?
Common treatments Here are some common treatments for different types of cardiovascular disease: Heart Valve Problems Medications Heart valve surgery Arrhythmia Medications Pacemaker Heart Attack Medications — clotbusters (should be administered as soon as possible for certain types of heart attacks) Coronary angioplasty
What is the best treatment for heart disease?
Dec 10, 2021 · Also called biventricular pacing, CRT is a treatment for heart failure in people whose lower heart chambers (ventricles) aren't pumping in sync with each other. A device called a biventricular pacemaker sends electrical signals to the ventricles.
Is there a cure for cardiovascular disease?
Jun 05, 2020 · Treatment Treatment for coronary artery disease usually involves lifestyle changes and, if necessary, drugs and certain medical procedures. Lifestyle changes Making a commitment to the following healthy lifestyle changes can go a long way toward promoting healthier arteries: Quit smoking. Eat healthy foods. Exercise regularly. Lose excess weight.

What are 4 treatments for cardiovascular disease?
Find out more about heart treatments that may be available to help you and your loved ones.Angioplasty and stents. Angioplasty is a treatment that uses stents to improve blood flow to the heart. ... Coronary artery bypass graft surgery. ... Heart valve surgery.
What are the 4 types of cardiovascular disease?
4 of the main types are described on this page.Coronary heart disease. Coronary heart disease occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle is blocked or reduced. ... Strokes and TIAs. ... Peripheral arterial disease. ... Aortic disease.
What is cardiovascular healthcare?
Cardiovascular health refers to the health of the heart and blood vessels. Cardiovascular disease is a group of diseases of the heart and blood vessels, including coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, heart arrhythmias, and heart valve problems.
What are 5 cardiovascular diseases?
What Are Cardiovascular Diseases?Abnormal heart rhythms, or arrhythmias.Aorta disease and Marfan syndrome.Congenital heart disease.Coronary artery disease (narrowing of the arteries)Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.Heart attack.Heart failure.Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy)More items...•
What are the early signs of heart problem?
SymptomsChest pain, chest tightness, chest pressure and chest discomfort (angina)Shortness of breath.Pain, numbness, weakness or coldness in your legs or arms if the blood vessels in those parts of your body are narrowed.Pain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper abdomen or back.
What causes cardiovascular?
What are the risk factors for cardiovascular disease? The most important behavioural risk factors of heart disease and stroke are unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use and harmful use of alcohol.
What are the most common cardiovascular diseases?
A List of Cardiovascular Diseases: The 5 Most CommonHeart Attack. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, usually tops the list of cardiovascular diseases in the United States — statistically and anecdotally. ... Stroke. ... Heart Failure. ... Arrhythmia. ... Heart Valve Complications.
Is cardiovascular disease curable?
Heart disease can't be cured or reversed. It requires a lifetime of treatment and careful monitoring. Many of the symptoms of heart disease can be relieved with medications, procedures, and lifestyle changes. When these methods fail, coronary intervention or bypass surgery might be used.
What is the difference between heart disease and cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease, is an umbrella term covering diseases of both the heart (cardio) and blood vessels (vascular) in the body. Heart disease and coronary heart disease are cardiovascular diseases, but so are other diseases affecting blood vessels such as high blood pressure and peripheral artery disease.
What are the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
What are the symptoms of cardiovascular heart disease?chest pain.pain, weakness or numb legs and/or arms.breathlessness.very fast or slow heartbeat, or palpitations.feeling dizzy, lightheaded or faint.fatigue.swollen limbs.
What organs does cardiovascular disease affect?
Cardiovascular diseases are conditions that affect your heart and blood vessels. Without appropriate treatment, cardiovascular disease can lead to heart attacks or strokes. You can make lifestyle changes or take medications to manage cardiovascular disease.
What exercises improve cardiovascular health?
Examples: Brisk walking, running, swimming, cycling, playing tennis and jumping rope. Heart-pumping aerobic exercise is the kind that doctors have in mind when they recommend at least 150 minutes per week of moderate activity.
How to treat heart disease?
You can lower your risk of heart disease by eating a low-fat and low-sodium diet, getting at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol intake. Medications.
How to reduce risk of heart disease?
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease, especially atherosclerosis. Quitting is the best way to reduce your risk of heart disease and its complications. Control your blood pressure. Ask your doctor for a blood pressure measurement at least every two years.
What tests are needed to diagnose heart disease?
The tests you'll need to diagnose your heart disease depend on what condition your doctor thinks you might have. Besides blood tests and a chest X-ray, tests to diagnose heart disease can include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). An ECG is a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in your heart.
What is the best test for heart disease?
Besides blood tests and a chest X-ray, tests to diagnose heart disease can include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). An ECG is a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in your heart. It can spot abnormal heart rhythms.
Can heart disease be detected without an appointment?
Some types of heart disease will be discovered without an appointment — for example, if a child is born with a serious heart defect, it will be detected soon after birth. In other cases, your heart disease may be diagnosed in an emergency situation, such as a heart attack.
Can heart disease be diagnosed in an emergency?
In other cases, your heart disease may be diagnosed in an emergency situation, such as a heart attack . If you think you have heart disease or are worried about your heart disease risk because of your family history, see your family doctor. You may be referred to a heart specialist (cardiologist).
What is the noninvasive exam that shows how your heart beats and pumps blood?
Echocardiogram. This noninvasive exam uses sound waves to produce detailed images of your heart's structure. It shows how your heart beats and pumps blood. Stress test. This type of test involves raising your heart rate with exercise or medicine while performing heart tests and imaging to check how your heart responds.
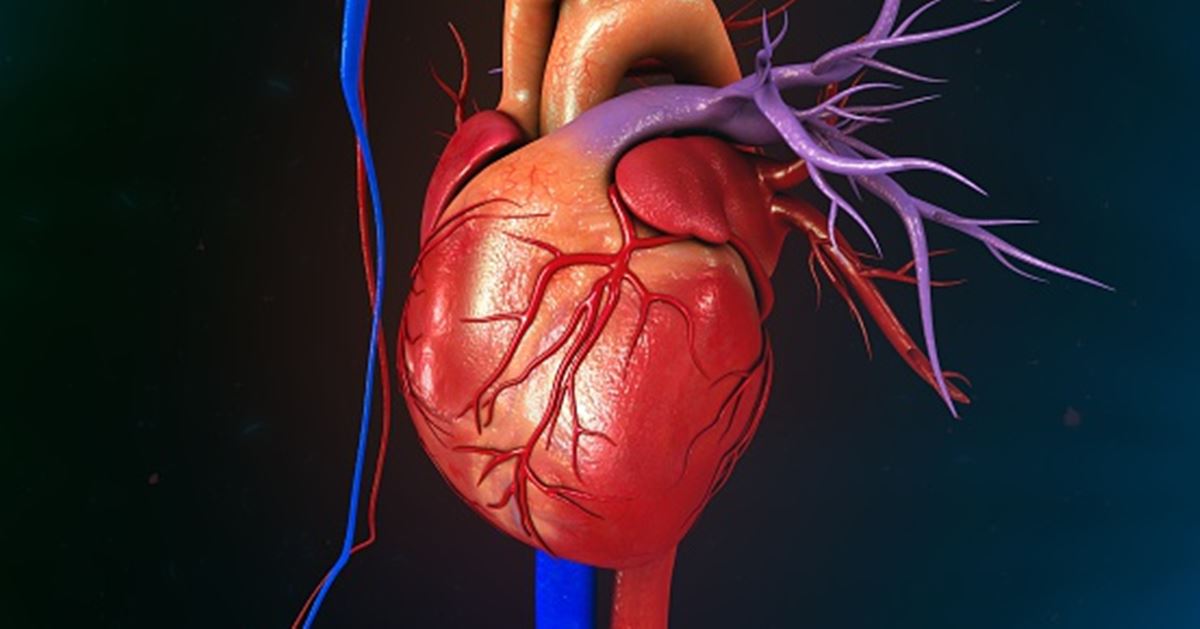
Overview of cardiovascular treatments
If you have heart disease, many treatments can help restore your heart’s function and ease symptoms. From minimally invasive procedures to open heart surgery, there are a wide range of cardiovascular treatments that our doctors at Dignity Health use to diagnose and treat heart and blood vessel conditions.
Tests
Dignity Health cardiologists perform many diagnostic tests to identify heart conditions. During an evaluation, your cardiologist will review your medical history, perform a physical exam, and order tests.
Visit a Provider near you
This list has been handpicked just for you. You may also search our networks by clicking the button below.
Is cardiovascular disease preventable?
1 Nevertheless, 70% of cardiovascular disease is preventable through lifestyle changes alone. 2 Clearly, we have work to do.
What are the pathological processes in the cardiovascular system?
Generally, pathological processes in the cardiovascular system are associated with a characteristic cascade of altered intracellular signaling and gene expression [1]. Thus, the various signaling pathways that underlie pathological changes have been the subject of intense investigation.
What is the role of epigenetic regulation in cardiovascular disease?
As a postmitotic cell, cardiac myocytes must rely on comprehensive protein quality control mechanisms to maintain cellular function and homeostasis. Autophagy, an evolutionarily conserved catabolic pathway responsible for degradation of long-lived proteins and defective organelles, is one such quality control mechanism and has been proposed as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. Recent studies have demonstrated that alteration of epigenetic pathways can modify autophagic activity and impact cardiac function and cardiac myocyte survival. Here, we summarize the current knowledge regarding the functions of autophagy and epigenetics in cardiovascular disease.
How do cardiovascular diseases affect the world?
Although significant progress has been made in clinical treatment, cardiovascular diseases (CVD) remain a leading cause of death worldwide. Heart-related diseases lead to more deaths than cancer (26.6% versus 22.8%) per year. 1 If stroke is included, CVDs are responsible for almost one-third of all deaths. Meanwhile, CVDs also contribute a major economic burden to our health-care system. Current existing treatments for CVDs are still limited and advanced therapies, especially for myocardial infarction (MI) and atherosclerosis, are scarce. After an acute myocardial infarction, cardiomyocytes cannot be replaced or regenerated to replace the dead cells through stem cell recruitment and the self-renewal rate is far behind the rate of loss of the cardiomyocytes. Non-contractile scar tissue then forms in the area of the infarct. Finally, the myocardium may lose its contractile function, which leads to congestive heart failure. Traditional treatments include the implantation of mechanical valves or biological valves (auto- or allo-grafts). However, the limited number of donors is far behind the number of patients requiring treatment. A promising approach includes the construction of stem cells and cardiac tissue or engineered cardiac tissue. For example, a decade ago, Li et al. seeded fetal rat myocytes on biodegradable gelatin meshes (15 × 15 × 5 mm 3 ). 2 After 1 week of culture, meshes were implanted into the subcutaneous tissue or myocardial scar tissue in a cryoinjured rat heart. Five weeks later, the grafts in the subcutaneous tissue contracted regularly and spontaneously. For grafts in myocardial scar tissue, the cells within the graft survived and formed junctions with the recipient heart cells. The ultimate goal of engineered cardiac tissues (ECTs) is to reconstruct a replica from the damaged cardiac tissues with structural and functional integrity. The graft needs to meet multiple requirements including (1) sufficient elastic (tension and compressive) properties to minimize the risks of arrhythmias or dysfunctions, (2) biocompatibility, and (3) improvement of stem cell regrowth and differentiation.
What is cardioprotective diet?
A cardioprotective diet is an important lifestyle practice that is the cornerstone of CVD risk management ( Mozaffarian et al., 2011 ). The purpose of this article is to review the current evidence in support of contemporary dietary recommendations for CVD prevention and treatment.
Is CVD a risk factor for ESRD?
CVD is highly prevalent in patients with ESRD, with a risk for CVD mortality 10- to 100-fold higher than in the general population. 15 In part, this reflects shared risk factors for CVD and chronic kidney disease (CKD), particularly diabetes and hypertension. However, traditional risk factors do not fully account for this excess mortality, and clinical trials have shown no benefit to standard CVD treatments such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or statins in dialysis patients. 16,17 Derangements in erythropoiesis and mineral metabolism that arise with progressive kidney failure likely play a role in the pathogenesis of CVD in ESRD, but raising hemoglobin or lowering parathyroid hormone levels have also shown no benefit. 18,19 Thus there is significant interest in understanding how the uremic milieu contributes to accelerated CVD pathogenesis. From a clinical perspective, uremic CVD is characterized by left ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial fibrosis, medial vascular calcification, endothelial dysfunction, and sympathetic nervous system derangements. 20,21 Left ventricular hypertrophy is particularly common, present in up to 80% of individuals at dialysis initiation. 22 Approximately 50% of CVD mortality in dialysis patients is due to sudden death, although the relative contribution of malignant ventricular arrhythmias, bradyarrhythmias, asystolic arrests, or other events is unknown. 23
Is it easier to treat cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease is often easier to treat when healthcare providers catch it early. If you have any signs of cardiovascular disease, you should see your healthcare provider right away. Call 911 or seek emergency medical attention if you experience sudden: Chest pain.
What are the different types of cardiovascular diseases?
There are many different types of cardiovascular diseases including but not limited to: Arrhythmia: Problem with the electrical conduction system of the heart which can lead to abnormal heart rhythms or heart rates. Valve disease: Problem with the heart valves (structures that allow blood to flow from one chamber to another chamber ...
What is the name of the disease that affects the blood vessels in the arms, legs, and abdomen?
Peripheral artery disease: Problem with the blood vessels of the arms, legs or abdominal organs, such as narrowing or blockages. Aortic disease: Problem with the large blood vessel that directs blood from the heart to the brain and rest of the body, such as dilatation or aneurysm. Congenital heart disease: Heart problem that a person is born with, ...
What is the name of the disease that directs blood from the heart to the brain and rest of the body?
Aortic disease : Problem with the large blood vessel that directs blood from the heart to the brain and rest of the body, such as dilatation or aneurysm. Congenital heart disease: Heart problem that a person is born with, which can affect different parts of the heart. Pericardial disease: Problem with the lining of the heart, ...
What are the symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
Fluid build up. Heart palpitations (heart pounding or racing). Pain or numbness in your legs or arms. Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting. It is important to note that women or elderly persons may have more subtle symptoms, but still have serious cardiovascular disease.
Can you prevent heart disease?
You can't prevent some types of cardiovascular disease, such as congenital heart disease. But lifestyle changes can reduce your risk of many types of cardiovascular disease. Managing other health conditions, such as diabetes, high cholesterol or high blood pressure. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
How many people have CVD?
Almost half of all adults in the U.S. have at least one CVD. You may make lifestyle changes to manage cardiovascular disease or your healthcare provider may prescribe medications. The sooner you detect cardiovascular disease, the easier it is to treat. Appointments 800.659.7822. Appointments & Locations.
What are the basic medications for cardiovascular disease?
Basic medicines that should be available include: aspirin; beta-blockers; angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; and. statins. An acute event such as a heart attack or stroke should be promptly managed.
How can cardiovascular disease be prevented?
Most cardiovascular diseases can be prevented by addressing behavioural risk factors such as tobacco use, unhealthy diet and obesity, physical inactivity and harmful use of alcohol. It is important to detect cardiovascular disease as early as possible so that management with counselling and medicines can begin.
What is the term for a disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain?
cerebrovascular disease – a disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain; peripheral arterial disease – a disease of blood vessels supplying the arms and legs; rheumatic heart disease – damage to the heart muscle and heart valves from rheumatic fever, caused by streptococcal bacteria;
What are the risk factors for heart disease?
The most important behavioural risk factors of heart disease and stroke are unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use and harmful use of alcohol. The effects of behavioural risk factors may show up in individuals as raised blood pressure, raised blood glucose, raised blood lipids, and overweight and obesity.
What is the name of the disease that affects the blood vessels in the heart muscle?
They include: coronary heart disease – a disease of the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle; cerebrovascular disease – a disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain; peripheral arterial disease – a disease of blood vessels supplying the arms and legs;
How many people died from cardiovascular disease in 2019?
Key facts. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally. An estimated 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2019, representing 32% of all global deaths. Of these deaths, 85% were due to heart attack and stroke. Over three quarters of CVD deaths take place in low- and middle-income countries.
Is a heart attack a sign of underlying disease?
Often, there are no symptoms of the underlying disease of the blood vessels. A heart attack or stroke may be the first sign of underlying disease. Symptoms of a heart attack include:
What happens when blood clots in the heart?
Heart attack . A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked by a blood clot. If this clot cuts off the blood flow completely, the part of the heart muscle supplied by that artery begins to die. Most people survive their first heart attack and return to their normal lives, enjoying many more years of productive activity.
Does heart failure mean the heart stops beating?
Heart failure does not mean that the heart stops beating — that’s a common misperception. Instead, the heart keeps working, but the body’s need for blood and oxygen isn’t being met. Heart failure can get worse if left untreated. If your loved one has heart failure, it’s very important to follow the doctor’s orders.
What happens when a blood vessel bursts in the brain?
This can result in the loss of functions controlled by that part of the brain, such as walking or talking. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel within the brain bursts. This is most often caused by uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure).
Does heart failure get worse if left untreated?
Instead, the heart keeps working, but the body’s need for blood and oxygen isn’t being met. Heart failure can get worse if left untreated. If your loved one has heart failure, it’s very important to follow the doctor’s orders. Learn more about heart failure.
What happens when the blood supply to a part of the brain is cut off?
When the blood supply to a part of the brain is cut off, some brain cells will begin to die. This can result in the loss of functions controlled by that part of the brain, such as walking or talking. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel within the brain bursts.
What is the best treatment for heart failure?
Depending on your symptoms, you might take one or more medications, including: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. These drugs relax blood vessels to lower blood pressure, improve blood flow and decrease the strain on the heart.
Is heart failure treatment easier?
If heart failure is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective. Because appointments can be brief and there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared for your appointment. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and know what to expect from your doctor.
Can you be admitted to the hospital for heart failure?
You may be admitted to the hospital if you have a flare-up of heart failure symptoms. While in the hospital, you may receive additional medications to help your heart pump better and relieve your symptoms. You may also receive supplemental oxygen through a mask or small tubes placed in your nose.
What is a contrast test for heart?
A dye (contrast) is injected through the catheter to make the arteries show up more clearly on an X-ray, helping the doctor spot blockages. Myocardial biopsy. In this test, a doctor inserts a small, flexible cord into a vein in the neck or groin, and removes very small pieces of the heart muscle for examination.
What does a doctor check for in a heart?
Your doctor will also check to see if you have risk factors for heart failure, such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease or diabetes. Your doctor can listen to your lungs for signs of fluid buildup (lung congestion) and your heart for whooshing sounds (murmurs) that may suggest heart failure. The doctor may examine the veins in your neck ...
How to manage heart failure?
These steps may help you manage heart failure: Keep track of the medications you take. Make a list of all the medications you take, carry it with you and share it with your doctors. Don't stop taking any medications without first talking to your doctor.
How can heart failure help you live longer?
Proper heart failure treatment can sometimes improve symptoms and help you live longer. You and your doctor can work together to help make you most comfortable. Pay attention to your body and how you feel, and tell your doctor when you're feeling better or worse.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- The type of treatment you receive depends on the type of heart disease you have. In general, treatment for heart disease usually includes: 1. Lifestyle changes.You can lower your risk of heart disease by eating a low-fat and low-sodium diet, getting at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week, quitting smoking, and limiting al...